Abstract
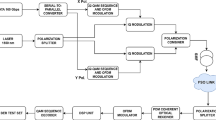
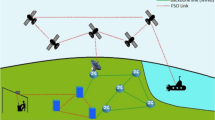
In all-optical WDM network an effective usability of wavelength converter and further its placement at appropriate node in the network is the key challenge. To fulfill this challenge we proposed an efficient Electro absorption modulator (EAM) based wavelength converter and further its placement in all-optical wavelength routed network based on arbitrary ring topology which employs 10 Gbps NRZ modulated signal to minimize the system blocking problem. Here EAM based wavelength converter is used due to its unique qualitiesi.e. the fast absorption recovery time as compared to gain recovery time of semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOAs), compactness, low cost and compatibility with monolithic integration.The performance of the system has been validated in terms of call blocking probability, impact of variation in fiber length at 280 km, 360 km, 480 km and 560 km on quality; with and without placement of wavelength converter. The main contribution of this work is to find the most congested nodes in the ring connected network and then placement of wavelength converter on that particular congested nodes to support maximum number of users to form resilient network. It has been concluded that EAM based wavelength converter placed at utmost congested nodes in WDM network for 480 km fiber length at 5dBm input power, the faithful quality is maintained for every channel.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Bonani, L.H., Fonseca, I.E.: Estimating the blocking probability in wavelength-routed optical networks. Opt. Switch. Netw. 10(4), 430–438 (2013)
Charbonneau, N., Vokkarane, V.M.: Routing and wavelength assignment of static manycast demands over all-optical wavelength-routed WDM networks. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2(7), 442–455 (2010)
Chlamtac, I., Ganz, A., Karmi, G.: Lightpath communications: an approach to high bandwidth optical WAN’s. IEEE Trans. Commun. 40(7), 1171–1182 (1992)
Edagawa, N., Suzuki, M., Yamamoto, S.: Novel wavelength converter using an electroabsorption modulator. IEICE Trans. Electron. 81(8), 1251–1257 (1998)
Fernando, G.C.: Ana Maria Sarmiento, Differentialevolution optimization applied to the wavelength converters placement problem in all optical network. Comput. Netw. 56, 2262–2275 (2012)
Iyad, D.M.: Adaptive alternate routing in WDM networks and its performance tradeoffs in the presence of wavelength converters. Opt. Switch. Netw. 6, 181–193 (2009)
Jia, X.H., Du, D.Z., Hu, X.D., Huang, H.J., Li, D.Y.: On the optimal placement of wavelength converters in WDM networks. Comput. Commun. 26(9), 986–995 (2003)
Kaur, T., Singh, S.: Performance analysis of electro-absorption modulator-based multi-wavelength converter. Photonic Netw. Commun. 35(1), 53–64 (2018)
Kuwatsuka, V.I.V.W.V.: Wavelength conversion technologies for photonic network systems. Fujitsu Sci. Tech. J 35(1), 126–138 (1999)
Lee, T., Lee, K., Park, S.: Optimal routing and wavelength assignment in WDM ring networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 18, 2146–2154 (2000)
Lezama, F., Castañón, G., Sarmiento, A.M.: Differential evolution optimization applied to the wavelength converters placement problem in all optical networks. Comput. Netw. 56(9), 2262–2275 (2012)
Ramamurthy, B., Mukherjee, B.: Wavelength conversion in WDM network. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 16(7), 1061–1073 (1998)
Ramamurthy, B., Mukherjee, B.: Wavelength conversion in WDM networking. IEEE J. Selected Areas Comm. 16(7), 1061–1073 (1998)
Ramaswami, R., Sivarajan, K.: Optical Networks: A Practical Perspective. Morgan Kaufmann, Los Altos (1998)
Singh, S.: Performance comparison of optical network topologies in the presence of optimized semiconductor optical amplifiers. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 1(4), 313–323 (2009)
Stubkjaer, K.E., Kloch, A., Hansen, P.B., Poulsen, H.N., Wolfson, D., Jepsen, K.S., Buxens, A.: Wavelength converter technology. IEICE Trans. Electron. 82(2), 338–348 (1999)
Thiagarajan, S., Somani, A.K.: Optimal wavelength converter placement in arbitrary topology wavelength-routed networks. Comput. Commun. 26, 975–985 (2003)
Uma Rathore Bhatt: Sanjiv tokekar, path length based wavelength assignment strategy: a Algorithm for efficient system performance in wavelength routed WDM networks. Optik 124, 483–486 (2013)
Venugopal, K.R., Kumar, M.S., Kumar, P.S.: A heuristic for placement of limited range wavelength converters in all-optical networks. Comput. Netw. 35(2–3), 143–163 (2001)
Waldman, H., Campelo, D.R.: Analytical Calculation of Blocking Probabilities in WDM Rings with Wavelength Conversion. In: IEEE, 2nd International Conference on Broadband Networks, 2005 Boston, MA, USA.Print ISBN: 0–7803–9276–0.
Wason, A., Kaler, R.S.: Blocking probability optimization in wavelength routed optical WDM networks. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 124(17), 3131–3133 (2013)
Yang, C., Chen, S.: Performance analysis of topologies for optical wavelength convertible networks. Optik 123(11), 1001–1005 (2012)
Zakouni, A., Toumi, H., Saidi, A., Mabrouk, A.: Wavelength assignment vs. wavelength converter placement in wavelength-routed optical WDM networks. Procedia Comput. Sci. 160, 766–771 (2019)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Science & Engineering Research Board, New Delhi for their funding under Core Research Grant vide sanction no: File No. EMR/2017/004162 dated: 01-11-18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, T., Singh, S. & Lovkesh Design and placement of EAM based wavelength converter in resilient network with arbitrary topology. Opt Quant Electron 55, 270 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-04442-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-04442-9