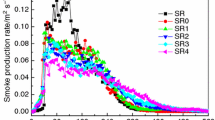
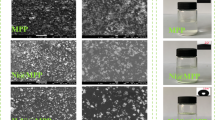
Abstract
Owing to the unsustainability of traditional petroleum-based char-forming agents, cyclodextrin (CD) as the bio-based polyhydroxy compounds has been employed to construct the intumescent flame-retardant system with ammonium polyphosphate (APP) for flammable and fire-hazardous silicone rubber (SR). On the basis of this, the poor compatibility and water resistance of SR composites have been improved by separately introducing the bio-inspired hydrophobic structure for CD and APP. The results have implied that limiting oxygen index (LOI) and vertical combustion of SR composites with 40 phr total fillers loadings could reach 30.7% and UL-94 V-0 rating. Moreover, the water soaking tests have verified that the flame retardancy of SR composites could be maintained under hot aqueous medium. Based on thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), the reason for elevated flame retardancy of SR composites can be interpreted by good thermal stability and char-forming ability via the interaction of modified APP and CD. With the aid of analyzing combustion residues in details, the synergistic flame-retardant mechanism can be mainly elaborated as the gas phase dilution of inert gases and the condensed phase barrier of dense expanded carbon layer. Furthermore, the retained mechanical properties of SR composites via hydrophobic modification are beneficial to improve its application value. Thus, this paper has open up a novel, green and effective route for overcoming the crucial flame retardancy problem of SR materials in real-life applications.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fang S, Hu Y, Song L, Zhan J, He Q. Mechanical properties, fire performance and thermal stability of magnesium hydroxide sulfate hydrate whiskers fame retardant silicone rubber. J Mater Sci. 2008;43(3):1057–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2241-2.
Wang X, Dou W. Preparation of graphite oxide (GO) and the thermal stability of silicone rubber/GO nanocomposites. Thermochim Acta. 2012;529:25–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2011.11.016.
Chai H, Tang X, Ni M, Chen F, Zhang Y, Chen D, et al. Preparation and properties of flexible flame-retardant neutron shielding material based on methyl vinyl silicone rubber. J Nucl Mater. 2015;464:210–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2015.04.048.
Li L, Qian Y, Jiao C. Synergistic fame retardant effect of melamine in ethylene-vinyl acetate/layered double hydroxides composites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;114(1):45–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-012-2808-2.
Karambar S, Tenbohlen S. Compatibility study of silicone rubber and mineral oil. Energies. 2021;14(18):5899. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14185899.
Huang P, Xia Z, Cui S. 3D printing of carbon fiber-filled conductive silicon rubber. Mater Design. 2018;142:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.12.051.
Qiu J, Lai X, Li H, Zeng X, Wu Y. Fabrication of polymethylphenylsiloxane decorated C60 via π-π stacking interaction for reducing the flammability of silicone rubber. Mater Lett. 2018;229:85–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.06.120.
Gu J, Meng X, Tang Y, Li Y, Zhuang Q, Kong J. Hexagonal boron nitride/polymethyl-vinyl siloxane rubber dielectric thermally conductive composites with ideal thermal stabilities. Compos Part A-Appl S. 2017;92:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2016.11.002.
Liu B, Gao X, Zhao Y, Dai L, Xie Z, Zhang Z. 9,10-Dihydro-9-oxa-10- phosphaphenanthrene 10-oxide-based oligosiloxane as a promising damping additive for methyl vinyl silicone rubber (VMQ). J Mater Sci. 2017;52:8603–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1085-7.
Hong L, Hu X. Mechanical and flame retardant properties and microstructure of expandable graphite/silicone rubber composites. J Macromol Sci B. 2016;55(2):175–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2015.1138029.
Qiu J, Wu T, Qu J. Fabrication of iron oxide nanoparticle decorated boron nitride nanosheet for flame-retarding silicone rubber. Mater Lett. 2021;283:12871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128712.
Zhou C, Wang J, Li J, Shi J. Thermal aging properties of flame retardant silicone rubber based on melamine cyanurate. J Appl Polym Sci. 2021;138(9):49919. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.49919.
Lou F, Yan W, Guo W, Wei T, Li Q. Preparation and properties of ceramifiable flame-retarded silicone rubber composites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;130(2):813–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6448-4.
Zhang N, Yildirim E, Zane CP, Shen J, Vinueza N, Hinks D, et al. Improved eco-friendliness of a common flame retardant through inclusion complexation with cyclodextrins. ACS Appl Polym Mater. 2019;1(10):2768–77. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.9b00708.
Jin H, Yang L, Ahonen JR, Schoenfisch MH. Nitric oxide-releasing cyclodextrins. J Am Chem Soc. 2018;140(43):14178–84. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b07661.
Shan X, Han J, Li J, Song Y, Hu Y. Preparation of β-CD@ferrocene@hollow mesoporous silica microsphere and investigation of its flame retardant EP. Polym Composite. 2020;41(5):2013–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25516.
Zhang K, Zhang G, Zhang R, Chen C, Wan C, Cai Y, et al. Synergistic effects of intercalation of layered double hydroxide with phytic acid-grafted β-cyclodextrin on the flame retardancy of polypropylene. Mater Today Commun. 2022;32:103904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.103904.
Cagno MPD. The potential of cyclodextrins as novel active pharmaceutical ingredients: a short overview. Molecules. 2016;22(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010001.
Feng J, Su S, Zhu J. An intumescent flame retardant system using β-cyclodextrin as a carbon source in polylactic acid (PLA). Polym Advan Technol. 2011;22(7):1115–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.1954.
Hădărugă NG, Bandur GN, David I, Hădărugă DI. A review on thermal analyses of cyclodextrins and cyclodextrin complexes. Environ Chem Lett. 2019;17(1):349–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0806-8.
Vahabi H, Shabanian M, Aryanasab F, Laoutid F, Benali S, Saeb MR, et al. Three in one: β-cyclodextrin, nanohydroxyapatite, and a nitrogen-rich polymer integrated into a new flame retardant for poly(lactic acid). Fire Mater. 2018;42(6):593–602. https://doi.org/10.1002/fam.2513.
Shan X, Jiang K, Li J, Song Y, Han J, Hu Y. Preparation of β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex and its application as an intumescent flame retardant for epoxy. Polymers. 2019;11(1):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010071.
Ding S, Liu P, Zhang S, Gao C, Wang F, Ding Y, et al. Crosslinking of β-cyclodextrin and combining with ammonium polyphosphate for flame-retardant polypropylene. J Appl Polym Sci. 2020;137(4):48320. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.48320.
Zheng Z, Zhang L, Liu Y, Wang H. A facile and novel modification method of β-cyclodextrin and its application in intumescent flame-retarding polypropylene with melamine phosphate and expandable graphite. J Polym Res. 2016;23(4):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-015-0905-1.
Zheng Z, Xia Y, Liao C, Liu Y, Dai B, Guo Z, et al. Facile fabrication of cyclodextrin-based and integrated fame retardant in intumescent fame-retarding polypropylene. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;146(6):2375–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10455-x.
Pan Y, Luo Z, Wang B. Cross-linking modification of ammonium polyphosphate via ionic exchange and self-assembly for enhancing the fire safety properties of polypropylene. Polymers. 2020;12(11):2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112761.
Pallmann J, Ren YL, Mahltig B, Huo T. Phosphorylated sodium alginate/APP/DPER intumescent flame retardant used for polypropylene. J Appl Polym Sci. 2019;136(29):47794. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.47794.
Chen Z, Yu Y, Zhang Q, Chen Z, Chen T, Li C, et al. Surface-modified ammonium polyphosphate with (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane, pentaerythritol and melamine dramatically improve flame retardancy and thermal stability of unsaturated polyester resin. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;143(5):3479–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10282-0.
Yu Y, Wang Q, Yuan J, Fan X, Wang P, Cui L. Hydrophobic modification of cotton fabric with octadecylamine via laccase/TEMPO mediated grafting. Carbohyd Polym. 2016;137:549–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.026.
Liu Y, Gao Y, Zhang Z, Wang Q. Preparation of ammonium polyphosphate and dye co-intercalated LDH/polypropylene composites with enhanced flame retardant and UV resistance properties. Chemosphere. 2021;277:130370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130370.
Xu J, Niu Y, Xie Z, Liang F, Guo F, Wu J. Synergistic flame retardant effect of carbon nanohorns and ammonium polyphosphate as a novel flame retardant system for cotton fabrics. Chem Eng J. 2023;451:138566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138566.
Qiu S, Ma C, Wang X, Zhou X, Feng X, Yuen RK, et al. Melamine-containing polyphosphazene wrapped ammonium polyphosphate: A novel multifunctional organic-inorganic hybrid flame retardant. J Hazard Mater. 2018;344:839–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.018.
Khanal S, Zhang W, Ahmed S, Ali M, Xu S. Effects of intumescent flame retardant system consisting of tris (2-hydroxyethyl) isocyanurate and ammonium polyphosphate on the flame retardant properties of high-density polyethylene composites. Compos Part A Appl S. 2018;112:444–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.06.030.
Ren Y, Yuan D, Li W, Cai X. Flame retardant efficiency of KH-550 modified urea-formaldehyde resin cooperating with ammonium polyphosphate on polypropylene. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2018;151:160–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2018.03.014.
Cabrera-Alvarez EN, Ramos-deValle LF, Sánchez-Valdes S, Candia-García A, Soriano-Corral F, Ramírez-Vargas E, et al. Study of the silane modification of magnesium hydroxide and their effects on the flame retardant and tensile properties of high density polyethylene nanocomposites. Polym Compos. 2014;35(6):1060–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.22753.
Jafari M, Keshavarz MH, Noorbala MR, Kamalvand M. A reliable method for prediction of the condensed phase enthalpy of formation of high nitrogen content materials through their gas phase information. Chem Select. 2016;1(16):5286–96. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201601184.
Huang Z, Ruan B, Wu J, Ma N, Jiang T, Tsai FC. High-efficiency ammonium polyphosphate intumescent encapsulated polypropylene flame retardant. J Appl Polym Sci. 2021;138(20):50413. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.50413.
Qi J, Wen Q, Zhu J. Synergistic effect of intumescent flame retardant system consisting of hexophenoxy cyclotriphosphazene and ammonium polyphosphate on methyl ethyl silicone rubber. Mater Lett. 2019;249:62–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.04.053.
Castrovinci A, Camino G, Drevelle C, Duquesne S, Magniez C, Vouters M. Ammonium polyphosphate-aluminum trihydroxide antagonism in fire retarded butadiene-styrene block copolymer. Eur Polym J. 2005;41:2023–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2005.03.010.
Hamdani S, Longuet C, Perrin D, Lopez-cuesta JM, Ganachaud F. Flame retardancy of silicone-based materials. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2009;94:465–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2008.11.019.
Jiang W, Hao J, Han Z. Study on the thermal degradation of mixtures of ammonium polyphosphate and a novel caged bicyclic phosphate and their flame retardant effect in polypropylene. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2012;97:632–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2012.01.001.
Hu S, Tan Z, Chen F, Li J, Shen Q, Huang Z, et al. Flame-retardant properties and synergistic effect of ammonium polyphosphate/aluminum hydroxide/mica/silicone rubber composites. Fire Mater. 2020;44(5):673–82. https://doi.org/10.1002/fam.2831.
Wang B, Li J, Lai X, Li H, Chen Y, Zeng X. Synthesis of a novel N-alkoxyamine containing macromolecular intumescent flame retardant and its synergism in flame-retarding polypropylene. Polym Advan Technol. 2021;32(6):2452–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5275.
Sun Y, Yuan B, Shang S, Zhang H, Shi Y, Yu B, et al. Surface modification of ammonium polyphosphate by supramolecular assembly for enhancing fire safety properties of polypropylene. Compos Part B Eng. 2020;181:107588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107588.
Rybiński P, Żukowski W, Bradło D. Effect of cenospheric fillers on the flammability and fire hazard of silicone rubber composites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;125(3):1373–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5741-y.
Gu L, Shi Y, Zhang L. Synthesis and characterization of bio-based “three sources in one” intumescent flame retardant monomer and the intrinsic flame retardant waterborne polyurethane. J Polym Res. 2022;29(5):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03033-2.
Zhou Y, Liu Q, Xu P, Cheng H, Liu Q. Molecular structure and decomposition kinetics of kaolinite/alkylamine intercalation compounds. Front Chem. 2018;6:310. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2018.00310.
Yuan B, Fan A, Yang M, Chen X, Hu Y, Bao C, et al. The effects of graphene on the flammability and fire behavior of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene composites at different flame scenarios. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2017;143:42–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2017.06.015.
Liu Y, Yi J, Cai X. The investigation of intumescent flame-retarded polypropylene using poly(hexamethylene terephthalamide) as carbonization agent. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;107(3):1191–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1874-1.
Zhang W, Li X, Fan H, Yang R. Study on mechanism of phosphorus-silicon synergistic flame retardancy on epoxy resins. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2012;97(11):2241–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2012.08.002.
Ding H, Huang K, Li S, Xu L, Xia J, Li M. Flame retardancy and thermal degradation of halogen-free flame-retardant biobased polyurethane composites based on ammonium polyphosphate and aluminium hypophosphite. Polym Test. 2017;62:325–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2017.07.017.
Zhang X, Zhang Q, Zheng J. Effect and mechanism of iron oxide modified carbon nanotubes on thermal oxidative stability of silicone rubber. Compos Sci Technol. 2014;99:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2014.05.003.
Chen X, Song W, Liu J, Jiao C, Qian Y. Synergistic flame-retardant effects between aluminum hypophosphite and expandable graphite in silicone rubber composites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;120(3):1819–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4428-0.
Zhan Y, Wu X, Wang S, Yuan B, Fang Q, Shang S, et al. Synthesis of a bio-based flame retardant via a facile strategy and its synergistic effect with ammonium polyphosphate on the flame retardancy of polylactic acid. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2021;191:109684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2021.109684.
Funding
The work was funded from National Natural Science Foundation of China, China (grant number 52005050), Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control, China (grant number 20201105), Science and Technology Development Project of Jilin Province, China (grant number YDZJ202201ZYTS334) and Science and Technology Research Project of Education Department of Jilin Province, China (grant number JJKH20220679KJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Su, X., Chai, W., Xia, Y. et al. Bio-inspired construction of hydrophobic, bio-based and halogen-free flame-retardant strategy for silicone rubber. J Therm Anal Calorim 148, 9857–9874 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12371-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12371-2