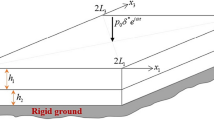
A modal analysis of forced vibrations caused by a time-harmonic force from a piezoelectric plate standing on a rigid foundation is presented. A 3D linearized elasticity theory for solids under initial stress (TLTESIS) is used. It is assumed that a uniformly distributed normal loadings acting on the lateral surfaces of the plate yield the initial stress state. The piezoelectric plate is under the action of a time-harmonic force poled in various directions. A mathematical model is developed, and the problem is solved employing the 3D finite-element method (3D-FEM). Some numerical results illustrating the influence of changes in the poling direction and other important factors, such as the initial stress, on the dynamic behavior of the plate are presented.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Kumar, M. Mahanty, A. Chattopadhyay and A. K. Singh, “Effect of interfacial imperfection on shear wave propagation in a piezoelectric composite structure: Wentzel–Kramers–Brillouin asymptotic approach,” J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct., 30, No. 18-19, 2789-2807 (2019).
M. Mahanty, A. Chattopadhyay, P. Kumar and A. K. Singh, “Effect of initial stress, heterogeneity and anisotropy on the propagation of seismic surface waves,” Mech. Adv. Mater. Struc., 27, No. 3, 177-188 (2020).
J. Yang, An Introduction to the Theory of Piezoelectricity, Springer, New York (2005).
H. F. Tiersten, Linear Piezoelectric Plate Vibrations: Elements of the Linear Theory of Piezoelectricity and the Vibrations Piezoelectric Plates, Springer, New York (2013).
R. V. Southwell, “On the general theory of elastic stability,” Philos. Trans. Royal Soc. Ser. A, 213, 187-244 (1914).
C. B. Biezeno and H. Hencky, “On the general theory of elastic stability,” In: Proceedings Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen, 31, 569-592 (1928).
M. A. Biot, “Nonlinear elasticity theory and the linearized case for a body under initial stress,” Philos. Mag. Ser., 7, No. 27, 468-489 (1939).
H. Neuber, “Die Grundgleichungen der elastischen Stabilität in allgemeinen Koordinaten und ihre Integration,” ZAMM, 23, 321-330 (1943).
E. Trefftz, “Zur Theorie der Stabilität des elastischen Gleichgewichts,” ZAMM, 12, No. 2, 160–165 (1933).
A. E. Green, R. S. Rivlin, and R. T. Shield, “General theory of small deformations superposed on large elastic deformations,” Proc. Roy. Soc. A, 211, 211–292 (1952).
A. N. Guz, “3D theory of elastic stability under finite subcritical deformations,” J. Appl. Mech., 8, No. 12, 25-44 (1972).
L. M. Zubov, “Theory of small deformations of prestressed thin shells,” J. Appl. Math. Mech., 40, No. 1, 73-82 (1976).
H. F. Tiersten, “Perturbation theory for linear electroelastic equations for small fields superimposed on a bias,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 64, No. 3, 832-837 (1978).
R. W. Ogden, Nonlinear Elastic Deformations, Ellis Horwood/Halsted Press, New York (1984).
S. D. Akbarov and A. N. Guz, Mechanics of Curved Composites, Kluwer Acad. Publ., Dordrecht-Boston-London (2000).
J. N. Reddy, Mechanics of Laminated Composite Plates and Shells: Theory and Analysis, CRC press, Florida (2003).
A. N. Guz, Fundamentals of the 3D Theory of Stability of Deformable Bodies, Springer, New York (1999).
S. D. Akbarov, Dynamics of Pre-Strained Bi-Material Elastic Systems: Linearized 3D Approach, Springer, New York (2015).
S. D. Akbarov, A. Yildiz, and M. Eroz, “Forced vibration of the prestressed bi-layered plate-strip with finite length resting on a rigid foundation,” Appl. Math. Model., 35, No. 1, 250-256 (2011).
S. Gupta, D. K. Majhi, S. Kundu, and S. K. Vishwakarma, “Propagation of torsional surface waves in a homogeneous layer of finite thickness over an initially stressed heterogeneous half-space,” Appl. Math. Comput., 218, No. 9, 5655-5664 (2012).
W. T. Hu and W. Y. Chen, “Influence of lateral initial pressure on axisymmetric wave propagation in hollow cylinder based on first power hypo-elastic model,” J. Cent. South Univ., 21, No. 2, 753-760 (2014).
X. Guo and P. Wei, “Dispersion relations of elastic waves in one-dimensional piezoelectric/piezomagnetic phononic crystal with initial stresses,” Ultrasonics, 66, 72-85 (2016).
U. B. Yesil, “Forced and natural vibrations of an orthotropic prestressed rectangular plate with neighboring two cylindrical cavities,” Comput. Mater. Continua., 53, No. 1, 1-22 (2017).
A. Dașdemir, “Forced vibrations of prestressed sandwich plate-strip with elastic layers and piezoelectric core,” Int. Appl. Mech., 54, No. 4, 480-493 (2018).
A. Daşdemir, “Effect of imperfect bonding on the dynamic response of a prestressed sandwich plate-strip with elastic layers and a piezoelectric core,” Acta Mech. Solida Sin., 30, No. 6, 658-667 (2017).
A. N. Guz, “Elastic waves in bodies with initial (residual) stresses,” Int. Appl. Mech., 38, No. 1, 23-59 (2002).
S. D. Akbarov, “Recent investigations on dynamic problems for an elastic body with initial (residual) stresses,” Int. Appl. Mech., 43, No. 12, 1305-1324 (2007).
S. D. Akbarov, Stability Loss and Buckling Delamination. Springer, Berlin (2012).
A. Daşdemir, “A mathematical model for forced vibration of prestressed piezoelectric plate-strip resting on rigid foundation,” Matematika: MJIAM, 34, No. 2, 419-431 (2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Russian translation published in Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 58, No. 1, pp. 97-114, January-February, 2021. Russian DOI: 10.22364/mkm.58.1.06.
Appendix A
Appendix A
Depending on the case considered, the matrix \( \overset{\sim }{\mathbf{M}} \) of constitutive equations changes accordingly. Although our analysis is modal, the numerical results and discussions given here were presented for three different cases. The matrices \( \overset{\sim }{\mathbf{M}} \) for polarization in the directions of Ox1, Ox2, and Ox3 axes are
and
respectively.
Acknowledgements. The author wishes to express deep thanks to the anonymous referees for their constructive comments and suggestions, which significantly improved the quality of the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daşdemir, A. A Modal Analysis of Forced Vibration of a Piezoelectric Plate with Initial Stress by the Finite-Element Simulation. Mech Compos Mater 58, 69–80 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-022-10012-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-022-10012-7