Abstract
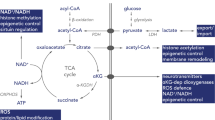
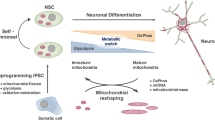
Brain is the major consumer of glucose in the human body, whose pattern of consumption changes through lifetime, decreasing during adolescence up to adulthood. This evidence leads to the hypothesis that, in cerebral developmental stages, glycolysis might be the driving force for the high-energy requirement. Furthermore, several studies claim that neurogenesis process is accompanied by a shift into mitochondrial oxidative metabolism. Herein, we discuss recent work about cell metabolism during neuronal differentiation process, in particular the mitochondrial role in cellular bioenergy dynamics.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramón CS (1928) Degeneration and regeneration of the nervous system. Hafner Publishing Company, New York
Balu DT, Lucki I (2009) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis: regulation, functional implications, and contribution to disease pathology. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 33(3):232–252
Kempermann G, Gast D, Kronenberg G, Yamaguchi M, Gage FH (2003) Early determination and long-term persistence of adult-generated new neurons in the hippocampus of mice. Development 130(2):391–399
Ahlenius H, Visan V, Kokaia M, Lindvall O, Kokaia Z (2009) Neural stem and progenitor cells retain their potential for proliferation and differentiation into functional neurons despite lower number in aged brain. J Neurosci 29(14):4408–4419
Tropepe V, Craig CG, Morshead CM, van der Kooy D (1997) Transforming growth factor-alpha null and senescent mice show decreased neural progenitor cell proliferation in the forebrain subependyma. J Neurosci 17(20):7850–7859
Enwere E, Shingo T, Gregg C, Fujikawa H, Ohta S, Weiss S (2004) Aging results in reduced epidermal growth factor receptor signaling, diminished olfactory neurogenesis, and deficits in fine olfactory discrimination. J Neurosci 24(38):8354–8365
Darsalia V, Heldmann U, Lindvall O, Kokaia Z (2005) Stroke-induced neurogenesis in aged brain. Stroke 36(8):1790–1795
Palmer TD, Takahashi J, Gage FH (1997) The adult rat hippocampus contains primordial neural stem cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 8(6):389–404
Reynolds BA, Weiss S (1996) Clonal and population analyses demonstrate that an EGF-responsive mammalian embryonic CNS precursor is a stem cell. Dev Biol 175(1):1–13
Reynolds BA, Weiss S (1992) Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science 255(5052):1707–1710
Raineteau O, Rietschin L, Gradwohl G, Guillemot F, Gähwiler BH (2004) Neurogenesis in hippocampal slice cultures. Mol Cell Neurosci 26(2):241–250
Mistry SK, Keefer EW, Cunningham BA, Edelman GM, Crossin KL (2002) Cultured rat hippocampal neural progenitors generate spontaneously active neural networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(3):1621–1626
Song H, Stevens CF, Gage FH (2002) Astroglia induce neurogenesis from adult neural stem cells. Nature 417(6884):39–44
Song H, Stevens CF, Gage FH (2002) Neural stem cells from adult hippocampus develop essential properties of functional CNS neurons. Nat Neurosci 5(5):438–445
Burns TC, Verfaillie CM, Low WC (2009) Stem cells for ischemic brain injury: a critical review. J Comp Neurol 515(1):125–144
Weiss S, Dunne C, Hewson J, Wohl C, Wheatley M, Peterson AC et al (1996) Multipotent CNS stem cells are present in the adult mammalian spinal cord and ventricular neuroaxis. J Neurosci 16(23):7599–7609
Markakis EA, Gage FH (1999) Adult-generated neurons in the dentate gyrus send axonal projections to field CA3 and are surrounded by synaptic vesicles. J Comp Neurol 406(4):449–460
van Praag H, Schinder AF, Christie BR, Toni N, Palmer TD, Gage FH (2002) Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature 415(6875):1030–1034
Shors TJ, Miesegaes G, Beylin A, Zhao M, Rydel T, Gould E (2001) Neurogenesis in the adult is involved in the formation of trace memories. Nature 410(6826):372–376
Shors TJ, Townsend DA, Zhao M, Kozorovitskiy Y, Gould E (2002) Neurogenesis may relate to some but not all types of hippocampal-dependent learning. Hippocampus 12(5):578–584
Aberg MA, Aberg ND, Hedbacker H, Oscarsson J, Eriksson PS (2000) Peripheral infusion of IGF-I selectively induces neurogenesis in the adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 20(8):2896–2903
Cameron HA, McKay RD (1999) Restoring production of hippocampal neurons in old age. Nat Neurosci 2(10):894–897
Liu J, Solway K, Messing RO, Sharp FR (1998) Increased neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus after transient global ischemia in gerbils. J Neurosci 18(19):7768–7778
van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage FH (2000) Neural consequences of environmental enrichment. Nat Rev Neurosci 1(3):191–198
Panchision DM (2009) The role of oxygen in regulating neural stem cells in development and disease. J Cell Physiol 220(3):562–568
Simon MC, Keith B (2008) The role of oxygen availability in embryonic development and stem cell function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9(4):285–296
Maltepe E, Krampitz GW, Okazaki KM, Red-horse K, Mak W, Simon MC et al (2005) Hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent histone deacetylase activity determines stem cell fate in the placenta. Development 132:3393–3403
Dings J, Meixensberger J, Jager A, Roosen K (1998) Clinical experience with 118 brain tissue oxygen partial pressure catheter probes. Neurosurgery 43(5):1082–1095
Da Silveira Paulsen B, Souza Da Silveira M, Galina A, Kastrup Rehen S (2013) Pluripotent stem cells as a model to study oxygen metabolism in neurogenesis and neurodevelopmental disorders. Arch Biochem Biophys 534(1–2):3–10
Pourié G, Blaise S, Trabalon M, Nédélec E, Guéant J-L, Daval J-L (2006) Mild, non-lesioning transient hypoxia in the newborn rat induces delayed brain neurogenesis associated with improved memory scores. Neuroscience 140(4):1369–1379
Chen C-T, Hsu S-H, Wei Y-H (2012) Mitochondrial bioenergetic function and metabolic plasticity in stem cell differentiation and cellular reprogramming. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820(5):571–576
Vieira HLA, Alves PM, Vercelli A (2011) Modulation of neuronal stem cell differentiation by hypoxia and reactive oxygen species. Prog Neurobiol 93(3):444–455
Dirnagl U, Meisel A (2008) Endogenous neuroprotection: mitochondria as gateways to cerebral preconditioning? Neuropharmacology 55(3):334–344
Naylor M, Bowen KK, Sailor K a, Dempsey RJ, Vemuganti R (2005) Preconditioning-induced ischemic tolerance stimulates growth factor expression and neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. Neurochem Int 47(8):565–572
Ara J, De montpellier S (2013) Hypoxic-preconditioning enhances the regenerative capacity of neural stem/progenitors in subventricular zone of newborn piglet brain. Stem Cell Res 11(2):669–686
Varela-Nallar L, Rojas-Abalos M, Abbott AC, Moya EA, Iturriaga R, Inestrosa NC (2014) Chronic hypoxia induces the activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway and stimulates hippocampal neurogenesis in wild-type and APPswe-PS1DeltaE9 transgenic mice in vivo. Front Cell Neurosci 8:17
Zhang K, Zhou Y, Zhao T, Wu L, Huang X, Wu K et al (2015) Reduced cerebral oxygen content in the DG and SVZ in situ promotes neurogenesis in the adult rat brain in vivo. PLoS One 10(10)
Pedroso D, Nunes AR, Diogo LN, Oudot C, Monteiro EC, Brenner C, Vieira HL (2016) Hippocampal neurogenesis response: what can we expect from two different models of hypertension? Brain Res 1646:199–206
Prozorovski T, Schneider R, Berndt C, Hartung H-P, Aktas O (2015) Redox-regulated fate of neural stem progenitor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1850(8):1543–1554
Ostrakhovitch EA, Semenikhin OA (2013) The role of redox environment in neurogenic development. Arch Biochem Biophys 534(1–2):44–54
Le Belle JE, Orozco NM, Paucar AA, Saxe JP, Mottahedeh J, Pyle AD et al (2011) Proliferative neural stem cells have high endogenous ROS levels that regulate self-renewal and neurogenesis in a PI3K/Akt-dependant manner. Cell Stem Cell 8(1):59–71
Almeida AS, Soares NL, Vieira M, Gramsbergen JB, Vieira HLA (2016) Carbon monoxide releasing molecule-A1 (CORM-A1) improves neurogenesis: increase of neuronal differentiation yield by preventing cell death. PLoS One 11(5):e0154781
Tsatmali M, Walcott EC, Crossin KL (2005) Newborn neurons acquire high levels of reactive oxygen species and increased mitochondrial proteins upon differentiation from progenitors. Brain Res 1040(1–2):137–150
Cho YM, Kwon S, Pak Y, Seol H, Choi Y, Park D et al (2006) Dynamic changes in mitochondrial biogenesis and antioxidant enzymes during the spontaneous differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348:1472–1478
Nitti M, Furfaro AL, Cevasco C, Traverso N, Marinari UM, Pronzato MA et al (2010) PKC delta and NADPH oxidase in retinoic acid-induced neuroblastoma cell differentiation. Cell Signal 22(5):828–835
Suzukawa K, Miura K, Mitsushita J, Resau J, Hirose K, Crystal R et al (2000) Nerve growth factor-induced neuronal differentiation requires generation of Rac1-regulated reactive oxygen species. J Biol Chem 275(18):13175–13178
Schmidt-Kastner R, van Os J, Steinbusch H WM, Schmitz C (2006) Gene regulation by hypoxia and the neurodevelopmental origin of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 84(2–3):253–271
Le Belle JE, Orozco NM, Paucar A a, Saxe JP, Mottahedeh J, Pyle AD et al (2011) Proliferative neural stem cells have high endogenous ROS levels that regulate self-renewal and neurogenesis in a PI3K/Akt-dependant manner. Cell Stem Cell 8(1):59–71
Kennedy K a M, Sandiford SDE, Skerjanc IS, Li SS-C (2012) Reactive oxygen species and the neuronal fate. Cell Mol Life Sci 69(2):215–221
Margineantu DH, Hockenbery DM (2016) Mitochondrial functions in stem cells. Curr Opin Genet Dev 38:110–117
Lavelle A (1963) Mitochondrial changes in developing neurons. Am J Anat 113:175–187
Andrew W, Johnson H (1956) Staining mitochondria in fixed blood smears. Stain Technol 31(1):21–23
Kasahara A, Scorrano L (2014) Mitochondria: from cell death executioners to regulators of cell differentiation. Trends Cell Biol 24(12):761–770
Facucho-Oliveira JM, Alderson J, Spikings EC, Egginton S, St. John JC (2007) Mitochondrial DNA replication during differentiation of murine embryonic stem cells. J Cell Sci 120(22):4025–4034
Varum S, Rodrigues AS, Moura MB, Momcilovic O, Easley CA, Ramalho-Santos J et al (2011) Energy metabolism in human pluripotent stem cells and their differentiated counterparts. PLoS One 6(6):e20914
Zhang J, Khvorostov I, Hong JS, Oktay Y, Vergnes L, Nuebel E et al (2011) UCP2 regulates energy metabolism and differentiation potential of human pluripotent stem cells. EMBO J 30(24):4860–4873
Chen C-TCT, Hsu S-H, Wei Y-HYH (2009) Upregulation of mitochondrial function and antioxidant defense in the differentiation of stem cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1800(3):1–7
Vayssiere JL, Larcher JC, Gros F, Croizat B (1987) Changes in the beta-subunit of mitochondrial F1 ATPase during neurogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 145(1):443–452
Cordeau-Lossouarn L, Vayssiere JL, Larcher JC, Gros F, Croizat B (1991) Mitochondrial maturation during neuronal differentiation in vivo and in vitro. Biol Cell 71(1–2):57–65
Zheng X, Boyer L, Jin M, Mertens J, Kim Y, Ma L et al (2016) Metabolic reprogramming during neuronal differentiation from aerobic glycolysis to neuronal oxidative phosphorylation. Elife 5:e13374
O’Brien LC, Keeney PM, Bennett JPJ (2015) Differentiation of human neural stem cells into motor neurons stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis and decreases glycolytic flux. Stem Cells Dev 24(17):1984–1994
Agostini M, Romeo F, Inoue S, Niklison-Chirou MV, Elia AJ, Dinsdale D et al (2016) Metabolic reprogramming during neuronal differentiation. Cell Death Differ 23(9):1502–1514
Cheng A, Wan R, Yang J, Kamimura N, Son T, Ouyang X et al (2012) Involvement of PGC-1α in the formation and maintenance of neuronal dendritic spines. Nat Commun 3:1250
Pereira SL, Grãos M, Rodrigues AS, Anjo SI, Carvalho R a, Oliveira PJ et al (2013) Inhibition of mitochondrial complex III blocks neuronal differentiation and maintains embryonic stem cell pluripotency. PLoS One 8(12):e82095
Schneider L, Giordano S, Zelickson BR, S Johnson M, A Benavides G, Ouyang X et al (2011) Differentiation of SH-SY5Y cells to a neuronal phenotype changes cellular bioenergetics and the response to oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 51(11):2007–2017
Chung S, Dzeja PP, Faustino RS, Perez-Terzic C, Behfar A, Terzic A (2007) Mitochondrial oxidative metabolism is required for the cardiac differentiation of stem cells. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 4(Suppl 1):S60–S67
St John JC, Ramalho-Santos J, Gray HL, Petrosko P, Rawe VY, Navara CS et al (2005) The expression of mitochondrial DNA transcription factors during early cardiomyocyte in vitro differentiation from human embryonic stem cells. Cloning Stem Cells 7(3):141–153
Mandal S, Lindgren AG, Srivastava AS, Clark AT, Banerjee U (2011) Mitochondrial function controls proliferation and early differentiation potential of embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 29(3):486–495
Han YH, Kim SH, Kim SZ, Park WH (2008) Antimycin A as a mitochondria damage agent induces an S phase arrest of the cell cycle in HeLa cells. Life Sci 83(9–10):346–355
Han YH, Kim SH, Kim SZ, Park WH (2008) Antimycin A as a mitochondrial electron transport inhibitor prevents the growth of human lung cancer A549 cells. Oncol Rep 20(3):689–693
Han YH, Park WH (2009) Growth inhibition in antimycin A treated-lung cancer Calu-6 cells via inducing a G1 phase arrest and apoptosis. Lung Cancer 65(2):150–160
Stoll E, Makin R, Sweet I, Trevelyan A, Miwa S, Horner P et al (2015) Neural stem cells in the adult subventricular zone oxidize fatty acids to produce energy and support neurogenic activity. Stem Cells 33(7):2306–2319
Wilkins HM, Harris JL, Carl SM, Lezi E, Lu J, Selfridge JE et al (2014) Oxaloacetate activates brain mitochondrial biogenesis, enhances the insulin pathway, reduces inflammation and stimulates neurogenesis. Hum Mol Genet 23(24):6528–6541
Mils V, Bosch S, Roy J, Bel-Vialar S, Belenguer P, Pituello F et al (2015) Mitochondrial reshaping accompanies neural differentiation in the developing spinal cord. PLoS One 10(5):e0128130
Wilkerson DC, Sankar U (2011) Mitochondria: a sulfhydryl oxidase and fission GTPase connect mitochondrial dynamics with pluripotency in embryonic stem cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43(9):1252–1256
Fathi A, Hatami M, Vakilian H, Han C-L, Chen Y-J, Baharvand H et al (2014) Quantitative proteomics analysis highlights the role of redox hemostasis and energy metabolism in human embryonic stem cell differentiation to neural cells. J Proteom 101:1–16
Komarova SV, Ataullakhanov FI, Globus RK (2000) Bioenergetics and mitochondrial transmembrane potential during differentiation of cultured osteoblasts. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 279(4):C1220–C1229
Kim J-M, Jeong D, Kang HK, Jung SY, Kang SS, Min B-M (2007) Osteoclast precursors display dynamic metabolic shifts toward accelerated glucose metabolism at an early stage of RANKL-stimulated osteoclast differentiation. Cell Physiol Biochem 20(6):935–946
Pattappa G, Heywood HK, de Bruijn JD, Lee DA (2011) The metabolism of human mesenchymal stem cells during proliferation and differentiation. J Cell Physiol 226(10):2562–2570
Mischen BT, Follmar KE, Moyer KE, Buehrer B, Olbrich KC, Levin LS et al (2008) Metabolic and functional characterization of human adipose-derived stem cells in tissue engineering. Plast Reconstr Surg 122(3):725–738
Malladi P, Xu Y, Chiou M, Giaccia AJ, Longaker MT (2006) Effect of reduced oxygen tension on chondrogenesis and osteogenesis in adipose-derived mesenchymal cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 290(4):C1139–C1146
Grayson WL, Zhao F, Bunnell B, Ma T (2007) Hypoxia enhances proliferation and tissue formation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 358(3):948–953
Miharada K, Karlsson G, Rehn M, Rörby E, Siva K, Cammenga J et al (2011) Cripto regulates hematopoietic stem cells as a hypoxic-niche-related factor through cell surface receptor GRP78. Cell Stem Cell 9(4):330–344
Simsek T, Kocabas F, Zheng J, Deberardinis RJ, Ahmed I, Olson EN et al (2010) The distinct metabolic profile of hematopoietic stem cells reflects their location in a hypoxic niche. Cell Stem Cell 7(3):380–390
Unwin RD, Smith DL, Blinco D, Wilson CL, Miller CJ, Evans CA et al (2006) Quantitative proteomics reveals posttranslational control as a regulatory factor in primary hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 107(12):4687–4695
Alvarez Z, Hyrossova P, Perales JC, Alcantara S (2014) Neuronal progenitor maintenance requires lactate metabolism and PEPCK-M-directed cataplerosis. Cereb Cortex 26(3):1046–1058
Bond AM, Ming G-L, Song H (2015) Adult mammalian neural stem cells and neurogenesis: five decades later. Cell Stem Cell 17(4):385–395
Homem CCF, Steinmann V, Burkard TR, Jais A, Esterbauer H, Knoblich JA (2014) Ecdysone and mediator change energy metabolism to terminate proliferation in Drosophila neural stem cells. Cell 158(4):874–888
Jády AG, Nagy ÁM, Kőhidi T, Ferenczi S, Tretter L, Madarász E (2016) Differentiation-dependent energy production and metabolite utilization: a comparative study on neural stem cells, neurons, and astrocytes. Stem Cells Dev 25(13):scd.2015.0388
Gascon S, Murenu E, Masserdotti G, Ortega F, Russo GL, Petrik D et al (2016) Identification and successful negotiation of a metabolic checkpoint in direct neuronal reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 18(3):396–409
Almeida AS, Sonnewald U, Alves PM, Vieira HLA (2016) Carbon monoxide improves neuronal differentiation and yield by increasing the functioning and number of mitochondria. J Neurochem 138(3):423–435
Fornazari M, Nascimento IC, Nery A a, da Silva CCC, Kowaltowski AJ, Ulrich H (2011) Neuronal differentiation involves a shift from glucose oxidation to fermentation. J Bioenerg Biomembr 43(5):531–539
Aubert A, Costalat R, Magistretti PJ, Pellerin L (2005) Brain lactate kinetics: modeling evidence for neuronal lactate uptake upon activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(45):16448–16453
Pellerin L, Bouzier-Sore A-K, Aubert A, Serres S, Merle M, Costalat R et al (2007) Activity-dependent regulation of energy metabolism by astrocytes: an uptade. Glia 55:1251–1262
Pellerin L, Magistretti PJ (2012) Sweet sixteen for ANLS. J Cereb Blood Flow 32(7):1152–1166
Wohnsland S, Burgers HF, Kuschinsky W, Maurer MH (2010) Neurons and neuronal stem cells survive in glucose-free lactate and in high glucose cell culture medium during normoxia and anoxia. Neurochem Res 35(10):1635–1642
Uittenbogaard M, Baxter KK, Chiaramello A (2010) The neurogenic basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor NeuroD6 confers tolerance to oxidative stress by triggering an antioxidant response and sustaining the mitochondrial biomass. ASN Neuro 2(2):115–133
Zhao F, Wu T, Lau A, Jiang T, Huang Z, Wang X-J et al (2009) Nrf2 promotes neuronal cell differentiation. Free Radic Biol Med 47(6):867–879
Dringen R, Hoepken HH, Minich T, Ruedig C (2007) Handbook of neurochemistry and molecular neurobiology: brain energetics. In: Gibson GE, Dienel GA, Lajtha A (eds) Integration of molecular and cellular processes. Springer US, Boston, pp 41–62
Zhao Y, Pan X, Zhao J, Wang Y, Peng Y, Zhong C (2009) Decreased transketolase activity contributes to impaired hippocampal neurogenesis induced by thiamine deficiency. J Neurochem 111(2):537–546
Kathagen A, Schulte A, Balcke G, Phillips HS, Martens T, Matschke J et al (2013) Hypoxia and oxygenation induce a metabolic switch between pentose phosphate pathway and glycolysis in glioma stem-like cells. Acta Neuropathol 126(5):763–780
Dekkers MPJ, Barde Y-A (2013) Developmental biology. Programmed cell death in neuronal development. Science 340(6128):39–41
Boya P, De La Rosa EJ (2005) Cell death in early neural life. Birth Defects Res Part C Embryo Today Rev 75(4):281–293
Wang S, Rosengren LE, Hamberger A, Haglid KG (1998) An acquired sensitivity to H2O2-induced apoptosis during neuronal differentiation of NT2/D1 cells. Neuroreport 9(14):3207–3211
de la Rosa EJ, de Pablo F (2000) Cell death in early neural development: beyond the neurotrophic theory. Trends Neurosci 23(10):454–458
Yeo W, Gautier J (2004) Early neural cell death: dying to become neurons. Dev Biol 274(2):233–244
Buss R, Oppenheim R (2004) Special review based on a presentation made at the 16th international congress of the IFAA role of programmed cell death in normal neuronal development and function. Anat Sci Int 79:191–197
Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Kroemer G (2012) Mitochondria: master regulators of danger signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(12):780–788
Acknowledgements
The funding was provided by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (Grant Nos. ANR/NEU-NMC/0022/2012, IF/00185/2012, SFRH/BD/78440/2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almeida, A.S., Vieira, H.L.A. Role of Cell Metabolism and Mitochondrial Function During Adult Neurogenesis. Neurochem Res 42, 1787–1794 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2150-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2150-3