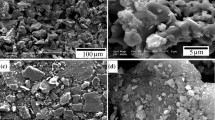
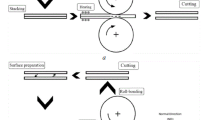
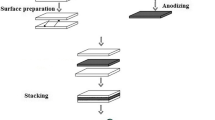
Aluminum alloy 1050 strips are roll-bonded with interlayer Al2O3 particles. The effect of rolling parameters on the bond strength, such as the content of Al2O3 particles, plastic deformation, and rolling temperature are investigated by peel test. It is established that higher bond strength can be obtained by increasing the rolling temperature, reducing the thickness, and decreasing the alumina content. The peeling surface of samples versus alumina content is characterized by scanning electron microscopy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. H. W. Seah, J. Hemanth, and S. C. Sharma, “Effect of high-rate heat transfer during casting on the strength, hardness and wear behaviour of aluminium-quartz particulate metal matrix composites,” Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B: J. Eng. Manuf., 217, No. 5, 651–659 (2003).
S. V. Prasad and R. Asthana, “Aluminum metal-matrix composites for automotive applications: Tribological considerations,” Tribol. Letters, 17, No. 3, 445–453 (2004).
M. Sedighi, P. Farhadipour, and M. Heydari vini, “Mechanical properties and microstructural evolution of bimetal 1050/Al2O3/5083 composites fabricated by warm accumulative roll bonding,” JOM, 68, No.12, 3193–3200 (2016).
M. Alizadeh, “Effects of temperature and B4C content on the bonding properties of roll-bonded aluminum strips,” J. Mater. Sci., 47, No. 11, 4689–4695 (2012).
O. Emadinia, S. Simões, F. Viana, et al., “Cold rolled versus sputtered Ni/Ti multilayers for reactionassisted diffusion bonding,” Weld. World, 60, No. 2, 337–344 (2016).
H. Alvandi and K. Farmanesh, “Microstructural and mechanical properties of nano/ultra-fine structured 7075 aluminum alloys by accumulative roll-bonding process,” Proc. Mater. Sci.., 11, 17–23 (2015).
V. Jindal, V. C. Srivastava, and R. N. Ghosh, “Development of IF steel–Al multilayer composite by repetitive roll bonding and annealing process,” Mater. Sci. Technol., 24, No. 7, 798–802 (2008).
M. Eizadjou, H. D. Manesh, and K. Janghorban, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of ultra-fine grains (UFGs) aluminum strips produced by ARB,” J. Alloys Comp., 474, Nos. 1–2, 406–415 (2009).
R. Jamaati and M. R. Toroghinejad, “The role of surface preparation parameters on cold roll bonding of aluminum strips,” J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 20, No. 2, 191–197 (2011).
M. Reihanian, F. K. Hadadian, and M. H. Paydar, “Fabrication of Al–2 vol.% Al2O3/SiC hybrid composite via accumulative roll bonding (ARB): An investigation of the microstructure and mechanical properties,” Mater. Sci. Eng.: A, 607, 188–196 (2014).
M. Abbasi and M. R. Toroghinejad, “Effects of processing parameters on the bond strength of Cu/Cu rollbonded strips,” J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 210, No. 3, 560–563 (2010).
K. S. Suresh, S. Sinha, A. Chaudhary, and S. Suwas, “Development of microstructure and texture in Copper during warm accumulative roll bonding,” Mater. Character., 70, 74–82 (2012).
M. Eizadjou, H. D. Manesh, and K. Janghorban, “Mechanism of warm and cold roll bonding of aluminum alloy strips,” Mater. Design, 30, No. 10, 4156–4161 (2009).
S. Attar, M. Nagaral, H. N. Reddappa, and V. Auradi, “Effect of B4C particulates addition on wear properties of Al7025 alloy composites,” Am. J. Mater. Sci., 5(3C), 53–57 (2015).
M. Hosseini and H. Danesh Manesh, “Bond strength optimization of Ti/Cu/Ti clad composites produced by roll-bonding,” Mater. Design, 81,122–132 (2015).
P. Farhadipour, M. Sedighi, and M. Heydari vini, “Using warm accumulative roll bonding method to produce Al–Al2O3 metal matrix composite,” Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B: J. Eng. Manufact., 231, No. 5, 889–896 (2017).
A. Fattah-Alhosseini, A. Naseri, and M. H. Alemi, “Corrosion behavior assessment of finely dispersed and highly uniform Al/B4C/SiC hybrid composite fabricated via accumulative roll bonding process,” J. Manufact. Proc., 22, 120–126 (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Vol. 56, Nos. 5–6 (515), pp. 3–9, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heydari Vini, M., Sedighi, M. & Farhadipour, P. Effect of Al2O3 Particles on Bond Strength in the Roll Bonding Process of Al-1050 Bi-Layers. Powder Metall Met Ceram 56, 239–244 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-017-9891-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-017-9891-7