Abstract
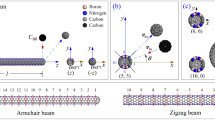
The nonlinear dynamic behavior of a clamped–clamped nanobeam built with boron nitride carbon (BNC) nanotube is investigated as for its potential application in a mass sensor. To make it anisotropic in terms of bending stiffness, the cross section of the tube contains symmetrically two B–N zones and two carbon zones which accommodate 60% of atoms in the whole nanotube. The dynamic behavior of the nanosensor, colliding with a high-speed \(\hbox {C}_{60}\) at the central part of the beam, is evaluated using molecular dynamics simulations and fast Fourier transform approaches. Results obtained show that the amplitude of vibration of the tube depends on the magnitude \((v_{\mathrm{In}})\) and direction (\(\theta \)) of the incident velocity of the \(\hbox {C}_{60}\). When \(v_{\mathrm{In}}\) is higher than a critical value, the beam will be damaged in the collision. The position of the damage on the nanobeam and the critical value depend on \(\theta \). If \(v_{\mathrm{In}}\) is lower than the critical value, the first-order frequency of the vibration at the beam centroid is lower when impacted by a faster \(\hbox {C}_{60}\). The second-order frequency depends on the configuration of the beam’s central cross section. The intervals of the first-order frequency with respect to \(\theta = 0^{\circ }\) and \(90^{\circ }\) are not overlapped. These findings hint that a BNC nanobeam can be used to measure the mass of a molecular under a known incident velocity or an incident velocity of a known molecular via this model.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Poncharal, P., Wang, Z., Ugarte, D., De Heer, W.A.: Electrostatic deflections and electromechanical resonances of carbon nanotubes. Science 283(5407), 1513–1516 (1999)
Burg, T.P., Godin, M., Knudsen, S.M., Shen, W., Carlson, G., Foster, J.S., et al.: Weighing of biomolecules, single cells and single nanoparticles in fluid. Nature 446(7139), 1066–1069 (2007)
Zhang, Y., Liu, Y.: Detecting both the mass and position of an accreted particle by a micro/nano-mechanical resonator sensor. Sensors 14(9), 16296–16310 (2014)
Sazonova, V., Yaish, Y., Üstünel, H., Roundy, D., Arias, T.A., McEuen, P.L.: A tunable carbon nanotube electromechanical oscillator. Nature 431(7006), 284–287 (2004)
Garcia-Sanchez, D., San Paulo, A., Esplandiu, M.J., Perez-Murano, F., Forró, L., Aguasca, A., et al.: Mechanical detection of carbon nanotube resonator vibrations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99(8), 085501 (2007)
Imboden, M., Mohanty, P.: Dissipation in nanoelectromechanical systems. Phys. Rep. 534(3), 89–146 (2014)
Yang, Y.-T., Callegari, C., Feng, X., Ekinci, K.L., Roukes, M.L.: Zeptogram-scale nanomechanical mass sensing. Nano Lett. 6(4), 583–586 (2006)
Jensen, K., Kim, K., Zettl, A.: An atomic-resolution nanomechanical mass sensor. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3(9), 533 (2008)
Chaste, J., Eichler, A., Moser, J., Ceballos, G., Rurali, R., Bachtold, A.: A nanomechanical mass sensor with yoctogram resolution. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7(5), 301 (2012)
Qiu, W., Kang, Y.L., Lei, Z.K., Qin, Q.H., Li, Q., Wang, Q.: Experimental study for Raman Strain Rosette based on carbon nanotube strain sensor. J. Raman Spectroscopy 41, 1216–1220 (2010)
Cai, K., Yu, J., Wan, J., Yin, H., Qin, Q.H.: Configuration jumps of rotor in a nanomotor from carbon nanostructures. Carbon 101, 168–176 (2016)
Cai, K., Li, Y., Qin, Q.H., Yin, H.: Gradientless temperature-driven rotating motor from a double-walled carbon nanotube. Nanotechnology 25(50), 505701 (2014)
Qin, Z., Qin, Q.H., Feng, X.Q.: Mechanical property of carbon nanotubes with intramolecular junctions: molecular dynamics simulations. Phys. Lett. A 372(44), 6661–6666 (2008)
Qiu, W., Kang, Y.L., Lei, Z.K., Qin, Q.H., Li, Q.: A new theoretical model of a carbon nanotube strain sensor. Chin. Phys. Lett. 26(8), 080701 (2009)
Xu, T., Ruzziconi, L., Younis, M.I.: Global investigation of the nonlinear dynamics of carbon nanotubes. Acta Mech. 228(3), 1029–1043 (2017)
Xu, T., Younis, M.I.: Nonlinear dynamics of carbon nanotubes under large electrostatic force. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 11(2), 021009 (2016)
Qiu, W., Li, Q., Lei, Z.K., Qin, Q.H., Deng, W.L., Kang, Y.L.: The use of a carbon nanotube sensor for measuring strain by micro-Raman spectroscopy. Carbon 53, 161–168 (2013)
Chopra, N.G., Luyken, R., Cherrey, K., Crespi, V.H.: Boron nitride nanotubes. Science 269(5226), 966 (1995)
Loiseau, A., Willaime, F., Demoncy, N., Hug, G., Pascard, H.: Boron nitride nanotubes with reduced numbers of layers synthesized by arc discharge. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76(25), 4737–4740 (1996)
Arenal, R., Stephan, O., Cochon, J.-L., Loiseau, A.: Root-growth mechanism for single-walled boron nitride nanotubes in laser vaporization technique. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129(51), 16183–16189 (2007)
Knobel, R.G.: Mass sensors: weighing single atoms with a nanotube. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3(9), 525–526 (2008)
Enouz, S., Stéphan, O., Cochon, J.-L., Colliex, C., Loiseau, A.: C–BN patterned single-walled nanotubes synthesized by laser vaporization. Nano Lett. 7(7), 1856–1862 (2007)
Zhang, G., Liu, Z., Zhang, L., Jing, L., Shi, K.: Growth and characterization of BCN nanotubes with high boron and nitrogen content. J. Chem. Sci. 125(5), 1169–1176 (2013)
Zhang, J., Meguid, S.: Composition-dependent buckling behaviour of hybrid boron nitride-carbon nanotubes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17(19), 12796–12803 (2015)
Chiang, W.-H., Hsieh, C.-Y., Lo, S.-C., Chang, Y.-C., Kawai, T., Nonoguchi, Y.: C/BCN core/shell nanotube films with improved thermoelectric properties. Carbon 109, 49–56 (2016)
Cai, K., Yang, L.-K., Shi, J., Qin, Q.-H.: Critical conditions for escape of a high-speed fullerene from a BNC nanobeam after collision. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 913 (2018)
Kroto, H.W., Heath, J.R., Obrien, S.C., Curl, R.F., Smalley, R.E.: C60—Buckminsterfullerene. Nature 318(6042), 162–163 (1985)
Mohlenkamp, M.J.: A fast transform for spherical harmonics. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 5(2–3), 159–184 (1999)
Heideman, M., Johnson, D., Burrus, C.: Gauss and the history of the fast Fourier transform. IEEE ASSP Mag. 1(4), 14–21 (1984)
Tersoff, J.: Modeling solid-state chemistry: interatomic potentials for multicomponent systems. Phys. Rev. B 39(8), 5566 (1989)
Stuart, S.J., Tutein, A.B., Harrison, J.A.: A reactive potential for hydrocarbons with intermolecular interactions. J. Chem. Phys. 112(14), 6472–6486 (2000)
Jones, J.E.: On the determination of molecular fields. II. From the equation of state of a gas. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 106, 463–477 (1924)
Weaver Jr., W., Timoshenko, S.P., Young, D.H.: Vibration Problems in Engineering. Wiley, New York (1990)
Smirnov, V., Manevitch, L.: Semi-inverse method in nonlinear mechanics: application to couple shell-and beam-type oscillations of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nonlinear Dyn. 93, 205–218 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for financial support from National Key Research and Development Plan, China (Grant No.: 2017YFC0405102), National Natural Science Foundation, China (11772204; 51505388), Research Foundation for PhD in Northwest A&F University (Grant No.: 2452016176), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No.: 2452017119).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Cai, K., Shi, J. et al. Nonlinear dynamic behavior of a clamped–clamped beam from BNC nanotube impacted by fullerene. Nonlinear Dyn 96, 1133–1145 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-04845-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-04845-6