Abstract
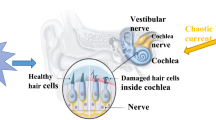
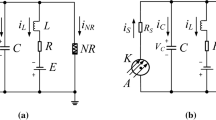
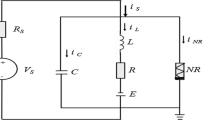
Based on an auditory neuron model developed from the piezoelectric neuronal circuit, the Hamilton energy function is obtained by using the Helmholtz’s theorem, and this energy is contributed by the electric field and magnetic field described by capacitor and inductor, respectively. Three auditory neuronal circuits with different firing states are connected in a ring network by resistor, inductor, and capacitor. The coupling channels can be tamed under voltage, magnetic field, and electric field couplings simultaneously. These three types of coupling can modulate synchronization via continuous energy exchange and pumping, and the resistor channel consumes Joule heat, while the capacitor and inductor channels can pump and conserve field energy. The proportion of field energy maintained in each electrical component in the network is calculated separately to distinguish the dependence of firing state and synchronization mode on the energy. It is found that strong coupling increases the proportion of electric field energy in periodic neurons or the proportion of magnetic field energy in chaotic neurons. The total energy proportion of the three coupling channels continuously increases if all neurons in the network exhibit periodic firing. But the presence of neurons with chaotic firing causes the total energy proportion of the coupling channels to increase first and then decrease. In fact, more energy is injected into the inductor channel compared to resistor and capacitor, thus facilitating the synchronization of neurons connected by inductor.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed in this work are available upon request from the corresponding author.
References
Leuthardt, E.C., Schalk, G., Wolpaw, J.R., et al.: A brain-computer interface using electrocorticographic signals in humans. J. Neural Eng. 1(2), 63 (2004)
Hodgkin, A.L., Huxley, A.F.: Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J. Physiol. 116(4), 449–472 (1952)
FitzHugh, R.: Mathematical models of threshold phenomena in the nerve membrane. Bull. Math. Biophys. 17(4), 257–278 (1955)
FitzHugh, R.: An active pulse transmission line simulating nerve axon. IEEE Trans. Electron. Comput. EC-12(2), 158–158 (1963)
Hindmarsh, J.L., Rose, R.M.: A model of the nerve impulse using two first-order differential equations. Nature 296(5853), 162–164 (1982)
Hindmarsh, J.L., Rose, R.M.: A model of neuronal bursting using three coupled first order differential equations. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 221(1222), 87–102 (1984)
Morris, C., Lecar, H.: Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber. Biophys. J. 35(1), 193–213 (1981)
Baysal, V., Saraç, Z., Yilmaz, E.: Chaotic resonance in Hodgkin-Huxley neuron. Nonlinear Dyn. 97, 1275–1285 (2019)
Calim, A., Baysal, V.: Chaotic resonance in an astrocyte-coupled excitable neuron. Chaos, Solit. Fract. 176, 114105 (2023)
Baysal, V., Solmaz, R., Ma, J.: Investigation of chaotic resonance in Type-I and Type-II Morris-Lecar neurons. Appl. Math. Comput. 448, 127940 (2023)
Njitacke, Z.T., Awrejcewicz, J., Ramakrishnan, B., et al.: Hamiltonian energy computation and complex behavior of a small heterogeneous network of three neurons: circuit implementation. Nonlinear Dyn. 107(3), 2867–2886 (2022)
Wu, F.Q., Hu, X.K., Ma, J.: Estimation of the effect of magnetic field on a memristive neuron. Appl. Math. Comput. 432, 127366 (2022)
Xu, Y., Ren, G.D., Ma, J.: Patterns stability in cardiac tissue under spatial electromagnetic radiation. Chaos, Solit. Fract. 171, 113522 (2023)
Guo, Y.T., Xie, Y., Ma, J.: Nonlinear responses in a neural network under spatial electromagnetic radiation. Physica A 626, 129120 (2023)
Zhang, Y., Xu, Y., Yao, Z., et al.: A feasible neuron for estimating the magnetic field effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 102, 1849–1867 (2020)
Louodop, P., Tchitnga, R., Fagundes, F.F., et al.: Extreme multistability in a Josephson-junction-based circuit. Phys. Rev. E 99(4), 042208 (2019)
Xu, Y., Guo, Y.Y., Ren, G.D., et al.: Dynamics and stochastic resonance in a thermosensitive neuron. Appl. Math. Comput. 385, 125427 (2020)
Xu, Y., Liu, M., Zhu, Z.G., et al.: Dynamics and coherence resonance in a thermosensitive neuron driven by photocurrent. Chin. Phys. B 29(9), 098704 (2020)
Yang, F.F., Ma, J.: A controllable photosensitive neuron model and its application. Opt. Laser Technol. 163, 109335 (2023)
Zhou, P., Yao, Z., Ma, J., et al.: A piezoelectric sensing neuron and resonance synchronization between auditory neurons under stimulus. Chaos, Solit. Fract. 145, 110751 (2021)
Yang, F.F., Ma, J., An, X.L.: Mode selection and stability of attractors in Chua circuit driven by piezoelectric sources. Chaos, Solit. Fract. 162, 112450 (2022)
Liu, Z.L., Yu, Y., Wang, Q.Y.: Functional modular organization unfolded by chimera-like dynamics in a large-scale brain network model. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 65(7), 1435–1444 (2022)
Yu, Y., Fan, Y.B., Han, F., et al.: Transcranial direct current stimulation inhibits epileptic activity propagation in a large-scale brain network model. Sci. China Technol. Sci. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-022-2341-x
Liu, Z.L., Han, F., Wang, Q.Y.: A review of computational models for gamma oscillation dynamics: from spiking neurons to neural masses. Nonlinear Dyn. 108(3), 1849–1866 (2022)
Bao, H., Chen, Z.G., Cai, J.M., et al.: Memristive cyclic three-neuron-based neural network with chaos and global coexisting attractors. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 65(11), 2582–2592 (2022)
Liu, Y., Nazarimehr, F., Khalaf, A.J.M., et al.: Detecting bifurcation points in a memristive neuron model. The Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 228, 1943–1950 (2019)
Yao, Y.: Logical chaotic resonance in the FitzHugh-Nagumo neuron. Nonlinear Dyn. 107(4), 3887–3901 (2022)
Rajagopal, K., Nazarimehr, F., Karthikeyan, A., et al.: Dynamics of a neuron exposed to integer-and fractional-order discontinuous external magnetic flux. Front. Inform. Technol. Electr. Eng. 20, 584–590 (2019)
Wang, G.W., Xu, Y., Ge, M.Y., et al.: Mode transition and energy dependence of FitzHugh-Nagumo neural model driven by high-low frequency electromagnetic radiation. AEU-Int. J. Electr. Commun. 120, 153209 (2020)
Wang, R.B., Zhang, Z.K.: On energy principle of couple neuron activities. Acta Biophysica Sinica 21(6), 436–442 (2005)
Wang, C.N., Wang, Y., Ma, J.: Calculation of Hamilton energy function of dynamical system by using Helmholtz theorem. Acta Physica Sinica 65(24), 240501 (2016)
Jia, J.E., Yang, F.F., Ma, J.: A bimembrane neuron for computational neuroscience. Chaos, Solit. Fract. 173, 113689 (2023)
Xie, Y., Yao, Z., Ren, G.D., et al.: Estimate physical reliability in Hindmarsh-Rose neuron. Phys. Lett. A 464, 128693 (2023)
Njitacke, Z.T., Koumetio, B.N., Ramakrishnan, B., et al.: Hamiltonian energy and coexistence of hidden firing patterns from bidirectional coupling between two different neurons. Cogn. Neurodyn. 16, 899–916 (2022)
Ma, J.: Energy function for some maps and nonlinear oscillators. Appl. Math. Comput. 463, 128379 (2024)
Xie, Y., Zhou, P., Yao, Z.: Response mechanism in a functional neuron under multiple stimuli. Physica A 607, 128175 (2022)
Xie, Y., Ma, J.: How to discern external acoustic waves in a piezoelectric neuron under noise? J. Biol. Phys. 48(3), 339–353 (2022)
Xie, Y., Ye, Z., Li, X., et al.: A novel memristive neuron model and its energy characteristics. Cogn. Neurodyn. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-024-10065-5
Yang, F.F., Xu, Y., Ma, J.: A memristive neuron and its adaptability to external electric field. Chaos: An Interdisc. J. Nonlinear Sci. 33, 023110 (2023)
Shahverdiev, E.M., Hashimova, L.H., Bayramov, P.A., et al.: Chaos synchronization between time delay coupled Josephson junctions governed by a central junction. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 28(12), 3499–3505 (2015)
Zhang, Y., Wang, C.N., Tang, J., et al.: Phase coupling synchronization of FHN neurons connected by a Josephson junction. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 63(11), 2328–2338 (2020)
Bao, H., Hua, M.J., Ma, J., et al.: Offset-control plane coexisting behaviors in two-memristor-based Hopfield neural network. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 70(10), 10526–10535 (2023)
Wu, F.Q., Guo, Y.T., Ma, J.: Reproduce the biophysical function of chemical synapse by using a memristive synapse. Nonlinear Dyn. 109, 2063–2084 (2022)
Liu, Z.L., Wang, C.N., Zhang, G., et al.: Synchronization between neural circuits connected by hybrid synapse. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 32(16), 1950170 (2019)
Iqbal, M.: Modeling and behavioral analysis of neurons under direction-dependent resistive, inductive and capacitive coupling. Res. Control Optim. 3, 100016 (2021)
Yao, Z., Wang, C.N.: Collective behaviors in a multiple functional network with hybrid synapses. Physica A 605, 127981 (2022)
Wu, F.Q., Guo, Y.T., Ma, J., et al.: Synchronization of bursting memristive Josephson junctions via resistive and magnetic coupling. Appl. Math. Comput. 455, 128131 (2023)
Zhou, P., Ma, J., Xu, Y.: Phase synchronization between neurons under nonlinear coupling via hybrid synapse. Chaos Solit. Fract. 169, 113238 (2023)
Liu, Z.L., Wang, C.N., Jin, W.Y., et al.: Capacitor coupling induces synchronization between neural circuits. Nonlinear Dyn. 97, 2661–2673 (2019)
Sun, G.P., Yang, F.F., Ren, G.D., et al.: Energy encoding in a biophysical neuron and adaptive energy balance under field coupling. Chaos Solit. Fract. 169, 113230 (2023)
Zhang, L., An, X.L., Zhang, J.G., et al.: Bifurcation analysis and synchronous patterns between field coupled neurons with time delay. Complexity 2022, 7487477 (2022)
Zhang, L., An, X.L., Xiong, L., et al.: Synchronization, extreme multistability, and its control for a field coupled neurons with time delays. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 36(19), 2250114 (2022)
Yao, Z., Wang, C.N., Zhou, P., et al.: Regulating synchronous patterns in neurons and networks via field coupling. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 95, 105583 (2021)
Ma, J.: Biophysical neurons, energy, and synapse controllability: a review. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. A 24(2), 109–129 (2023)
Hou, B., Ma, J., Yang, F.F.: Energy-guided synapse coupling between neurons under noise. J. Biol. Phys. 49(1), 49–76 (2023)
Zhang, L., Xiong, L., An, X.L., et al.: Hamilton energy balance and synchronization behaviors of two functional neurons. Cogn. Neurodyn. 17, 1683–1702 (2023)
Zhou, P., Zhang, X.F., Ma, J.: How to wake up the electric synapse coupling between neurons? Nonlinear Dyn. 108(2), 1681–1695 (2022)
Acknowledgements
The authors thanks Dr Feifei Yang for helpful verification and checking in the proof.
Funding
This work is supported from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.12062009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm no conflict of interest with publication of this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Jin, W. & An, X. Energy evolution in function neuronal network under different coupling channels. Nonlinear Dyn 112, 8581–8602 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09469-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09469-z