Abstract
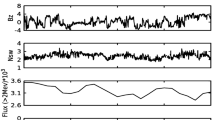
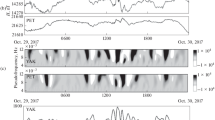
We analyzed the behavior of Cosmic-Ray (CR) intensity during five geomagnetic events over 9-day periods of varying disturbance, using ground-based CR measurements from the Bartol Research Institute neutron-monitor program that occurred on 25th October – 2nd November 2003, 23rd – 31st July 2004, 13th – 21st May 2005, 13th – 21st Mar 2015, and 19th – 27th June 2015. A nine-day time frame gives us a reasonable time interval for data analysis before, during, and after the main event(s). These events have been deliberately chosen, intending to track Forbush Decreases (FDs) at high-latitude stations following geomagnetic storms of different intensity and duration from the perspectives of their origin and geoeffectiveness. FDs are observed when the magnetic fields entangled in and around a Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) exert a deflecting effect on galactic cosmic radiation, resulting in a sudden reduction in their intensities. The results revealed that the CR intensity dropped by 4 – 17% in the chosen events. The FDs examined were not typical, with multistage decrement during the event period. Furthermore, we have used the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) technique to detect a singularity on the CR intensity at the stations described. The first three decomposition levels have proved sufficient to isolate the transients in CR intensity in conjunction with varying nature and intensities, ranging from intense to superintense geomagnetic storms to a high-intensity long-duration continuous auroral electrojet activity (HILDCAA) event. Finally, the findings of the detrended crosscorrelation technique showed a good association of percentage decrease in cosmic-ray intensity with the Dst index during the process. No noticeable lag has been found between the parameters discussed, which indicates a strong correlation between the IMF-Bz and the Dst index and the FD.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
25 May 2022
The original online version of this article was revised: Table 1 was replaced and a typographical error corrected.
20 May 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-022-02000-w
References
Adhikari, B., Chapagain, N.P.: 2015, Polar cap potential and merging electric field during high-intensity long duration continuous auroral activity. J. Nepal Phys. Soc. 3(1), 6. DOI.
Adhikari, B., Dahal, S., Chapagain, N.P.: 2017, Study of field-aligned current (FAC), interplanetary electric field component (Ey), interplanetary magnetic field component (Bz), and northward (x) and eastward (y) components of geomagnetic field during supersubstorm. Earth Space Sci. 4(5), 257. DOI.
Alex, S., Mukherjee, S., Lakhina, G.S.: 2006, Geomagnetic signatures during the intense geomagnetic storms of 29 October and 20 November 2003. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 68(7), 769. DOI.
Arunbabu, K.P., Antia, H.M., Dugad, S.R., Gupta, S.K., Hayashi, Y., Kawakami, S., Mohanty, P.K., Nonaka, T., Oshima, A., Subramanian, P.: 2013, High-rigidity Forbush decreases: Due to CMEs or shocks? Astron. Astrophys. 555, A139. DOI.
Astafyeva, E., Zakharenkova, I., Hozumi, K., Alken, P., Coïsson, P., Hairston, M.R., Coley, W.R.: 2018, Study of the equatorial and low-latitude electrodynamic and ionospheric disturbances during the 22–23 June 2015 geomagnetic storm using ground-based and spaceborne techniques. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 123(3), 2424. DOI.
Barnett, T.P.: 1991, The interaction of multiple time scales in the tropical climate system. J. Climate 4(3), 269. DOI.
Belov, A.: 2000, Large scale modulation: View from the Earth. Cosmic Rays Earth 93, 79. DOI.
Belov, A.V.: 2008, Forbush effects and their connection with solar, interplanetary and geomagnetic phenomena. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 4(S257), 439. DOI.
Belov, A.V., Eroshenko, E.A., Yanke, V.G.: 1997, Modulation effects in 1991-1994 years. In: Correlated Phenomena at the Sun, in the Heliosphere and in Geospace, ESA SP-415, ESTEC, Noordwijk, 463.
Belov, A.V., Eroshenko, E.A., Yanke, V.G.: 1999, Cosmic ray effects caused by great disturbances of the interplanetary medium in 1990-1996. In: Proc. 26th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 6, 431.
Cane, H.V.: 2000, Coronal mass ejections and Forbush decreases. Space Sci. Rev. 93(1/2), 55. DOI.
Cane, H.V., Richardson, I.G., Von Rosenvinge, T.T.: 1996, Cosmic ray decreases: 1964–1994. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 101(A10), 21561.
Cane, H.V., Richardson, I.G., Wibberenz, G.: 1995, The response of energetic particles to the presence of ejecta material. In: Proc. 24th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 4, 377.
Chapagain, N.P., Taylor, M.J., Makela, J.J., Duly, T.M.: 2012, Equatorial plasma bubble zonal velocity using 630.0 nm airglow observations and plasma drift modeling over Ascension Island. J. Geophys. Res. 117(A6), A06316. DOI.
Chauhan, M.L., Shrivastava, S.K., Richharia, M.K., Jain, M., Jain, A.: 2008, Study of two major Forbush decrease events of 2005. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Mexico City 1(SH), 307.
Chi, Y., Shen, C., Luo, B., Wang, Y., Xu, M.: 2018, Geoeffectiveness of stream interaction regions from 1995 to 2016. Space Weather 16(12), 1960. DOI.
Chui, C.: 1992, An Introduction to Wavelets 1, Academic Press, New York.
Chui, C.: 1994, Wavelets Theory, Algorithms and Applications, Academic Press, San Diego, 5.
Dashora, N., Sharma, S., Dabas, R.S., Alex, S., Pandey, R.: 2009, Large enhancements in low latitude total electron content during 15 May 2005 geomagnetic storm in Indian zone. Ann. Geophys. 27, 1803. DOI.
Daubechies, I.: 1990, The wavelet transforms, time-frequency localization and signal analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 36(5), 961. DOI.
Daubechies, I.: 1992, Ten lectures on wavelets. In: CBMS-NSF Regional Conference, Series in Applied Mathematics 61, SIAM, Philadelphia.
Davis, C.J., Wild, M.N., Lockwood, M., Tulunay, Y.K.: 1997, Ionospheric and geomagnetic responses to changes in IMF B z: A superposed epoch study. Ann. Geophys. 15(2), 217.
Domingues, M.O., Mendes, O., da Costa, A.M.: 2005, Wavelet techniques in atmospheric sciences. Adv. Space Res. 35(5), 831. DOI.
Du, D., Xu, W.Y., Zhao, M.X., Chen, B., Lu, J.Y., Yang, G.L.: 2010, A sensitive geomagnetic activity index for space weather operation. Space Weather. 8, S12006. DOI.
Dungey, J.W.: 1961, Interplanetary magnetic field and the auroral zones. Phys. Rev. Lett. 6(2), 47.
Fenton, A.G., McCracken, K.G., Rose, D.C., Wilson, B.G.: 1959, The onset times of Forbush-type cosmic ray intensity decrease. Can. J. Phys. 37(9), 970. DOI.
Forbush, S.E.: 1938, On worldwide changes in cosmic-ray intensity. Phys. Rev. 54(12), 975. DOI.
Foufoula-Georgiou, E.K., Kumar, P. (eds.): 1995, Wavelet in Geophysics 4, Academic Press, New York, 373 pp.
Gao, R.X., Yan, R.: 2011, From Fourier transform to wavelet transform: A historical perspective. In: Wavelets, Springer, Boston, 17. DOI.
Gonzalez, W.D., Josely, J.A., Kamide, Y., Korehi, H.W., Rostoker, G., Tsuruntani, B.T., Vasylianas, V.M.: 1994, What is a geomagnetic storm? J. Geophys. Res. 99, 5771. DOI.
Hajra, R., Tsurutani, B.T., Echer, E., Gonzalez, W.D., Brum, C.G.M., Vieira, L.E.A., Santolik, O.: 2015, Relativistic electron acceleration during HILDCAA events: Are precursor CIR magnetic storms important? Earth Planets Space 67(1), 1. DOI.
Heber, B., Sanderson, T.R., Zhang, M.: 1999, Corotating interaction regions. Adv. Space Res. 23, 567. DOI.
Huang, N.E., Shen, Z., Long, S.R., Wu, M.C., Shih, H.H., Zheng, Q., Yen, N.C., Tung, C.C., Liu, H.H.: 1998, The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond., Ser. A, Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 454(1971), 903. DOI.
Huang, D.H., Hu, H.Q., Zhang, J.L., Lu, H., Zhang, D.L., Xue, B.S., Lu, J.T.: 2017, Study on 2015 June 22 Forbush decrease with the muon telescope in Antarctic. arXiv preprint. arXiv.
Joselyn, J.A.: 1986, In: Kamide, F., Slavin, J.A. (eds.) Proceedings of Chapmaan Conference on Solar Wind Magnetosphere Coupling 127, Terra Sci., Tokyo.
Kane, R.P.: 1977, A comparative study of geomagnetic, interplanetary, and cosmic ray storms. J. Geophys. Res. 82(4), 561. DOI.
Karki, M., Silwal, A., Chapagain, N.P., Poudel, P., Gautam, S.P., Mishra, R.K., Adhikari, B., Migoya-Orue, Y.O.: 2020, GPS observations of ionospheric TEC variations during 2015 Mw 7.8 Nepal Earthquake. Preprint. DOI.
Katz, R.W.: 1988, Use of cross correlations in the search for teleconnections. J. Climatol. 8(3), 241. DOI.
Khanal, K., Adhikari, B., Chapagain, N.P., Bhattarai, B.: 2019, HILDCAA-related GIC and possible corrosion Hazard in underground pipelines: A comparison based on wavelet transform. Space Weather 17(2), 238. DOI.
Kichigin, G.N., Kravtsova, M.V., Sdobnov, V.E.: 2018, Spatial-energy characteristics of cosmic rays and parameters of magnetospheric current systems in March and June 2015. Geomagn. Aeron. 58, 586. DOI.
Klausner, V., González, A.O., Domingues, M.O., Mendes, O., Papa, A.R.R.: 2014a, Study of local regularities in solar wind data and ground magnetograms. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 112, 10. DOI.
Klausner, V., Mendes, O., Domingues, M.O., Papa, A.R., Tyler, R.H., Frick, P., Kherani, E.A.: 2014b, Advantage of wavelet technique to highlight the observed geomagnetic perturbations linked to the Chilean tsunami (2010). J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119(4), 3077. DOI.
Klausner, V., Domingues, M.O., Mendes, O., Papa, A.R.R.: 2011, Tsunami effects on the Z component of the geomagnetic field. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. arXiv [physics.space-ph].
Klausner, V., Gonzalez, A.O., Domingues, M.O., Papa, A.R.: 2020, Orthogonal discrete wavelet decomposition: Part 2. Analysis of magnetogram data.
Kravtsova, M.V., Sdobnov, V.E.: 2017, Analyzing the June 2015 Forbush effect by the spectrographic global survey. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci., Phys. 81, 177. DOI.
Kuwabara, T., Bieber, J.W., Evenson, P., Munakata, K., Yasue, S., Kato, C., Fushishita, A., Tokumaru, M., Duldig, M.L., Humble, J.E., Silva, M.R., Dal Lago, A., Schuch, N.J.: 2009, Determination of interplanetary coronal mass ejection geometry and orientation from ground-based observations of galactic cosmic rays. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 114(A5), A05109. DOI.
Le Roux, J.A., Potgieter, M.S.: 1991, The simulation of Forbush decreases with time-dependent cosmic-ray modulation models of varying complexity. Astron. Astrophys. 243, 531.
Lee, S., Oh, S., Yi, Y.: 2013, Simultaneity of Forbush decrease events observed at middle-latitude neutron monitors. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 118(2), 608. DOI.
Lee, S., Oh, S., Yi, Y., Evenson, P., Jee, G., Choi, H.: 2015, Long-term statistical analysis of the simultaneity of Forbush decrease events at middle latitudes. J. Astron. Space Sci. 32(1), 33. DOI.
Li, G., Ning, B., Hu, L., Liu, L., Yue, X., Wan, W., Zhao, B., Igarashi, K., Kubota, M., Otsuka, Y., Xu, J.S.: 2010, Longitudinal development of low-latitude ionospheric irregularities during the geomagnetic storms of July 2004. J. Geophys. Res. 115, A04304. DOI.
Liou, K., Newell, P.T., Meng, C.L.: 2001, Seasonal effect on auroral particle acceleration and precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. 106(A4), 551. DOI.
Lockwood, J.: 1971, Forbush decreases in the cosmic radiation. Space Sci. Rev. 12(5), 658. DOI.
Mallat, S.G.: 1989, Multiresolution approximations and wavelet orthonormal bases of \(L^{2}\) (\(R\)). Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 315(1), 69. DOI.
Mallat, S.G., Falzon, F.: 1997, Understanding wavelet image compression. In: Wavelet Applications IV. International Society for Optics and Photonics 3078, 74.
Mathpal, C., Prasad, L., Pokharia, M., Bhoj, C.: 2018, Study of cosmic ray intensity in relation to the interplanetary magnetic field and geomagnetic storms for solar cycle 24. Astrophys. Space Sci. 363(8), 177. DOI.
Mendes, O., Domingues, M.O., da Costa, A.M., Clúa de Gonzalez, A.L.: 2005, Wavelet analysis applied to magnetograms: Singularity detections related to geomagnetic storms. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 67(17–18), 1827. DOI.
Menke, W., Menke, J.: 2012 Environmental Data Analysis with MatLab, Academic Press, San Diego, 1. ISBN 9780123918864. DOI.
Mewaldt, R.A.: 2010, Cosmic Rays. California Institute of Technology. http://www.srl.caltech.edu/personnel/dick/cos_encyc.html.
Meyer, Y.: 1990, Ondelettes Et Operateurs, Hermann, Paris.
Mishra, R.K., Adhikari, B., Chapagain, N.P., Baral, R., Das, P.K., Klausner, V., Sharma, M.: 2020, Variation on solar wind parameters and total electron content over middle-to low-latitude regions during intense geomagnetic storms. Radio Sci. 55(11), e2020RS007129. DOI.
Momani, M., Al Smadi, T., al-taweel, F., Ghaidan, K.: 2011, GPS ionospheric total electron content and scintillation measurements during the October 2003 magnetic storm. Am. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 4(2), 301. DOI.
Nava, B., Rodríguez-Zuluaga, J., AlazoCuartas, K., Kashcheyev, A., Migoya-Orué, Y., Radicella, S.M., Amory-Mazaudier, C., Fleury, R.: 2016, Middle- and low-latitude ionosphere response to 2015 St. Patrick’s Day geomagnetic storm. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 121(4), 3421. DOI.
Ngwira, C.M., McKinnell, L.A., Cilliers, P.J., Coster, A.J.: 2012, Ionospheric observations during the geomagnetic storm events on 24–27 July 2004: Long-duration positive storm effects. J. Geophys. Res. 117, A00L02. DOI.
Oh, S.Y.: 2008, Magnetic cloud and its interplanetary shock sheath as a modulator of the cosmic ray intensity. J. Astron. Space Sci. 25(2), 149. DOI.
Oh, S.Y., Yi, Y.: 2009, Statistical reality of globally non simultaneous Forbush decrease events. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 114(A11), A11102. DOI.
Ojeda, A.G., Correa, M.S., Klausner, V., Domingues, M.O., Mendes, O. Jr., Papa, A.R.R.: 2009, Orthogonal discrete wavelet decomposition: Part 1. Using ACE satellite data. In: 8th Brazilian Conference on Dynamics, Control and Applications, May 18–22. Google Scholar link: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=Orthogonal+discrete+wavelet+decomposition%3A+Part+1.+Using+ACE+satellite+data.&btnG=.
Ojeda, A.G., Junior, O.M., Menconi, V.E., Domingues, M.O.: 2014, Daubechies wavelet coefficients: A tool to study interplanetary magnetic field fluctuations. Geofís. Int. 53(2), 101. DOI.
Patel, K., Singh, A., Singh, S.B., Singh, A.K.: 2019, Causes responsible for intense and severe storms during the declining phase of Solar Cycle 24. J. Astrophys. Astron. 40(1), 4. DOI.
Pedatella, N.M., Forbes, J.M., Lei, J., Thayer, J.P., Larson, K.M.: 2008, Changes in the longitudinal structure of the low-latitude ionosphere during the July 2004 sequence of geomagnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. 113, A11315. DOI.
Poudel, P., Parajuli, N., Gautam, A., Sapkota, D., Adhikari, H., Adhikari, B., Silwal, A., Gautam, S.P., Karki, M., Mishra, R.K.: 2020, Wavelet and cross-correlation analysis of relativistic electron flux with sunspot number, solar flux, and solar wind parameters. J. Nepal Phys. Soc. 6(2), 104. DOI.
Puccio, L., Montefusco, L., Chui, C.K.: 1994, Wavelets: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications 5, Academic Press, New York.
Raghav, A., Shaikh, Z., Bhaskar, A., Datar, G., Vichare, G.: 2017, Forbush decrease: A new perspective with classification. Solar Phys. 292(8), 99. DOI.
Richardson, I.G.: 2004, Energetic particles and corotating interaction regions in the solar wind. Space Sci. Rev. 111, 267.
Ruskai, M.B., Beylkin, G., Coifman, R., Daubechies, I., Mallat, S., Meyer, Y., Raphael, L. (eds.): 1992, Wavelets and Their Applications, Jones and Bartlett, Boston.
Samara, E., Smponias, A., Lytrosyngounis, I., Lingri, D., Mavromichalaki, H., Sgouropoulos, C.: 2018, Unusual cosmic ray variations during the Forbush decreases of June 2015. Solar Phys. 293(4), 67. DOI.
Sharma, S., Galav, P., Dashora, N., Pandey, R.: 2011, Longitudinal study of the ionospheric response to the geomagnetic storm of 15 May 2005 and manifestation of TADs. Ann. Geophys. 29(6), 1063. DOI.
Sifuzzaman, M., Islam, M.R., Ali, M.Z.: 2009, Application of wavelet transform and its advantages compared to Fourier transform. J. Phys. Sci. 13, 121.
Silwal, A., Gautam, S.P., Poudel, P., Karki, M., Adhikari, B., Chapagain, N.P., Mishra, R.K., Ghimire, B.D., Migoya-Orue, Y.: 2021, GPS observations of ionospheric TEC variations during the 15 January 2010 and 21 June 2020 solar eclipse. Radio Sci. 56(5), e2020RS007215. DOI.
Singh, A.K., Singh, D., Singh, R.P.: 2011, Impact of galactic cosmic rays on Earth’s atmosphere and human health. Atmos. Environ. 45(23), 3806. DOI.
Singh, P.K., Tripathi, L., Singh, A., Tiwari, J., Tiwari, A.K.: 2008, Solar winds streams and their impact on cosmic ray intensity decreases in year 2003. Rom. J. Phys. 53(7–8), 917.
Strang, G.: 1993, Wavelet transforms versus Fourier transforms. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 28(2), 288. DOI.
Strang, G., Nguyen, T.: 1996, Wavelet and Filters Bank, Wellesley-Cambridge, Cambridge.
Tomova, D., Velinov, P.I., Tassev, Y.: 2017, Comparison between extreme solar activity during periods March 15-17, 2015 and September 4-10, 2017 at different phases of solar cycle 24. Bulg. Acad. Sci., Space Res. Technol. Inst., Aerosp. Res. Bulgaria 29, 10.
Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D.: 1987, The cause of high-intensity long-duration continuous AE activity (HILDCAAs): Interplanetary Alfvén wave trains. Planet. Space Sci. 35(4), 405. DOI.
Usoro, A.E.: 2015, Some basic properties of cross-correlation functions of n-dimensional vector time series. J. Stat. Econ. Methods 4(1), 63.
Usoskin, I.G., Braun, I., Gladysheva, O.G., Hörandel, J.R., Jämsén, T., Kovaltsov, G.A., Starodubtsev, S.A.: 2008, Forbush decreases of cosmic rays: Energy dependence of the recovery phase. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 113(A7), A07102. DOI.
Xu, W.H., Xing, Z.Y., Balan, N., Liang, L.K., Wang, Y.L., Zhang, Q.H., Sun, Z.D., Li, W.B.: 2021, Spectral analysis of geomagnetically induced current and local magnetic field during the 17 March 2013 geomagnetic storm. DOI
Yuan, N., Fu, Z., Zhang, H., Piao, L., Xoplaki, E., Luterbacher, J.: 2015, Detrended partial-cross-correlation analysis: A new method for analyzing correlations in complex system. Sci. Rep. 5(1), 1.
Zhang, J., Richardson, I.G., Webb, D.F., Gopalswamy, N., Huttunen, E., Kasper, J.C., Nitta, N.V., Poomvises, W., Thompson, B.J., Wu, C.C., Yashiro, S.: 2007 Oct, Solar and interplanetary sources of major geomagnetic storms (Dst\(\leq -100\) nT) during 1996–2005. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys., 112(A10). DOI.
Zhao, L.L., Zhang, H.: 2016, Transient galactic cosmic-ray modulation during solar cycle 24: A comparative study of two prominent Forbush decrease events. Astrophys. J. 827(1), 13. DOI.
Acknowledgment
Geomagnetic index Dst and solar-wind parameter IMF-Bz data were obtained from the OMNI (http://omniweb.gsfc.nasa.gov/) site. In addition, cosmic-ray intensity data of five different high-latitude stations, corrected for pressure and efficiency, were downloaded from the Bartol Research Institute Neutron Monitor Data site, supported by the National Science Foundation (http://neutronm.bartol.udel.edu/). We want to thank staff members of NASA and the Bartol Research Institute for making the data available.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: Table 1 was replaced and a typographical error corrected.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, R.K., Silwal, A., Baral, R. et al. Wavelet Analysis of Forbush Decreases at High-Latitude Stations During Geomagnetic Disturbances. Sol Phys 297, 26 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-022-01948-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-022-01948-z