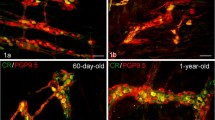
Immunohistochemical and morphometric methods were used to study the locations, relative contents, and cross-sectional areas of calbindin (CB)- and calretinin (CR)-immunopositive neurons in the intramural ganglia of the intermuscular plexus of the rat duodenum (n = 37) during postnatal ontogeny (days 1, 10, 20, 30, and 60 and 1 and 2 years of age). CB- and CR-immunopositive neurons were detected in all the rats studied, from neonatal to aged. Proportions of CR-immunopositive neurons increased over the first 10 days of life and then showed no significant changes, including in aged animals. Proportions of CB-containing neurons increased to reach a maximum by day 20 of life, decreased insignificantly to day 30, and then remained without significant change. The mean sizes of CB- and CR-immunopositive neurons were significantly greater than the mean cross-sectional area of immunonegative neurons in all age groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. B. Korzina, A. A. Korobkin, O. A. Vasil’eva, and P. M. Maslyukov, “Morphological characteristics of the stellate ganglion in white rats,” Morfologiya, 137, No. 2, 23–26 (2010).
P. M. Maslyukov, A. A. Korobkin, V. V. Konovalov, et al., “Age-related development of calbindin-immunopositive neurons in the sympathetic ganglia of the rat,” Morfologiya, 141, No. 1, 77–80 (2012).
P. M. Maslyukov, A. D. Nozdrachev, and J. P. Timmermans, “Developmental characteristics of the neurotransmitter composition of stellate ganglion neurons,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh., 92, No. 2, 214–221 (2006).
C. Andressen, I. Blumcke, and M. R. Celio, “Calcium-binding proteins: selective markers of nerve cells,” Cell Tissue Res., 271, 181–208 (1993).
T. Bellido, M. Huening, M. Raval-Pandya, et al., “Calbindin-D28k is expressed in osteoblastic cells and suppresses their apoptosis by inhibiting caspase-3 activity,” J. Biol. Chem., 275, 26,328–26,332 (2000).
P. S. Chard, D. Bleakman, S. Christakos, et al., “Calcium buffering properties of calbindin-D28k and parvalbumin in rat sensory neurons,” J. Physiol., 472, 341–357 (1993).
T. Endo and T. Onaya, “Immunohistochemical localization of parvalbumin in rat and monkey autonomic ganglia,” J. Neurocytol., 17, 73–77 (1988).
R. Franconville, G. Revet, G. Astorga, et al., “Somatic calcium level reports integrated spiking activity of cerebellar interneurons in vitro and in vivo,” J. Neurophysiol., 106, 1793–1805 (2011).
D. Lee, A. G. Obukhov, Q. Shen, et al., “Calbindin-D28k decreases L-type calcium channel activity and modulates intracellular calcium homeostasis in response to K+ depolarization in a rat beta cell line RINr1046–38,” Cell Calcium, 39, 475–485 (2006).
P. M. Masliukov, “Sympathetic neurons of the cat stellate ganglion in postnatal ontogenesis: morphometric analysis,” Auton. Neurosci., 89, No. 1–2, 48–53 (2001).
P. M. Masliukov, A. A. Korobkin, A. D. Nozdrachev, and J. P. Timmermans, “Calbindin-D28k immunoreactivity in sympathetic ganglionic neurons during development,” Auton. Neurosci., 167, No. 1–2, 27–33 (2012).
R. Mitsui, “Immunohistochemical analysis of substance P-containing neurons in rat small intestine,” Cell Tissue Res., 343, 331–341 (2011).
A. I. Sayegh and R. C. Ritter, “Morphology and distribution of nitric oxide synthase-, neurokinin-1 receptor-, calretinin-, calbindin-, and neurofilament-M-immunoreactive neurons in the myenteric and submucosal plexuses of the rat small intestine,” Anat. Rec. A. Discov. Mol. Cell. Evol. Biol., 271, No. 1, 209–216 (2003).
B. Schwaller, “The regulation of a cell’s Ca(2+) signaling toolkit: the Ca(2+) homeostasome,” Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 740, 1–25 (2012).
S. Yano, H. Tokumitsu, and T. R. Soderling, “Calcium promotes cell survival through CaM-K kinase activation of the protein-kinase-B pathway,” Nature, 396, 584–587 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Morfologiya, Vol. 146, No. 6, pp. 33–37, November–December, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emanuilov, A.I., Moiseev, K.Y., Filippov, I.V. et al. Developmental Characteristics of Neurons in the Intramural Ganglia of the Small Intestine Containing Different Types of Calcium-Binding Proteins. Neurosci Behav Physi 45, 986–990 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-015-0175-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-015-0175-8