Abstract
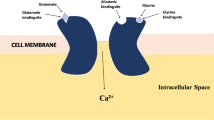
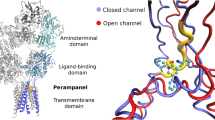
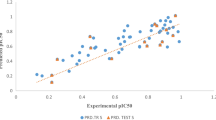
The N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) is the family of glutamate receptor, which is involved in controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function; but overactivation of this receptor results to excess intracellular calcium formation, triggers neuronal injury and also involves in several pathologies. Both ligand- and structure-based quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR), pharmacophore, docking and simulation studies have been performed on a set of structurally diverse inhibitors to explore prime molecular structural features involve for specific binding to NMDA, and vis-à-vis inhibiting enzyme activity. 3D QSAR studies, comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) and comparative molecular similarity indices analysis (CoMSIA) models showed the importance of steric, electrostatic and hydrophobic features; while hydrogen bond acceptor and hydrophobic features are depicted as important pharmacophore features of the molecule. Molecular docking and simulation studies corroborated the consequence of the features obtained from ligand-based Bayesian model (AUROCcv = 0.878); 3D QSAR CoMFA (R2 = 0.895, se = 0.513, Q2 = 0.602, R2pred = 0.673); CoMSIA (R2 = 0.877, se = 0.555, Q2 = 0.615, R2pred = 0.727); hologram QSAR (Q2 = 0.812, R2 = 0.941, R2pred = 0.772), and pharmacophore models (Q2 = 0.926, R2 = 0.927, R2pred = 0.621). Presence of aromatic ring, hetero and halogen atoms along with alkyl group of molecular scaffold shows their importance for binding affinity to NMDA receptor. Stability of the complex is adjudged by both docking and simulation studies.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gitto R, De Luca L, Ferro S, Occhiuto F, Samperi S, De Sarro G, Russo E, Ciranna L, Costa L, Chimirri A (2008) Computational studies to discover a new NR2B/NMDA receptor antagonist and evaluation of pharmacological profile. ChemMedChem 3:1539–1548
Gitto R, De Luca L, Ferro S, Citraro R, De Sarro G, Costa L, Ciranna L, Chimirri A (2009) Development of 3-substituted-1H-indole derivatives as NR2B/NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorganic Med Chem 17:1640–1647
Yosa J, Blanco M, Acevedo O, Lareo LR (2009) Molecular orbital differentiation of agonist and antagonist activity in the GlycineB-iGluR-NMDA receptor. Eur J Med Chem 44:2960–2966
Sobolevsky AI, Rosconi MP, Gouaux E (2009) X-ray structure, symmetry and mechanism of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor. Nature 462:745–756
Hynd MR, Scott HL, Dodd PR (2004) Glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int 45:583–595
Chen HS, Lipton SA (2006) The chemical biology of clinically tolerated NMDA receptor antagonists. J Neurochem 97:1611–1626
Farlow MR (2004) NMDA receptor antagonists. A new therapeutic approach for Alzheimer’s disease. Geriatrics 59:22–27
Kubinyi H (1997) QSAR and 3D QSAR in drug design. Drug Discov Today 2:457–467
Zambre VP, Hambarde VA, Petkar NN, Patel CN, Sawant SD (2015) Structural investigations by in silico modeling for designing NR2B subunit selective NMDA receptor antagonists. RSC Adv 5:23922–23940
Ugale VG, Bari SB (2016) Identification of potential Gly/NMDA receptor antagonists by cheminformatics approach: a combination of pharmacophore modelling, virtual screening and molecular docking studies. SAR QSAR Environ Res 27:125–145
Avram S, Maria M, Bagci E, Hritcu L, Borcan LC, Mihailescu D (2017) Advanced structure-activity relationships applied to Mentha spicata L. subsp. spicata essential oil compounds as AChE and NMDA ligands, in comparison with donepezil, galantamine and memantine—new approach in brain disorders pharmacology. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 16:800–811
Abreu PA, Castro HC, Paes-de-Carvalho R, Rodrigues CR, Giongo V, Paixao IC, Santana MV, Ferreira JM, Caversan OM, Leao RA, Marins LM, Henriques AM, Farias FM, Albuquerque MG, Pinheiro S (2013) Molecular modeling of a phenyl-amidine class of NMDA receptor antagonists and the rational design of new triazolyl-amidine derivatives. Chem Biol Drug Des 81:185–197
Buyukbingol E, Sisman A, Akyildiz M, Alparslan FN, Adejare A (2007) Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS): a new approach to predictive modeling in QSAR applications: a study of neuro-fuzzy modeling of PCP-based NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorganic Med Chem 15:4265–4282
Tikhonova IG, Baskin II, Palyulin VA, Zefirov NS (2003) CoMFA and homology-based models of the glycine binding site of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor. J Med Chem 46:1609–1616
Tikhonova IG, Baskin II, Palyulin VA, Zefirov NS (2004) 3D-model of the ion channel of NMDA receptor: qualitative and quantitative modeling of the blocker binding. Doklady 396:181–186
Chenard BL, Bordner J, Butler TW, Chambers LK, Collins MA, De Costa DL, Ducat MF, Dumont ML, Fox CB, Mena EE et al (1995) (1S,2S)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(4-hydroxy-4-phenylpiperidino)-1-propanol: a potent new neuroprotectant which blocks N-methyl-D-aspartate responses. J Med Chem 38:3138–3145
Ornstein PL, Schoepp DD, Arnold MB, Leander JD, Lodge D, Paschal JW, Elzey T (1991) 4-(Tetrazolylalkyl)piperidine-2-carboxylic acids. Potent and selective N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor antagonists with a short duration of action. J Med Chem 34:90–97
Varano F, Catarzi D, Colotta V, Filacchioni G, Galli A, Costagli C, Carla V (2002) Synthesis and biological evaluation of a new set of pyrazolo[1,5-c]quinazoline-2-carboxylates as novel excitatory amino acid antagonists. J Med Chem 45:1035–1044
Fray MJ, Bull DJ, Carr CL, Gautier EC, Mowbray CE, Stobie A (2001) Structure-activity relationships of 1,4-dihydro-(1H,4H)-quinoxaline-2,3-diones as N-methyl-D-aspartate (glycine site) receptor antagonists. 1. Heterocyclic substituted 5-alkyl derivatives. J Med Chem 44:1951–1962
Kinney WA, Abou-Gharbia M, Garrison DT, Schmid J, Kowal DM, Bramlett DR, Miller TL, Tasse RP, Zaleska MM, Moyer JA (1998) Design and synthesis of [2-(8,9-dioxo-2,6-diazabicyclo[5.2.0]non-1(7)-en-2-yl)-ethyl]phosphonic acid (EAA-090), a potent N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist, via the use of 3-cyclobutene-1,2-dione as an achiral alpha-amino acid bioisostere. J Med Chem 41:236–246
Torres E, Duque MD, Lopez-Querol M, Taylor MC, Naesens L, Ma C, Pinto LH, Sureda FX, Kelly JM, Vazquez S (2012) Synthesis of benzopolycyclic cage amines: NMDA receptor antagonist, trypanocidal and antiviral activities. Bioorganic Med Chem 20:942–948
Varano F, Catarzi D, Colotta V, Calabri FR, Lenzi O, Filacchioni G, Galli A, Costagli C, Deflorian F, Moro S (2005) 1-substituted pyrazolo[1,5-c]quinazolines as novel Gly/NMDA receptor antagonists: synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular modeling study. Bioorganic Med Chem 13:5536–5549
Kinney WA, Lee NE, Garrison DT, Podlesny Jr EJ, Simmonds JT, Bramlett D, Notvest RR, Kowal DM, Tasse RP (1992) Bioisosteric replacement of the alpha-amino carboxylic acid functionality in 2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid yields unique 3,4-diamino-3-cyclobutene-1,2-dione containing NMDA antagonists. J Med Chem 35:4720–4726
Kanungo TM, Mount DM, Netanyahu NS, Piatko CD, Silverman R, Wu AY (2002) An efficient k-means clustering algorithm: analysis and implementation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24:881–892
Everitt BS, Dunn G (2013) Applied multivariate data analysis2nd edn. Wiley Online Library Arnold, London
Balaji S, Prasanna DS, Rangappa KS (2013) Docking, QSAR and CoMFA studies on arecoline analogues as muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) M1 agonists. Proc Indian Natl Sci Acad 79:41–50
Lu X, Lv M, Huang K, Ding K, You Q (2012) Pharmacophore and molecular docking guided 3D-QSAR study of bacterial enoyl-ACP reductase (FabI) inhibitors. Int J Mol Sci 13:6620–6638
Srivastava V, Kumar A, Mishra BN, Siddiqi MI (2008) CoMFA and CoMSIA 3D-QSAR analysis of DMDP derivatives as anti-cancer agents. Bioinformation 2:384–391
Halder AK, Saha A, Jha T (2013) Exploration of structural and physicochemical requirements and search of virtual hits for aminopeptidase N inhibitors. Mol Div 17:123–137
Discovery studio 2.5 (2009) a) LigandFit, (b) Pharmacophore (c) Bayesian model; Accelrys Software Inc., San Diego
Yang XL, Zhou Y, Liu XL (2014) Hologram quantative structure–activity relationship studies on 1-(5-carboxyindol-1-yl) propan-2-one inhibitors of human cytosolic phospholipase A2α. Med Chem Res 23:1512–1518
Sybyl (2006) Tripos Inc.
Jacquez JA, Jacquez GM (2002) Fisher’s randomization test and Darwin’s data—a footnote to the history of statistics. Math Biosci 180:23–28
Ramar V, Pappu S (2016) Exploring the inhibitory potential of bioactive compound from Luffa acutangula against NF-kappaB-A molecular docking and dynamics approach. Comput Biol Chem 62:29–35
Karakas E, Simorowski N, Furukawa H (2011) Subunit arrangement and phenylethanolamine binding in GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptors. Nature 475:249–253
Taha MO, Habash M, Al-Hadidi Z, Al-Bakri A, Younis K, Sisan S (2011) Docking-based comparative intermolecular contacts analysis as new 3-D QSAR concept for validating docking studies and in silico screening: NMT and GP inhibitors as case studies. J Chem Inf Model 51:647–669
Sastry GM, Adzhigirey M, Day T, Annabhimoju R, Sherman W (2013) Protein and ligand preparation: parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J Comput Aided Mol Des 27:221–234
Bas DC, Rogers DM, Jensen JH (2008) Very fast prediction and rationalization of pKa values for protein-ligand complexes. Proteins 73:765–783
Li H, Robertson AD, Jensen JH (2005) Very fast empirical prediction and rationalization of protein pKa values. Proteins 61:704–721
Maestro v9.7. a) Glide, (b) LigPrep; Protien prep wizard. Schrodinger
Tyagi C, Gupta A, Goyal S, Dhanjal J, Grover A (2014) Fragment based group QSAR and molecular dynamics mechanistic studies on arylthioindole derivatives targeting the alpha-beta interfacial site of human tubulin. BMC Genomics 15(Suppl 9):S3
Pradeepkiran JA, Kumar KK, Kumar YN, Bhaskar M (2015) Modeling, molecular dynamics, and docking assessment of transcription factor rho: a potential drug target in Brucella melitensis 16M. Drug Des Dev Ther 9:1897–1912
Kallubai M, Amineni U, Mallavarapu M, Kadiyala V (2015) In silico approach to support that p-Nitrophenol monooxygenase from Arthrobacter sp. strain JS443 catalyzes the initial two sequential monooxygenations. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 7:157–167
Roy K, Ambure P, Kar S, Ojha PK (2018) Is it possible to improve the quality of predictions from an “intelligent” use of multiple QSAR/QSPR/QSTR models? J Chemom:1–18
Funding
Financial assistance for major research project (MRP) from University Grants Commission (UGC) is thankfully acknowledged. One of the authors, Tabassum Hossain wishes to thank UGC-MANF for awarding senior research fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 814 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hossain, T., Mukherjee, A. & Saha, A. Exploration of structural and physicochemical properties of small molecules to inhibit NMDA functionality. Struct Chem 29, 1175–1187 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-018-1103-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-018-1103-7