Abstract
Background and aims
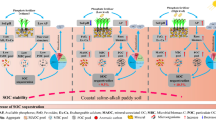
Phosphorus (P) availability in calcareous soils is limited. Acidifying the soil by adding sulfur (S) or enhancing microbial activity by adding carbon (C) can increase P bioavailability. However, understanding of the impact of the combined application of P, S and C on P availability in calcareous soils is lacking. In this study, we investigated the effects of heterogeneous (co-localized) supply of different combinations of P, S and C on the maize (Zea mays L.) shoot and root growth and soil P availability in calcareous soil with low available P.
Methods
A rhizo-box experiment with heterogeneous supply of P, S and C was conducted to assess the responses of maize growth, root morphology and physiology, as well as soil P availability.
Results
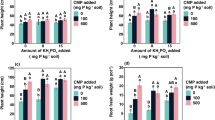
Heterogeneous low P (P1) with S supply significantly increased shoot and root biomass, shoot P content and P-use efficiency (PUE) compared to homogenous or heterogeneous P1 supply alone. Application of S decreased the rhizosphere soil pH and stimulated the proliferation of maize roots. By contrast, heterogeneous P1 and C supply did not change shoot biomass, P uptake or PUE but decreased root biomass. The addition of C, however, enhanced acid phosphatase activity and carboxylates concentration in the rhizosphere, and increased NaHCO3-extractable P, implying enhanced P availability.
Conclusion
Adding S combined with P is an effective approach to engineer the rhizosphere by increasing maize growth and PUE in calcareous soil, whereas adding C increased NaHCO3-extractable soil P but did not influence maize shoot growth.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Besharati H (2017) Effects of sulfur application and Thiobacillus inoculation on soil nutrient availability, wheat yield and plant nutrient concentration in calcareous soils with different calcium carbonate content. J Plant Nutr 40:447–456. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2016.1245326
Bloom AJ, Meyerhoff PA, Taylor AR, Rost TL (2002) Root development and absorption of ammonium and nitrate from the rhizosphere. J Plant Growth Regul 21:416–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-003-0009-8
Brookes P, Powlson D, Jenkinson D (1982) Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 14:319–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(82)90001-3
Brownrigg S, McLaughlin MJ, McBeath T, Vadakattu G (2022) Effect of acidifying amendments on P availability in calcareous soils. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 124:247–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-022-10241-1
Butterly CR, Bünemann EK, McNeill AM, Baldock JA, Marschner P (2009) Carbon pulses but not phosphorus pulses are related to decreases in microbial biomass during repeated drying and rewetting of soils. Soil Biol Biochem 41:1406–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.03.018
Chen J, Yu Z, Ouyang J, Van Mensvoort M (2006) Factors affecting soil quality changes in the North China plain: a case study of Quzhou County. Agric Syst 91:171–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2006.02.005
Corrales I, Amenós M, Poschenrieder C, Barceló J (2007) Phosphorus efficiency and root exudates in two contrasting tropical maize varieties. J Plant Nutr 30:887–900. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226510701375085
Deluca T, Skogley E, Engel R (1989) Band-applied elemental sulfur to enhance the phytoavailability of phosphorus in alkaline calcareous soils. Biol Fert Soils 7:346–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00257831
Demoling F, Figueroa D, Bååth E (2007) Comparison of factors limiting bacterial growth in different soils. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2485–2495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.05.002
Drew M (1975) Comparison of the effects of a localised supply of phosphate, nitrate, ammonium and potassium on the growth of the seminal root system, and the shoot, in barley. New Phytol 75:479–490. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1975.tb01409.x
Edelmann HG, Fry SC (1992) Kinetics of integration of xyloglucan into the walls of suspension-cultured rose cells. J Exp Bot 43:463–470. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/43.4.463
Evans J, McDonald L, Price A (2006) Application of reactive phosphate rock and Sulphur fertilisers to enhance the availability of soil phosphate in organic farming. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 75:233–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-006-9030-1
Gaume A, Mächler F, De León C, Narro L, Frossard E (2001) Low-P tolerance by maize (Zea mays L.) genotypes: significance of root growth, and organic acids and acid phosphatase root exudation. Plant Soil 228:253–264. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004824019289
Havlin JL, Beaton J, Tisdale S, Nelson W (2005) Soil fertility and fertilizers: an introduction to nutrient management. Pretice Hall, New Jersey
Hopkins B, Ellsworth J (2005) Phosphorus availability with alkaline/calcareous soil. Western nutrient management conference. University of Idaho, Idaho Falls
Jaggi RC, Aulakh MS, Sharma R (2005) Impacts of elemental S applied under various temperature and moisture regimes on pH and available P in acidic, neutral and alkaline soils. Biol Fert Soils 41:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-004-0792-9
Jakobsen I, Leggett ME, Richardson AE (2005) Rhizosphere microorganisms and plant phosphorus uptake. Phosphorus: agriculture and the environment 46:437–494. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronmonogr46.c14
Jing J, Rui Y, Zhang F, Rengel Z, Shen J (2010) Localized application of phosphorus and ammonium improves growth of maize seedlings by stimulating root proliferation and rhizosphere acidification. Field Crop Res 119:355–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2010.08.005
Jing J, Gao W, Cheng L, Wang X, Duan F, Yuan L, Rengel Z, Zhang F, Li H, Cahill JF Jr, Shen J (2022) Harnessing root-foraging capacity to improve nutrient-use efficiency for sustainable maize production. Field Crop Res 279:108462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2022.108462
Johnson CM, Ulrich A (1959) Analytical methods for use in plant analysis. Calif Agric Exp Stat, Berkeley, California
Karlova R, Boer D, Hayes S, Testerink C (2021) Root plasticity under abiotic stress. Plant Physiol 187:1057–1070. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiab392
Kumar A, Shahbaz M, Koirala M, Blagodatskaya E, Seidel SJ, Kuzyakov Y, Pausch J (2019) Root trait plasticity and plant nutrient acquisition in phosphorus limited soil. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 182:945–952. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201900322
Kuzyakov Y, Xu X (2013) Competition between roots and microorganisms for nitrogen: mechanisms and ecological relevance. New Phytol 198:656–669. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12235
Lambers H, Shane MW, Cramer MD, Pearse SJ, Veneklaas EJ (2006) Root structure and functioning for efficient acquisition of phosphorus: matching morphological and physiological traits. Ann Bot 98:693–713. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcl114
Li H, Shen J, Zhang F, Marschner P, Cawthray G, Rengel Z (2010) Phosphorus uptake and rhizosphere properties of intercropped and monocropped maize, faba bean, and white lupin in acidic soil. Biol Fert Soils 46:79–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-009-0411-x
Li H, Ma Q, Li H, Zhang F, Rengel Z, Shen J (2014) Root morphological responses to localized nutrient supply differ among crop species with contrasting root traits. Plant Soil 376:151–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1965-9
Lindemann W, Aburto J, Haffner W, Bono A (1991) Effect of sulfur source on sulfur oxidation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 55:85–90. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1991.03615995005500010015x
Liu Y, Mi G, Chen F, Zhang J, Zhang F (2004) Rhizosphere effect and root growth of two maize (Zea mays L.) genotypes with contrasting P efficiency at low P availability. Plant Sci 167:217–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.02.026
Liu H, White PJ, Li C (2016) Biomass partitioning and rhizosphere responses of maize and faba bean to phosphorus deficiency. Crop Pasture Sci 67:847–856. https://doi.org/10.1071/CP16015
Lyu Y, Tang H, Li H, Zhang F, Rengel Z, Whalley WR, Shen J (2016) Major crop species show differential balance between root morphological and physiological responses to variable phosphorus supply. Front Plant Sci 7:1939. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01939
Malik KM, Khan KS, Billah M, Akhtar MS, Rukh S, Alam S, Munir A, Mahmood Aulakh A, Rahim M, Qaisrani MM (2021) Organic amendments and elemental sulfur stimulate microbial biomass and sulfur oxidation in alkaline subtropical soils. Agronomy 11:2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11122514
Marschner P (2007) Plant-microbe interactions in the rhizosphere and nutrient cycling. In: Marschner P, Rengel Z (eds) Nutrient cycling in terrestrial ecosystems, 1st edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 159–182
Marschner P, Crowley D, Rengel Z (2011) Rhizosphere interactions between microorganisms and plants govern iron and phosphorus acquisition along the root axis–model and research methods. Soil Biol Biochem 43:883–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.01.005
McKeague J, Day J (1966) Dithionite-and oxalate-extractable Fe and Al as aids in differentiating various classes of soils. Can J Soil Sci 46:13–22. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjss66-003
McLaughlin MJ, McBeath TM, Smernik R, Stacey SP, Ajiboye B, Guppy C (2011) The chemical nature of P accumulation in agricultural soils—implications for fertiliser management and design: an Australian perspective. Plant Soil 349:69–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0907-7
Neumann G (2006) Quantitative determination of acid phosphatase activity in the rhizosphere and on the root surface. Handbook of methods used in rhizosphere research Birmensdorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Research Institute WSL: 79–85
Neumann G, George TS, Plassard C (2009) Strategies and methods for studying the rhizosphere—the plant science toolbox. Plant Soil 321:431–456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-9953-9
Norris M, Titshall L (2012) The distribution of inherent phosphorus in fifteen water treatment residues from South Africa. Water SA 38:715–720. https://doi.org/10.4314/wsa.v38i5.9
Oburger E, Schmidt H (2016) New methods to unravel rhizosphere processes. Trends Plant Sci 21:243–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2015.12.005
Pearse SJ, Veneklaas EJ, Cawthray G, Bolland MD, Lambers H (2007) Carboxylate composition of root exudates does not relate consistently to a crop species’ ability to use phosphorus from aluminium, iron or calcium phosphate sources. New Phytol 173:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01897.x
Richardson AE (2001) Prospects for using soil microorganisms to improve the acquisition of phosphorus by plants. Funct Plant Biol 28:897–906. https://doi.org/10.1071/PP01093
Richardson AE, Barea JM, McNeill AM, Prigent-Combaret C (2009) Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant Soil 321:305–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-9895-2
Richardson AE, Lynch JP, Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Smith FA, Smith SE, Harvey PR, Ryan MH, Veneklaas EJ, Lambers H (2011) Plant and microbial strategies to improve the phosphorus efficiency of agriculture. Plant Soil 349:121–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0950-4
Robinson D (1994) The responses of plants to non-uniform supplies of nutrients. New Phytol 127:635–674. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1994.tb02969.x
Robinson D (2001) Root proliferation, nitrate inflow and their carbon costs during nitrogen capture by competing plants in patchy soil. Plant Soil 232:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010377818094
Rowell DL (1994) Soil science: methods and applications. Longman, London
Rukshana F, Butterly CR, Baldock JA, Tang C (2011) Model organic compounds differ in their effects on pH changes of two soils differing in initial pH. Biol Fert Soils 47:51–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-010-0498-0
Santangeli M, Steininger-Mairinger T, Vetterlein D, Hann S, Oburger E (2024) Maize (Zea mays L.) root exudation profiles change in quality and quantity during plant development–a field study. Plant Sci 338:111896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2023.111896
Schachtman DP, Reid RJ, Ayling SM (1998) Phosphorus uptake by plants: from soil to cell. Plant Physiol 116:447–453. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.116.2.447
Scherer HW (2001) Sulphur in crop production. Eur J Agron 14:81–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1161-0301(00)00082-4
Shen J, Yuan L, Zhang J, Li H, Bai Z, Chen X, Zhang W, Zhang F (2011) Phosphorus dynamics: from soil to plant. Plant Physiol 156:997–1005. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.175232
Soltangheisi A, Haygarth PM, Pavinato PS, Cherubin MR, Teles APB, de Oliveira BR, Carvalho JLN, Withers PJ, Martinelli LA (2021) Long term sugarcane straw removal affects soil phosphorus dynamics. Soil Till Res 208:104898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104898
Stevenson FJ, Cole MA (1999) Cycles of soils: carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, micronutrients. Wiley
Stutter MI, Shand CA, George TS, Blackwell MS, Dixon L, Bol R, MacKay RL, Richardson AE, Condron LM, Haygarth PM (2015) Land use and soil factors affecting accumulation of phosphorus species in temperate soils. Geoderma 257:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.03.020
Vance CP, Uhde-Stone C, Allan DL (2003) Phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol 157:423–447. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00695.x
Vermeiren C, Kerckhof P, Reheul D, Smolders E (2022) Increasing soil organic carbon content can enhance the long-term availability of phosphorus in agricultural soils. Eur J Soil Sci 73:e13191. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.13191
Wang J, Wu Y, Zhou J, Bing H, Sun H (2016) Carbon demand drives microbial mineralization of organic phosphorus during the early stage of soil development. Biol Fert Soils 52:825–839. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-016-1123-7
Wang L, Li X, Mang M, Ludewig U, Shen J (2021) Heterogeneous nutrient supply promotes maize growth and phosphorus acquisition: additive and compensatory effects of lateral roots and root hairs. Ann Bot 128:431–440. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcab097
Wen Z, Li H, Shen Q, Tang X, Xiong C, Li H, Pang J, Ryan MH, Lambers H, Shen J (2019) Tradeoffs among root morphology, exudation and mycorrhizal symbioses for phosphorus-acquisition strategies of 16 crop species. New Phytol 223:882–895. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15833
Wu J, Huang M, Xiao H-A, Su Y-R, Tong C-L, Huang D-Y, Syers JK (2007) Dynamics in microbial immobilization and transformations of phosphorus in highly weathered subtropical soil following organic amendments. Plant Soil 290:333–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-9165-5
Xu Z, Qu M, Liu S, Duan Y, Wang X, Brown LK, George TS, Zhang L, Feng G (2020) Carbon addition reduces labile soil phosphorus by increasing microbial biomass phosphorus in intensive agricultural systems. Soil Use Manag 36:536–546. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12585
Yang H, Xu HS, Zhang WP, Li ZX, Fan HX, Lambers H, Li L (2022) Overyielding is accounted for partly by plasticity and dissimilarity of crop root traits in maize/legume intercropping systems. Funct Ecol 36:2163–2175. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.14115
Ye R, Wright AL, McCray JM, Reddy K, Young L (2010) Sulfur-induced changes in phosphorus distribution in Everglades agricultural area soils. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 87:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-009-9319-y
Yun SJ, Kaeppler SM (2001) Induction of maize acid phosphatase activities under phosphorus starvation. Plant Soil 237:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013329430212
Zhang W, Ma W, Ji Y, Fan M, Oenema O, Zhang F (2008) Efficiency, economics, and environmental implications of phosphorus resource use and the fertilizer industry in China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 80:131–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-007-9126-2
Zhang L, Ding X, Chen S, He X, Zhang F, Feng G (2014) Reducing carbon: phosphorus ratio can enhance microbial phytin mineralization and lessen competition with maize for phosphorus. J Plant Interact 9:850–856. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2014.977831
Zhang D, Zhang C, Tang X, Li H, Zhang F, Rengel Z, Whalley WR, Davies WJ, Shen J (2016) Increased soil phosphorus availability induced by faba bean root exudation stimulates root growth and phosphorus uptake in neighbouring maize. New Phytol 209:823–831. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13613
Zhao C, Degryse F, Gupta V, McLaughlin MJ (2015) Elemental sulfur oxidation in Australian cropping soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 79:89–96. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2014.08.0314
Zhou T, Du Y, Ahmed S, Liu T, Ren M, Liu W, Yang W (2016) Genotypic differences in phosphorus efficiency and the performance of physiological characteristics in response to low phosphorus stress of soybean in southwest of China. Front Plant Sci 7:1776. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01776
Zou T, Zhang X, Davidson E (2022) Global trends of cropland phosphorus use and sustainability challenges. Nature 611:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05220-z
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32130094), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFD1901502), the Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (321CXTD443), the 2115 Talent Development Program of China Agricultural University, the Yunnan Science and Technology Department project “Yunnan Modern Agricultural Green Technology Innovation Platform (No. 202102AE090053)”, Project of New Fertilizer Research and Development of Yun-Tian-Hua Group of Yunnan of China (YTH-4320-WB-FW-2021-031303-00), China Scholarship Council (No. 201913043) and Hainan University. We especially thank to Dr. Kai Zhang and Mr. Jie Xu for their kind help in experiment set up and sample collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jianbo Shen and Dongfang Zheng designed the study. Dongfang Zheng carried out the glasshouse and laboratory work, analysed the data and wrote the manuscript. Yang Lyu, Gerard H. Ros, Wim de Vries, Zed Rengel and Jianbo Shen contributed to the review and editing of the manuscript, data analysis, and language editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eusun Han.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, D., Lyu, Y., Ros, G.H. et al. Heterogeneous co-supplies of phosphorus, sulfur and carbon enhance phosphorus availability by improving rhizosphere processes in a calcareous soil. Plant Soil (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-024-06623-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-024-06623-9