Abstract
Aims
Seagrass beds occur globally and are substantial blue carbon sinks, yet factors that affect sediment organic carbon (SOC) sequestration are poorly characterized. We investigated the influences of eutrophication on SOC sequestration capacity in a mixed seagrass bed dominated by Thalassia hemprichii and Enhalus acoroides.
Methods
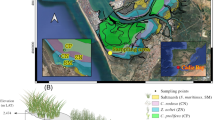
We surveyed a tropical seagrass bed in the South China Sea along fish farming-induced gradients of nutrients to assess the variability of SOC content and composition in 30-cm-long sediment cores.
Results
No significant difference was observed for the SOC content and stock between the two species. Significantly higher microbial biomass carbon and SOC density were observed at the surface 3 cm layer under E. acoroides, and the longer roots of E. acoroides enhanced the seagrass contribution to the SOC near the root tip. SOC had a statistically lower concentration in the sediment layers where the seagrass roots primarily thrive close to fish farming, but greater exchangeable organic carbon was found in all the sediment layers as they approached fish farming. Nutrient enrichment markedly induced a larger ratio of labile C pools in almost all sediment layers. The mean SOC stock in the seagrass bed in Xincun Bay was 6.80 ± 1.03 Mg C/ha, and it showed insignificant variation along the nutrient gradient.
Conclusions
Eutrophication may indirectly reduce the SOC sequestration capacity in the seagrass bed by enhancing labile organic carbon with a shorter resident time, and measures should be taken to reduce nutrient input into the seagrass bed to enhance its carbon sink.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ao K (2016) Increase of fish caging resulted in death of mass fish in Xinbun Bay, Lingshui. Sou Metro Dai. Hainan Daily Press, Hainan, http://www.hinews.cn/news/system/2016/04/05/030283948.shtml
Armitage A, Fourqurean JW (2016) Carbon storage in seagrass soils: long-term nutrient history exceeds the effects of near-term nutrient enrichment. Biogeosciences 13:313–321
Benbi DK, Kiranvir B, Sharma S (2015) Sensitivity of labile soil organic carbon pools to long-term fertilizer, straw and manure management in rice-wheat system. Pedosphere 25:534–545
Burkholder JM, Tomasko DA, Touchette BW (2007) Seagrasses and eutrophication. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 350:46–72
Buyanovsky G, Aslam M, Wagner G (1994) Carbon turnover in soil physical fractions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:1167–1173
Carreiro M, Sinsabaugh R, Repert D, Parkhurst D (2000) Microbial enzyme shifts explain litter decay responses to simulated nitrogen deposition. Ecology 81:2359–2365
Chambers LG, Osborne TZ, Reddy KR (2013) Effect of salinity-altering pulsing events on soil organic carbon loss along an intertidal wetland gradient: a laboratory experiment. Biogeochemistry 115:363–383
Cheng X, Chen J, Luo Y, Henderson R, An S, Zhang Q, Chen J, Li B (2008) Assessing the effects of short-term Spartina alterniflora invasion on labile and recalcitrant C and N pools by means of soil fractionation and stable C and N isotopes. Geoderma 145:177–184
Chun CH, Wu ZJ, Zhang GX (2011) Ecological status and sustainable utilization of seagrass bed in Xincun Bay. Ocean Dev Manag 11:74–78 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cleveland CC, Townsend AR (2006) Nutrient additions to a tropical rain forest drive substantial soil carbon dioxide losses to the atmosphere. P Natl Acad Sci USA 103:10316–10321
Dahl M, Deyanova D, Lyimo LD, Näslund J, Samuelsson G, Mtolera MS, Björk M, Gullström M (2016) Effects of shading and simulated grazing on carbon sequestration in a tropical seagrass meadow. J Ecol 104:654–664
Dauwe B, Middelburg JJ, Herman PM (2001) Effect of oxygen on the degradability of organic matter in subtidal and intertidal sediments of the North Sea area. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 215:13–22
Davies G, Ghabbour EA, Steelink C (2001) Humic acids: marvelous products of soil chemistry. J Chem Educ 78:1609
Dodla SK, Wang JJ, DeLaune RD (2012) Characterization of labile organic carbon in coastal wetland soils of the Mississippi River deltaic plain: relationships to carbon functionalities. Sci Total Environ 435:151–158
Duarte CM, Middelburg JJ, Caraco NF (2005) Major role of marine vegetation on the oceanic carbon cycle. Biogeosciences 2:1–8
Duarte CM, Marbà N, Gacia E, Fourqurean JW, Beggins J, Barrón C, Apostolaki ET (2010) Seagrass community metabolism: assessing the carbon sink capacity of seagrass meadows. Global Biogeochem Cy 24
Duarte CM, Losada IJ, Hendriks IE, Mazarrasa I, Marbà N (2013a) The role of coastal plant communities for climate change mitigation and adaptation. Nat Clim Chang 3:961–968
Duarte CM, Sintes T, Marbà N (2013b) Assessing the CO2 capture potential of seagrass restoration projects. J Appl Ecol 50:1341–1349
Ellis L, Osborne T, Clark D, Gommermann L, Hicks C (2013) Seagrass mitigation site modeling and assessment. The University of Florida Soil and Water Science Department, Florida
Fang C, Smith P, Moncrieff JB, Smith JU (2005) Similar response of labile and resistant soil organic matter pools to changes in temperature. Nature 433:57–59
Ferrera CM, Watanabe A, Miyajima T, San Diego-McGlone ML, Morimoto N, Umezawa Y, Herrera E, Tsuchiya T, Yoshikai M, Nadaoka K (2016) Phosphorus as a driver of nitrogen limitation and sustained eutrophic conditions in Bolinao and Anda, Philippines, a mariculture-impacted tropical coastal area. Mar Pollut Bull 105:237–248
Fonseca MS, Cahalan JA (1992) A preliminary evaluation of wave attenuation by four species of seagrass. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 35:565–576
Fourqurean JW, Duarte CM, Kennedy H, Marbà N, Holmer M, Mateo MA, Apostolaki ET, Kendrick GA, Krause-Jensen D, McGlathery KJ (2012) Seagrass ecosystems as a globally significant carbon stock. Nat Geosci 5:505–509
General Administration of Quality Supervision IaQotPsRoC, Standardization Aministration of the People’s Republic of China (2008) GB17378.4-2007. The specification for marine monitoring, part 4: seawater analysis (in Chinese). the Standards Press of China, Beijing
Ghani A, Dexter M, Perrott K (2003) Hot-water extractable carbon in soils: a sensitive measurement for determining impacts of fertilisation, grazing and cultivation. Soil Biol Biochem 35:1231–1243
Greiner JT, McGlathery KJ, Gunnell J, McKee BA (2013) Seagrass restoration enhances “blue carbon” sequestration in coastal waters. PLoS One 8:e72469
Guan SY, Zhang D, Zhang Z (1986) Soil enzyme and its research methods. Agricultural, Beijing
Hayes J (1993) Factors controlling 13 C contents of sedimentary organic compounds: principles and evidence. Mar Geol 113:111–125
Haynes R (2005) Labile organic matter fractions as central components of the quality of agricultural soils: an overview. Adv Agron 85:221–268
Hedges JI, Keil RG (1995) Sedimentary organic matter preservation: an assessment and speculative synthesis. Mar Chem 49:81–115
Hejnowicz AP, Kennedy H, Huxham MR, Rudd MA (2015) Harnessing the climate mitigation, conservation and poverty alleviation potential of seagrasses: prospects for developing blue carbon initiatives and payment for ecosystem service programmes. Front Mar Sci 2:32
Hicks CE (2007) Sediment organic carbon pools and sources in a recently constructed mangrove and seagrass ecosystem. University of Florida
Howard J, Hoyt S, Isensee K, Telszewski M, Pidgeon E (2014) Coastal blue carbon: methods for assessing carbon stocks and emissions factors in mangroves, tidal salt marshes, and seagrasses. Conservation International, Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO, International Union for Conservation of Nature, Arlington
Howard JL, Perez A, Lopes CC, Fourqurean JW (2016) Fertilization changes seagrass community structure but not blue carbon storage: results from a 30-Year field experiment. Estuar Coast 39:1–13
Hu Y, Wang S, Zeng D (2006) Effects of single Chinese fir and mixed leaf litters on soil chemical, microbial properties and soil enzyme activities. Plant Soil 282:379–386
Huang X, Huang L, Li Y, Xu Z, Fong C, Huang D, Han Q, Huang H, Tan Y, Liu S (2006) Main seagrass beds and threats to their habitats in the coastal sea of South China. Chin Sci Bull 51:136–142
Jamaludin MR (2015) Carbon storage and preservation in seagrass meadows. Edith Cowan University
Jiang ZJ, Huang XP, Zhang JP (2012) Effect of environmental stress on non-structural carbohydrates reserves and transfer in seagrass. Acta Ecol Sin 32:6242–6250 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jiang Z, Huang X, Zhang J (2013a) Dynamics of nonstructural carbohydrates in seagrass Thalassia hemprichii and its response to shading. Acta Oceanol Sin 32:61–67
Jiang Z, Huang X, Zhang J (2013b) Effect of nitrate enrichment and salinity reduction on the seagrass Thalassia hemprichii previously grown in low light. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 443:114–122
Keil R, Mayer L (2014) Mineral matrices and organic matter. In: Holland H, Turekian K (eds) Treatlse on Geochemmistry. Elsevier, Oxford
Kennedy H, Beggins J, Duarte CM, Fourqurean JW, Holmer M, Marbà N, Middelburg JJ (2010) Seagrass sediments as a global carbon sink: isotopic constraints. Glob Biogeochem Cy 24:6696–6705
Kenworthy JW, Thayer GW (1984) Production and decomposition of the roots and rhizomes of seagrasses, Zostera marina and Thalassia testudinum, in temperate and subtropical marine ecosystems. B Mar Sci 35:364–379
Lavery PS, Mateo M-Á, Serrano O, Rozaimi M (2013) Variability in the carbon storage of seagrass habitats and its implications for global estimates of blue carbon ecosystem service. PLoS One 8:e73748
Leoni V, Vela A, Pasqualini V, Pergent-Martini C, Pergent G (2008) Effects of experimental reduction of light and nutrient enrichments (N and P) on seagrasses: a review. Aquat Conserv 18:202–220
Li Q, Huang W, Zhou Y (2010) A preliminary study of eutrophication and occurrence of red tides in Xincun harbour. T Oceanol Limnol 4:9–15
Li X, Hou L, Liu M, Lin X, Li Y, Li S (2015) Primary effects of extracellular enzyme activity and microbial community on carbon and nitrogen mineralization in estuarine and tidal wetlands. Appl Microbiol Biot 99:2895–2909
Liu SL, Jiang ZJ, Zhang JP, Wu YC, Lian ZL, Huang XP (2016) Effect of nutrient enrichment on the source and composition of sediment organic carbon in tropical seagrass beds in the South China Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 110:274–280
Liu S, Jiang Z, Wu Y, Zhang J, Arbi I, Feng Y, Huang X, Macreadie PI (2017a) Effects of nutrient load on microbial activities within a seagrass-dominated ecosystem: implications of changes in seagrass blue carbon. Mar Pollut Bull 117:214–221
Liu S, Jiang Z, Zhang J, Wu Y, Huang X, Macreadie PI (2017b) Sediment microbes mediate the impact of nutrient loading on blue carbon sequestration by mixed seagrass meadows. Sci Total Environ 599–600:1479–1484
Macreadie PI, Allen K, Kelaher BP, Ralph PJ, Skilbeck CG (2012) Paleoreconstruction of estuarine sediments reveal human-induced weakening of coastal carbon sinks. Glob Chang Biol 18:891–901
Macreadie PI, York PH, Sherman CD, Keough MJ, Ross DJ, Ricart AM, Smith TM (2014) No detectable impact of small-scale disturbances on ‘blue carbon’within seagrass beds. Mar Biol 161:2939–2944
Marbà N, Arias-Ortiz A, Masqué P, Kendrick GA, Mazarrasa I, Bastyan GR, Garcia-Orellana J, Duarte CM (2015) Impact of seagrass loss and subsequent revegetation on carbon sequestration and stocks. J Ecol 103:296–302
Matocha CJ, Haszler GR, Grove JH (2004) Nitrogen fertilization suppresses soil phenol oxidase enzyme activity in no-tillage systems. Soil Sci 169:708–714
Mcglathery KJ (2008) Chapter 23—seagrass habitats. In: Nitrogen in the marine environment. Academic Press, New York
McGlathery KJ, Sundback K, Anderson IC (2007) Eutrophication in shallow coastal bays and lagoons: the role of plants in the coastal filter. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 348:1–18
Miyajima T, Hori M, Hamaguchi M, Shimabukuro H, Adachi H, Yamano H, Nakaoka M (2015) Geographic variability in organic carbon stock and accumulation rate in sediments of east and southeast Asian seagrass meadows. Glob Biogeochem Cy 29:397–415
Pang X, Zhu B, Lü X, Cheng W (2015) Labile substrate availability controls temperature sensitivity of organic carbon decomposition at different soil depths. Biogeochemistry 126:85–98
Phang VX, Chou L, Friess DA (2015) Ecosystem carbon stocks across a tropical intertidal habitat mosaic of mangrove forest, seagrass meadow, mudflat and sandbar. Earth Surf Proc Lan 40:1387–1400
Ralph PJ, Tomasko D, Moore K, Seddon S, Macinnis-Ng CM (2006) Human impacts on seagrasses: eutrophication, sedimentation, and contamination. Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation. Springer, Netherlands
Ralph P, Durako M, Enriquez S, Collier C, Doblin M (2007) Impact of light limitation on seagrasses. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 350:176–193
Rollón RN (1998) Spatial variation and seasonality in growth and reproduction of Enhalus acoroides (LF) Royle populations in the coastal waters off Cape Bolinao, NW Philippines. UNESCO-IHE, Institute for Water Education
Rozaimi M, Lavery PS, Serrano O, Kyrwood D (2016) Long-term carbon storage and its recent loss in an estuarine Posidonia australis meadow (Albany, Western Australia). Estuar Coast Shelf S 171:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2016.01.001
Saiya-Cork K, Sinsabaugh R, Zak D (2002) The effects of long term nitrogen deposition on extracellular enzyme activity in an Acer saccharum forest soil. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1309–1315
Samper-Villarreal J, Lovelock CE, Saunders MI, Roelfsema C, Mumby PJ (2016) Organic carbon in seagrass sediments is influenced by seagrass canopy complexity, turbidity, wave height, and water depth. Limnol Oceanogr 61:938–952
Schmidt AL, Wysmyk JK, Craig SE, Lotze HK (2012) Regional-scale effects of eutrophication on ecosystem structure and services of seagrass beds. Limnol Oceanogr 57:1389–1402
Serrano O, Lavery PS, Rozaimi M, Mateo MÁ (2014) Influence of water depth on the carbon sequestration capacity of seagrasses. Glob Biogeochem Cy 28:950–961
Tanaka Y, Go GA, Watanabe A, Miyajima T, Nakaoka M, Uy WH, Nadaoka K, Watanabe S, Fortes MD (2014) 17-year change in species composition of mixed seagrass beds around Santiago Island, Bolinao, the northwestern Philippines. Mar Pollut Bull 88:81–85
Trevathan-Tackett SM, Kelleway JJ, Macreadie PI, Beardall J, Ralph P, Bellgrove A (2015) Comparison of marine macrophytes for their contributions to blue carbon sequestration. Ecology 96:3043–3057
Vance E, Brookes P, Jenkinson D (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Wang H, He Z, Lu Z, Zhou J, Van Nostrand JD, Xu X, Zhang Z (2012) Genetic linkage of soil carbon pools and microbial functions in subtropical freshwater wetlands in response to experimental warming. Appl Environ Microb 78:7652–7661
Watanabe K, Kuwae T (2015) How organic carbon derived from multiple sources contributes to carbon sequestration processes in a shallow coastal system? Glob Chang Biol 21:2612–2623
Waycott M, Duarte CM, Carruthers TJ, Orth RJ, Dennison WC, Olyarnik S, Calladine A, Fourqurean JW, Heck KL, Hughes AR (2009) Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. P Natl Acad Sci USA 106:12377–12381
Xiao Y, Huang Z, Lu X (2015) Changes of soil labile organic carbon fractions and their relation to soil microbial characteristics in four typical wetlands of Sanjiang plain, Northeast China. Ecol Eng 82:381–389
Yin R, Deng H, Wang H-l, Zhang B (2014) Vegetation type affects soil enzyme activities and microbial functional diversity following re-vegetation of a severely eroded red soil in sub-tropical China. Catena 115:96–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2013.11.015
Zhang XL, Shi SL, Pan GX, Li LQ, Zhang XH, Li Z (2008) Changes in eco-chemical properties of a mangrove wetland under Spartina invasion from Zhangjiangkou, Fujian, China. Adv Earth Sci 23:974–981 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang J, Huang X, Jiang Z (2014) Physiological responses of the seagrass Thalassia hemprichii (Ehrenb.) Aschers as indicators of nutrient loading. Mar Pollut Bull 83:508–515
Zhou CY, Jiang ZJ, Lian ZL, Zhang JP, Ni ZX, Xu BY, Huang XP (2014) Characteristics of seagrass Thalassia hemprichii leaf litter and its response to the fish farming in the Xincun Bay, Hainan Island. Chin J Ecol 133:1546–1552 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zibilske L, Bradford J, Smart J (2002) Conservation tillage induced changes in organic carbon, total nitrogen and available phosphorus in a semi-arid alkaline subtropical soil. Soil Till Res 66:153–163
Funding
This research was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2015CB452905, 2015CB452902), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 41730529, 41306108, 41406128), the Natural Science Fund of Guangdong (nos. 2014A030313734, 2014A030313716), the National Specialized Project of Science and Technology (2015FY110600), and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFC0506104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Hans Lambers.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 5.11 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Z., Liu, S., Zhang, J. et al. Eutrophication indirectly reduced carbon sequestration in a tropical seagrass bed. Plant Soil 426, 135–152 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3604-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3604-y