Abstract
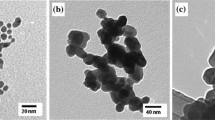
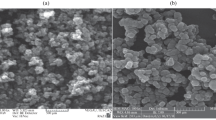
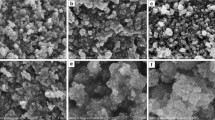
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) have attracted considerable concerns due to the increasing production and widespread applications, while their influences on other co-existing pollutants in real environment are not well studied. In this paper, the colloidal stability of TiO2 NPs in the exposure medium was first evaluated, and then, the medium was modified so that TiO2 NP suspension remained stable over the exposure period. Finally, using the optimized exposure medium, the effects of cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb) on Daphnia magna both in the absence and presence of TiO2 NPs were investigated. Results showed that 2 mg L−1 of TiO2 NPs was well dispersed in 1:20 diluted Elendt M7 medium without EDTA, and no immobility was observed. The presence of the nanoparticles increased the bioaccumulation and toxicity of Cd to the daphnias. On the contrary, while Pb bioaccumulation was enhanced by three to four times, toxicity of Pb was reduced in the presence of TiO2 NPs. The decreased toxicity of Pb was more likely attributed to the decreased bioavailability of free Pb ion due to adsorption and speciation change of Pb in the presence of TiO2 NPs. Additionally, surface-attached TiO2 NPs combined with adsorbed heavy metals caused adverse effects on daphnia swimming and molting behavior, which is supposed to lead to chronic toxicity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam V, Loyaux-Lawniczak S, Labille J, Galindo C, del Nero M, Gangloff S, Weber T, Quaranta G (2016) Aggregation behaviour of TiO2 nanoparticles in natural river water. J Nanopart Res 18:13. doi:10.1007/s11051-015-3319-4
Baun A, Hartmann NB, Grieger K, Kusk KO (2008) Ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to aquatic invertebrates: a brief review and recommendations for future toxicity testing. Ecotoxicology 17(5):387–395
Charde Manoj S, Ingole P, Welankiwar AS, Kumar J, Chakole RD (2014) Case study: three dimensional analysis of the swimming behaviour of Daphnia magna exposed to nanosized titanium dioxide. Int J Pharmacol Res 4(2):67–70
Clifford M, McGeer JC (2010) Development of a biotic ligand model to predict the acute toxicity of cadmium to Daphnia pulex. Aquat Toxicol 98(1):1–7
Cooper NL, Bidwell JR, Kumar A (2009) Toxicity of copper, lead, and zinc mixtures to Ceriodaphnia dubia and Daphnia carinata. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1523–1528
Cupi D, Hartmann NB, Baun A (2016) Influence of pH and media composition on suspension stability of silver, zinc oxide, and titanium dioxide nanoparticles and immobilization of Daphnia magna under guideline testing conditions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 127:144–152
Dabrunz A, Duester L, Prasse C, Seitz F, Rosenfeldt R, Schilde C, Schaumann GE, Schulz R (2011) Biological surface coating and molting inhibition as mechanisms of TiO2 nanoparticle toxicity in Daphnia magna. PLoS One 6(5):e20112. doi:10.1371/journal.-pone.0020112
Della Torre C, Balbib T, Grassia G, Frenzilli G, Bernardeschic M, Smerilli A, Guidic P, Canesib L, Nigroc M, Monacia F, Scarcelli V, Roccod L, Focardia S, Monopolie M, Corsia I (2015) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles modulate the toxicological response to cadmium in the gills of Mytilus galloprovincialis. J Hazard Mater 297:92–100
Engates KE, Shipley HJ (2011) Adsorption of Pb, Cd, Cu, Zn, and Ni to titanium dioxide nanoparticles: effect of particle size, solid concentration, and exhaustion. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:386–395
Geller W, Müller H (1981) The filtration apparatus of Cladocera: filter mesh-sizes and their implications on food selectivity. Oecologia 49:316–321
Gottschalk F, Sun TY, Nowack B (2013) Environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials: review of modeling and analytical studies. Environ Pollut 181:287–300
Guan R, Wang WX (2004) Cd and Zn uptake kinetics in Daphnia magna in relation to Cd exposure history. Environ Sci Technol 38:6051–6058
Guilhermino L, Diamantino T, Ribeiro R, Gonncalves F, Soares AMVM (1997) Suitability of test media containing EDTA for the evaluation of acute metal toxicity to Daphnia magna Straus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 38:292–295
Hall S, Bradley T, Moore JT, Kuykindall T, Minella L (2009) Acute and chronic toxicity of nano-scale TiO particles to freshwater fish, cladocerans, and green algae, and effects of organic and inorganic substrate on TiO toxicity. Nanotoxicology 3(2):91–97
Handy RD, Von der Kammer F, Lead JR, Hassellöv M, Owen R, Crane M (2008) The ecotoxicology and chemistry of manufactured nanoparticles. Ecotoxicology 17:287–314
Hartmann NB, Legros S, Von der Kammer F, Hofmann T, Baun A (2012) The potential of TiO2 nanoparticles as carriers for cadmium uptake in Lumbriculus variegatus and Daphnia magna. Aquat Toxicol 118-119:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2012.03.008
Hu J, Wang D, Wang J, Wang J (2012) Toxicity of lead on Ceriodaphnia dubia in the presence of nano-CeO2 and TiO2 NPs. Chemosphere 89:536–541
Hua M, Zhang S, Pan B, Zhang W, Lv L, Zhang Q (2012) Heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by nanosized metal oxides: a review. J Hazard Mater 211:317–331
Hughes MN, Poole RK (1991) Metal speciation and microbial growth—the hard (and soft) facts. J Gen Microbiol 137:725–734
Ju-Nam Y, Lead JR (2008) Manufactured nanoparticles: an overview of their chemistry, interactions and potential environmental implications. Sci Total Environ 400:396–414
Kim I, Lee BT, Kim HA, Kim KW, Kim SD, Hwang YS (2016) Citrate coated silver nanoparticles change heavy metal toxicities and bioaccumulation of Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 143:99–105
Klaine SJ, Alvarez PJJ, Batley GE, Fernandes TF, Handy RD, Lyon DY, Mahendra S, McLaughlin MJ, Lead JR (2008) Nanomaterials in the environment: behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1825–1851
Li L, Sillanpää M, Tuominen M, Lounatmaa K, Schultz E (2013) Behavior of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in Lemna minor growth test conditions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 88:89–94
Lin X, Li SX, Zheng FY (2016) An integrated system for field analysis of Cd (ii) and Pb (ii) via preconcentration using nano-TiO2/cellulose paper composite and subsequent detection with a portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer. RSC Adv 6(11):9002–9006
Liu W, Wang T, Borthwick AG, Wang Y, Yin X, Li X, Ni J (2013) Adsorption of Pb2+, Cd2+, Cu2+ and Cr3+ onto titanate nanotubes: competition and effect of inorganic ions. Sci Total Environ 456:171–180
Mager EM, Esbaugh AJ, Brix KV, Ryan AC, Grosell M (2011) Influences of water chemistry on the acute toxicity of lead to Pimephales promelas and Ceriodaphnia dubia. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 153(1):82–90
Mansfield CM, Alloy MM, Hamilton J, Verbeck GG, Newton K, Klaine SJ, Roberts AP (2015) Photo-induced toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to Daphnia magna under natural sunlight. Chemosphere 120:206–210
Marani D, Macchi G, Pagano M (1995) Lead precipitation in the presence of sulphate and caronate: testing of thermodynamic predictions. Water Res 29(4):1085–1092
Miao W, Zhu B, Xiao X, Li Y, Dirbaba NB, Zhou B, Wu H (2015) Effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on lead bioconcentration and toxicity on thyroid endocrine system and neuronal development in zebrafish larvae. Aquat Toxicol 161:117–126
OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) (2004) OECD guideline for testing of chemicals. Test No.202: Daphnia sp. acute immobilisation test. doi:10.1787/20745761
Okupnik A, Pflugmacher S (2016) Oxidative stress response of the aquatic macrophyte Hydrilla verticillata exposed to TiO2 nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Chem 35(11):2859–2866
Qin L, Huang QG, Wei ZB, Wang LS, Wang ZY (2014) The influence of hydroxyl-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes and pH levels on the toxicity of lead to Daphnia magna. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 38:199–204
Recillas S, Garcia A, Gonzalez E, Casals E, Puntes V, Sanchez A, Font X (2011) Use of CeO2, TiO2 and Fe3O4 nanoparticles for the removal of lead from water: toxicity of nanoparticles and derived compounds. Desalination 277(1):213–220
Rosenfeldt RR, Seitz F, Schulz R, Bundschuh M (2014) Heavy metal uptake and toxicity in the presence of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: a factorial approach using Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol 48(12):6965–6972
Seitz F, Lüderwald S, Rosenfeldt RR, Schulz R, Bundschuh M (2015) Aging of TiO2 nanoparticles transiently increases their toxicity to the pelagic microcrustacean Daphnia magna. PLoS One 10(5):e0126021. doi:10.1371/journal. pone.0126021
Smith F (1963) Population dynamics in Daphnia magna and a new model for population growth. Ecology 44:651–663
Sorvari J, Sillanpää M (1996) Influence of metal complex formation on heavy metal and free EDTA and DTPA acute toxicity determined by Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 33:1119–1127
Sun H, Zhang X, Zhang Z, Chen Y, Crittenden JC (2009) Influence of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on speciation and bioavailability of arsenite. Environ Pollut 157:1165–1170
Tan C, Wang WX (2014) Modification of metal bioaccumulation and toxicity in Daphnia magna by tiatanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environ Pollut 186:36–42
Tan C, Fan WH, Wang WX (2012) Role of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in the elevated uptake and retention of cadmium and zinc in Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol 46:469–476
USEPA (2002) Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms. United States Environmental Protection Agency EPA-821-R-02-012, 5th ed
Wang DM, Hu J, Irons DR, Wang JM (2011) Synergistic toxic effect of nano-TiO2 and As(V) on Ceriodaphnia dubia. Sci Total Environ 407:1351–1356
Xie X, Gao L (2009) Effect of crystal structure on adsorption behaviors of nanosized TiO2 for heavy-metal cations. Curr Appl Phys 9(3):185–188
Xiong D, Fang T, Yu L, Sima X, Zhu W (2011) Effects of nano-scale TiO2, ZnO and their bulk counterparts on zebrafish: acute toxicity, oxidative stress and oxidative damage. Sci Total Environ 409:1444–1452
Yang ZP, Zhang CJ (2010) Kinetics of photocatalytic reduction of Pb (II) on nanocrystalline TiO2 coatings: a quartz crystal microbalance study. Thin Solid Films 518(21):6006–6009
Zhang X, Sun H, Zhang Z, Niu Q, Chen Y, Crittenden JC (2007) Enhanced bioaccumulation of cadmium in carp in the presence of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Chemosphere 67:160–166
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Minna Sepponen for the technical help in exposure studies, DLS measurements, and ICP-OES analysis. Timo Sara-aho is acknowledged for the expertive advice in regards to ICP-OES analysis. Maa- ja Vesitekniikan Tuki ry and Ministry of the Environment are acknowledged for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Sillanpää, M. & Schultz, E. Influence of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on cadmium and lead bioaccumulations and toxicities to Daphnia magna . J Nanopart Res 19, 223 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-3916-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-3916-5