Abstract
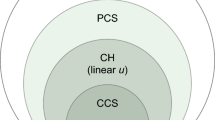
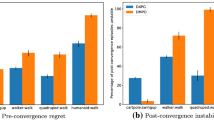
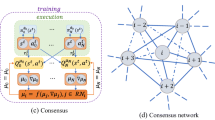
The paper addresses an event-triggered \(H_{\infty }\) containment control problem for multi-agent systems (MASs) with state constraints. Initially, the problem of state constraints is formulated as an equivalent unconstrained case by designing proper barrier functions. After that, the \(H_{\infty }\) optimal control problem is transformed into a two-player zero-sum game, and the \(H_{\infty }\) containment performance can be realized by obtaining the Nash equilibrium for zero-sum game. Then a novel event-triggered condition is designed for the optimal control and the worst disturbance. Compared with the existing event-triggered control results, the restriction on the disturbance attenuation level is relaxed. In addition, to further solve the event-triggered Hamilton–Jacobi–Isaacs equation (HJIE), a simplified reinforcement learning algorithm based on actor-critic-disturbance network is proposed by calculating the negative gradient of a constructed simple positive function. Meanwhile, such an algorithm can remove the requirement of persistent excitation condition. We also prove that, with the proposed effective strategy, all followers are driven into the convex hall spanned by multiple leaders and the state of each follower does not violate the desired set. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed scheme is verified by two simulation examples.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data available on request from the authors.
References
Meng, Z., Ren, W., You, Z.: Distributed finite-time attitude containment control for multiple rigid bodies. Automatica 46(12), 2092–2099 (2010)
Yu, Z., Liu, Z., Zhang, Y., Qu, Y., Su, C.: Distributed finite-time fault-tolerant containment control for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(6), 2077–2091 (2020)
Liu, D., Liu, Z., Chen, C.L.P., Zhang, Yun: Distributed adaptive fuzzy control approach for prescribed-time containment of uncertain nonlinear multi-agent systems with unknown hysteresis. Nonlinear Dyn. 105(1), 257C275 (2021)
Lou, Y., Hong, Y.: Target containment control of multi-agent systems with random switching interconnection topologies. Automatica 48(5), 879–885 (2012)
Zhao, Y., Duan, Z.: Finite-time containment control without velocity and acceleration measurements. Nonlinear Dyn. 82(1), 259–268 (2015)
Wang, W., Liang, H., Pan, Y., Li, T.: Prescribed performance adaptive fuzzy containment control for nonlinear multiagent systems using disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 50(9), 3879–3891 (2020)
Wang, X., Li, S., Shi, P.: Distributed finite-time containment control for double-integrator multiagent systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 44(9), 1518–1528 (2014)
Yang, C., Duan, M., Lin, P., Ren, W., Gui, W.: Distributed containment control of continuous-time multiagent systems with nonconvex control input constraints. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66(10), 7927–7934 (2019)
Liu, T., Qi, J., Jiang, Z.: Distributed containment control of multi-agent systems with velocity and acceleration saturations. Automatica 117, 108992 (2020)
Zhou, Q., Wang, W., Liang, H., Basin, M., Wang, B.: Observer-based event-triggered fuzzy adaptive bipartite containment control of multi-agent systems with input quantization. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 29(2), 372–384 (2021)
Yang, X., Wei, Q.: Adaptive critic learning for constrained optimal event-triggered control with discounted cost. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32(1), 91–104 (2021)
Luo, B., Yang, Y., Liu, D., Wu, H.: Event-triggered optimal control with performance guarantees using adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(1), 76–88 (2020)
Wen, G., Ge, S.S., Tu, F.: Optimized backstepping for tracking control of strict-feedback systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(8), 3850–3862 (2018)
Zhang, J., Zhang, H., Feng, T.: Distributed optimal consensus control for nonlinear multiagent system with unknown dynamic. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(8), 3339–3348 (2018)
Modares, H., Lewis, F.L.: Optimal tracking control of nonlinear partially-unknown constrained-input systems using integral reinforcement learning. Automatica 50(7), 1780–1792 (2014)
Abu-Khalaf, M., Huang, J., Lewis, F.L.: Nonlinear \(H_{2}/H_{\infty }\) constrained feedback control: a practical design approach using neural networks. Springer (2006)
Zhang, Z., Zhang, H., Wang, Z., Shan, Q.: Non-fragile exponential \({H}_{\infty }\) control for a class of nonlinear networked control systems with short time-varying delay via output feedback controller. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(8), 2008–2019 (2017)
Başar, T., Bernhard, P.: \({H}_{\infty }\) optimal control and related minimax design problems: a dynamic game approach. Springer (2008)
Yang, D., Li, T., Zhang, H., Xie, X.: Event-trigger-based robust control for nonlinear constrained-input systems using reinforcement learning method. Neurocomputing 340, 158–170 (2019)
Qin, C., Zhang, H., Wang, Y., Luo, Y.: Neural network-based online \({H}_{\infty }\) control for discrete-time affine nonlinear system using adaptive dynamic programming. Neurocomputing 198, 91–99 (2016)
Wei, Q., Song, R., Yan, P.: Data-driven zero-sum neuro-optimal control for a class of continuous-time unknown nonlinear systems with disturbance using ADP. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 27(2), 444–458 (2016)
Liu, Y., Tong, S.: Barrier Lyapunov functions for Nussbaum gain adaptive control of full state constrained nonlinear systems. Automatica 76, 143–152 (2017)
He, W., Chen, Y., Yin, Z.: Adaptive neural network control of an uncertain robot with full-state constraints. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 46(3), 620–629 (2016)
Zhang, T., Xia, M., Yi, Y.: Adaptive neural dynamic surface control of strict-feedback nonlinear systems with full state constraints and unmodeled dynamics. Automatica 81, 232–239 (2017)
Qiu, J., Sun, K., Rudas, I.J., Gao, H.: Command filter-based adaptive NN control for MIMO nonlinear systems with full-state constraints and actuator hysteresis. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 50(7), 2905–2915 (2020)
Tang, Z., Ge, S.S., Tee, K.P., He, W.: Robust adaptive neural tracking control for a class of perturbed uncertain nonlinear systems with state constraints. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst. 46(12), 1618–1629 (2016)
Li, H., Zhao, S., He, W., Lu, R.: Adaptive finite-time tracking control of full state constrained nonlinear systems with dead-zone. Automatica 100, 99–107 (2019)
Zhao, K., Song, Y., Chen, C.L.P., Chen, L.: Control of nonlinear systems under dynamic constraints: A unified barrier function-based approach. Automatica 119, 09102 (2020)
Yang, Y., Ding, D., Xiong, H., Yin, Y., Wunsch, D.C.: Online barrier-actor-critic learning for \({H}_{\infty }\) control with full-state constraints and input saturation. J. Franklin Inst. 357(6), 3316–3344 (2020)
Zhang, K., Zhao, T., Dian, S.: Dynamic output feedback control for nonlinear networked control systems with a two-terminal event-triggered mechanism. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(3), 2537–2555 (2020)
Xu, C., Wu, B., Cao, X., Zhang, Y.: Distributed adaptive event-triggered control for attitude synchronization of multiple spacecraft. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(4), 2625–2638 (2019)
Wang, L., Chen, C.L.P.: Reduced-order observer-based dynamic event-triggered adaptive NN control for stochastic nonlinear systems subject to unknown input saturation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32(4), 1678–1690 (2021)
Pan, Y., Wu, Y., Lam, H.K.: Security-based fuzzy control for nonlinear networked control systems with DoS attacks via a resilient event-triggered scheme. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2022.3148875
Li, H., Wu, Y., Chen, M., Lu, R.: Adaptive multigradient recursive reinforcement learning event-triggered tracking control for multiagent systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3090570
Pan, Y., Li, Q., Liang, H., Lam, H.K.: A novel mixed control approach for fuzzy systems via membership functions online learning policy. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2021.3130201
Jia, T., Pan, Y., Liang, H., Lam, H.K.: Event-based adaptive fixed-time fuzzy control for active vehicle suspension systems with time-varying displacement constraint. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2021.3075490
Zhao, J., Gan, M., Zhang, C.: Event-triggered \({H}_{\infty }\) optimal control for continuous-time nonlinear systems using neurodynamic programming. Neurocomputing 360, 14–24 (2019)
Wang, D., Mu, C., Yang, X., Liu, D.: Event-based constrained robust control of affine systems incorporating an adaptive critic mechanism. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst. 47(7), 1602–1612 (2017)
Wang, D., Mu, C., Zhang, Q., Liu, D.: Event-based input-constrained nonlinear \({H}_{\infty }\) state feedback with adaptive critic and neural implementation. Neurocomputing 214, 848–856 (2016)
Xue, S., Luo, B., Liu, D.: Event-triggered adaptive dynamic programming for zero-sum game of partially unknown continuous-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst. 50(9), 3189–3199 (2020)
Yang, X., He, H.: Event-driven \({H}_{\infty }\)-constrained control using adaptive critic learning. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 51(10), 4860–4872 (2021)
Zhao, K., Song, Y., Zhang, Z.: Tracking control of MIMO nonlinear systems under full state constraints: A single-parameter adaptation approach free from feasibility conditions. Automatica 107, 52–60 (2019)
Lewis, F.L., Vrabie, D., Syrmos, V.L.: Optimal Control. Wiley (2012)
Zhang, Q., Zhao, D., Wang, D.: Event-based robust control for uncertain nonlinear systems using adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(1), 37–50 (2018)
Rudin, W.: Principles of Mathematical Analysis. McGraw-Hill (1976)
Xue, L., Zhang, T., Zhang, W., Xie, X.: Global adaptive stabilization and tracking control for high-order stochastic nonlinear systems with time-varying delays. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 63(9), 2928–2943 (2018)
Liu, Y., Liu, X., Jing, Y., Wang, H., Li, X.: Annular domain finite-time connective control for large-scale systems with expanding construction. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst. 51(10), 6159–6169 (2021)
Funding
This work was partially supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (62103214, 62003097), the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (2021M700077), the Postdoctoral Innovation Project of Shandong Province under Grant (202101014), the Fund of Qingdao Postdoctoral Application Research Project and the Joint Funds of Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2019A1515110505).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Wang, L., Liu, Y. et al. Event-triggered optimal containment control for multi-agent systems subject to state constraints via reinforcement learning. Nonlinear Dyn 109, 1651–1670 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07513-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07513-4