Abstract
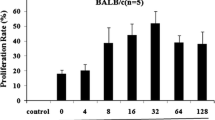
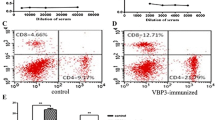
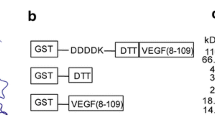
Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) play a critical role in tumor-associated angiogenesis and have become the targets of anti-tumor therapy. The BALB/c mice were immunized with VEGF/bFGF complex peptide (VBP3) constructed with different epitope peptides of human VEGF and bFGF. The results of the immunogenicity showed that the VBP3 could effectively stimulate immune response in mice and elicit the mice to produce high titer specific anti-VEGF and anti-bFGF antibodies (anti-VBP3 antibodies). The polyclonal anti-VBP3 antibodies separated from the mouse immune serum could effectively inhibit the proliferation, migration and tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and block the proliferation and migration of lung cancer A549 cells. Besides, the anti-VBP3 antibodies could effectively inhibit tumor growth and tumor angiogenesis in BABL/c nude mice. The results demonstrated that the VBP3 complex peptide could elicit the body to produce the high titer anti-VEGF and anti-bFGF antibodies, which showed anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic effects in vitro and in vivo. The results revealed that the VBP3 complex peptide could be used as a potential peptide vaccine in tumor therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abid MR et al (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor activates PI3K/Akt/forkhead signaling in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thrombosis Vasc Biol 24:294–300 doi:10.1161/01.atv.0000110502.10593.06
Aguzzi MS et al (2011) The FGF-2-derived peptide FREG inhibits melanoma growth in vitro and in vivo. Mol Ther 19:266–273. doi:10.1038/mt.2010.211
Aonuma M, Yoshitake Y, Nishikawa K, Tanaka NG (1999) Different antitumor activities of anti-bFGF neutralizing antibodies: heparin-binding domain provides an inefficient epitope for neutralization in vivo. Anticancer Res 19:4039–4044
Bergers G, Benjamin LE (2003) Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer 3:401–410
Cai Y et al (2016) Construction of a disulfide-stabilized diabody against fibroblast growth factor-2 and the inhibition activity in targeting breast cancer. Cancer Sci 107:1141–1150. doi:10.1111/cas.12981
Cao RH, Eriksson A, Kubo H, Alitalo K, Cao YH, Thyberg J (2004) Comparative evaluation of FGF-2-, VEGF-A-, and VEGF-C-induced angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, vascular fenestrations, and permeability. Circ Res 94:664–670. doi:10.1161/01.res.0000118600.91698.bb
Cao Y, Cao R, Hedlund E-M (2008) R Regulation of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis by FGF and PDGF signaling pathways. J Mol Med 86:785–789 doi:10.1007/s00109-008-0337-z
Carmeliet P (2004) VEGF as a key mediator of angiogenesis in cancer. Int Soc Cell 69:4–10
Chung AS, Ferrara N (2011) Developmental and pathological angiogenesis. In: Schekman R, Goldstein L, Lehmann R (eds) Annual review of cell and developmental biology, 27:563–584. doi:10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154002
Cross MJ, Claesson-Welsh L (2001) FGF and VEGF function in angiogenesis: signalling pathways, biological responses and therapeutic inhibition. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:201–207. doi:10.1016/s0165-6147(00)01676-x
Dvorak P, Dvorakova D, Hampl A (2006) Fibroblast growth factor signaling in embryonic and cancer stem cells. FEBS Lett 580:2869–2874 doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2006.01.095
El-Manzalawy Y, Dobbs D, Honavar V (2008) Predicting linear B-cell epitopes using string kernels. J Mol Recognit 21:243–255. doi:10.1002/jmr.893
Farhat FS et al (2012) Expression, prognostic and predictive impact of VEGF and bFGF in non-small cell lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 84:149–160. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2012.02.012
Ferrara N (2002) VEGF and the quest for tumour angiogenesis factors. Nat Rev Cancer 2:795–803
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J (2003) The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9:669–676. doi:10.1038/nm0603-669
Ferrara N, Hillan KJ, Novotny W (2005) Bevacizumab (Avastin), a humanized anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody for cancer therapy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 333:328–335. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.05.132
Finke J, Ko J, Rini B, Rayman P, Ireland J, Cohen P (2011) MDSC as a mechanism of tumor escape from sunitinib mediated anti-angiogenic therapy. Int Immunopharmacol 11:856–861. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2011.01.030
Folkman J (2006) Tumor suppression by p53 is mediated in part by the antiangiogenic activity of endostatin and tumstatin. Science’s STKE 2006:pe35-pe35. doi:10.1126/stke.3542006pe35
Foy KC, Miller MJ, Moldovan N, Carson WE, III, Kaumaya PTP (2012) Combined vaccination with HER-2 peptide followed by therapy with VEGF peptide mimics exerts effective anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic effects in vitro and in vivo. Oncoimmunology 1:1048–1060 doi:10.4161/onci.20708
Foy KC, Miller MJ, Moldovan N, Carson WE, III, Kaumaya PPT (2013) Combined vaccination with HER-2 peptide followed by therapy with VEGF peptide mimics exerts effective anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic effects in vitro and in vivo. Oncoimmunology 1:pg 1048, doi:10.4161/onci.23914
Fujio Y, Walsh K (1999) Akt mediates cytoprotection of endothelial cells by vascular endothelial growth factor in an anchorage-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 274:16349–16354. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.23.16349
Gacche RN, Meshram RJ (2014) Angiogenic factors as potential drug target: efficacy and limitations of anti-angiogenic therapy. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Rev Cancer 1846:161–179. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2014.05.002
Gavilondo JV et al (2014) Specific active immunotherapy with a VEGF vaccine in patients with advanced solid tumors. Results of the CENTAURO antigen dose escalation phase I clinical trial. Vaccine 32:2241–2250. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.11.102
Guo X, Liu T-s, Yu Y-y, Zhou Y-h, Chen Y, Zhuang R-y, Cui Y-h (2013) Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab (BEV) plus chemotherapeutic agents in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer, mCRC. Zhonghua zhong liu za zhi [Chin J Oncol] 35:604–607
Kano MR et al (2005) VEGF-A and FGF-2 synergistically promote neoangiogenesis through enhancement of endogenous PDGF-B-PDGFR beta signaling. J Cell Sci 118:3759–3768. doi:10.1242/jcs.02483
Kaumaya PTP, Foy KC (2012) Peptide vaccines and peptidomimetics targeting HER and VEGF proteins may offer a potentially new paradigm in cancer immunotherapy. Future Oncol 8:961–987. doi:10.2217/fon.12.95
Kilvaer TK, Valkov A, Sorbye SW, Smeland E, Bremnes RM, Busund L-T, Donnem T (2011) Fibroblast growth factor 2 orchestrates angiogenic networking in non-GIST STS patients. J Translational Med 9. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-9-104
Kuhn H, Konrad J, Holtz S, Salameh A, Gessner C, Hammerschmidt S, Wirtz H (2006) Enhanced expression of VEGF following bFGF inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Lung cancer 54:149–153 doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.07.016
Li D et al (2010) Monoclonal antibodies targeting basic fibroblast growth factor inhibit the growth of B16 melanoma in vivo and in vitro. Oncol Rep 24:457–463. doi:10.3892/or_00000879
Li Q et al (2012) A novel bFGF antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth. Mol Med Report 6:210–214. doi:10.3892/mmr.2012.882
Liu Y, Xia X, Zhou M, Liu X (2015) Avastin (R) in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin significantly inhibits tumor angiogenesis and increases the survival rate of human A549 tumor-bearing mice Experimental and Therapeutic. Medicine (Baltimore) 9:2180–2184. doi:10.3892/etm.2015.2402
Morera Y et al (2012) Antigen dose escalation study of a VEGF-based therapeutic cancer vaccine in non human primates. Vaccine 30:368–377. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.10.082
Pan L, Weng R, Zhang J, Wang J, Tang Y, Deng N (2014) Immune response of the VEGF/bFGF complex peptide vaccine and function of immune antibodies in inhibiting migration of HUVEC cells and proliferation of cancer cells. Int J Peptide Res Ther 20:565–574. doi:10.1007/s10989-014-9414-z
Plum SM, Holaday JW, Ruiz A, Madsen JW, Fogler WE, Fortier AH (2000) Administration of a liposomal FGF-2 peptide vaccine leads to abrogation of FGF-2-mediated angiogenesis and tumor development. Vaccine 19:1294–1303. doi:10.1016/s0264-410x(00)00210-3
Potente M, Gerhardt H, Carmeliet P (2011) Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell 146:873–887. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.039
Saha S, Raghava GPS (2004) BcePred: prediction of continuous B-cell epitopes in antigenic sequences using physico-chemical properties. In: Nicosia G, Cutello V, Bentley PJ, Timmis J (eds) Artificial immune systems, proceedings, vol 3239. Lecture notes in computer science. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 197–204
Sakurai T, Kudo M (2011) Signaling pathways governing tumor angiogenesis. Int Soc Cell 81:24–29. doi:10.1159/000333256
Samaniego F et al (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor present in Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS) are induced by inflammatory cytokines and synergize to promote vascular permeability and KS lesion development. Am J Pathol 152:1433–1443
Tsunenari I, Yamate J, Sharma KD, Kawachi M, Sakuma S (2000) Expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in tumors induced by two different cloned cell lines established from transplantable rat malignant fibrous histiocytoma. J Vet Med Sci 62:699–705. doi:10.1292/jvms.62.699
Wang B, Kaumaya PTP, Cohn DE (2010a) Immunization with synthetic VEGF peptides in ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 119:564–570. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2010.07.037
Wang H, Zhu Z, Yang Q, Xiang J, Yang H, Deng N (2010b) Screening the antigen epitopes of bFGF/VEGF and expressing and identifying their complex peptide. Immunol J 26:688–693
Wang P et al (2012) Survivin promotes glioma angiogenesis through vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in vitro and in vivo. Mol Carcinog 51:586–595. doi:10.1002/mc.20829
Willett CG et al. (2004a) Direct evidence that the VEGF-specific antibody bevacizumab has antivascular effects in human rectal cancer. Nat Med 10:145
Willett CG et al (2004b) Direct evidence that the VEGF-specific antibody bevacizumab has antivascular effects in human rectal cancer. Nat Med 10:649–649. doi:10.1038/nm0604-649c
Zhang Q et al (2015) Soluble production and function of vascular endothelial growth factor/basic fibroblast growth factor complex peptide. Biotechnol Progr 31:194–203. doi:10.1002/btpr.1997
Zhao M, Gao FH, Wang JY, Liu F, Yuan HH, Zhang WY, Jiang B (2011) JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway activation mediates tumor angiogenesis by upregulation of VEGF and bFGF in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung cancer 73:366–374 doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.01.002
Zhou M, Yu P, Qu X, Liu Y, Zhang J (2013) Phase III Trials of Standard Chemotherapy with or without Bevacizumab for Ovarian Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Plos ONE 8. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0081858
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the State Natural Science Foundation of China (81372281), the Shenzhen Science and Technique Plan (JCYJ20140416085544636), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (2015B020211009, 2016A010105008) and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou City (201604020099).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Participants
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Yanrui Deng and Hui Liang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Y., Liang, H., Pan, L. et al. The Polyclonal Antibodies Induced by VBP3 Complex Peptide Targeting Angiogenesis and Tumor Suppression. Int J Pept Res Ther 23, 469–479 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-017-9579-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-017-9579-3