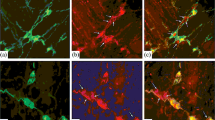
The calcium-binding protein parvalbumin is selectively expressed in various subpopulations of neurons in the central and peripheral nervous system. The localization and percentage composition of parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurons were determined in the metasympathetic enteric ganglia of the small and large intestine in rats of different ages (1, 10, 20, 30, and 60 days and two years). Parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurons were present in the intermuscular plexus during ontogeny, from birth to old age, and the percentage of these cells in the intermuscular plexus in the small intestine increased from day 10 to day 20 of life and in that of the large intestine in the first 10 days of life. Parvalbumin was absent from the submucous plexus of the small and large intestine in neonatal rats, but was present from day 10. The percentage of parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurons in the submucous plexus increased between day 10 and day 20 of life. On aging, the proportions of parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurons in the intermuscular and submucous plexuses did not change significantly. Thus, the proportion of parvalbumin-immunopositive neurons in the intramural intestinal ganglia increased in early postnatal ontogeny. This increase is probably associated with the buffer role of parvalbumin in relation to Ca2+ ions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Schwaller, “The regulation of a cell’s Ca2+ signaling toolkit: the Ca (2+) homeostasome,” Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 740, 1–25 (2012).
M. J. Simons and A. J. Pellionisz, “Genomics, morphogenesis and biophysics: triangulation of Purkinje cell development,” Cerebellum, 5, 27–35 (2006).
E. M. Permyakov, Calcium-Binding Proteins, Nauka, Moscow (1993).
P. M. Masliukov, A. D. Nozdrachev, and A. I. Emanuilov, “Agerelated characteristics of the expression of calcium-binding proteins in neurons in autonomic nervous system ganglia,” Usp. Gerontol., 29, No. 2, 247–253 (2016)
R. Mitsui, “Immunohistochemical analysis of substance P-containing neurons in rat small intestine,” Cell Tissue Res., 343, No. 2, 331–341 (2011).
Z. D. Qu, M. Thacker, P. Castelucci, et al., “Immunohistochemical analysis of neuron types in the mouse small intestine,” Cell Tissue Res., 334, No. 2, 147–161 (2008).
T. Endo and T. Onaya, “Immunohistochemical localization of parvalbumin in rat and monkey autonomic ganglia,” J. Neurocytol., 17, No. 1, 73–77 (1988).
M. R. Celio, “Calbindin D-28k and parvalbumin in the rat nervous system,” Neuroscience, 35, No. 2, 375–475 (1990).
M. Schemann, C. Schaaf, and M. Mäder, “Neurochemical coding of enteric neurons in the guinea pig stomach,” J. Comp. Neurol., 353, No. 2, 161–178 (1995).
A. D. Nozdrachev and P. M. Masliukov, Age-Related Development of Neurons in Autonomic Ganglia, Inform-Navigator, St. Petersburg (2014).
P. M. Masliukov, “Sympathetic neurons of the cat stellate ganglion in postnatal ontogenesis: morphometric analysis,” Auton. Neurosci., 89, No. 1–2, 48–53 (2001).
P. M. Masliukov, A. D. Nozdrachev, and J. P. Timmermans, “Developmental characteristics of the neurotransmitter composition of stellate ganglion neurons,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh., 92, No. 2, 214–221 (2006).
P. M. Masliukov, A. F. Budnik, and P. M. Nozdrachev, “Neurochemical characteristics of the ganglia of the metasympathetic system in ontogeny,” Usp. Gerontol., 30, No. 3, 347–355 (2017).
P. M. Masliukov, K. Moiseev, A. F. Budnik, et al., “Development of calbindin- and calretinin-immunopositive neurons in the enteric ganglia of rats,” Cell. Mol. Neurobiol., 37, No. 7, 1257–1267 (2017).
J. B. Furness, The Enteric Nervous System, Blackwell Publishing, Oxford (2006).
E. A. Permyakov, V. N. Uversky, and S. E. Permyakov, “Parvalbumin as a pleomorphic protein,” Curr. Protein Pept. Sci., 18, No. 8, 780–794 (2017).
D. Orduz, D. P. Bischop, B. Schwaller, et al., “Parvalbumin tunes spike-timing and efferent short-term plasticity in striatal fast spiking interneurons,” J. Physiol., 591, No. 13, 3215–3232 (2013).
G. J. Obermair, Z. Szabo, E. Bourinet, and B. E. Flucher, “Differential targeting of the L-type Ca2+ channel alpha 1C (CaV1.2) to synaptic and extrasynaptic compartments in hippocampal neurons,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 8, 2109–2122 (2004).
R. J. Gasperini, M. Pavez, A. C. Thompson, et al., “How does calcium interact with the cytoskeleton to regulate growth cone motility during axon pathfinding?” Mol. Cell Neurosci., 84, 29–35 (2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 106, No. 2, pp. 224–230, February, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nozdrachev, A.D., Budnik, A.F. & Masliukov, P.M. Parvalbumin-Containing Enteric Metasympathetic Neurons in Postnatal Ontogeny. Neurosci Behav Physi 50, 1079–1082 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-020-01008-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-020-01008-8