Abstract
Nano-crystalline powders of Bi(1-x)TrxFe(1-y)MnyO3 (where x & y = 0, 0.05 and Tr = Cr, Ni, Zn, Cu) were prepared using sol-gel autocombustion method. Structural studies on the calcined nanopowders using X-ray diffraction and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy confirm the perovskite phase with rhombohedrally distorted structures. Microstructural studies using scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy on the sintered surfaces display uniformly knitted fine grained microstructures with thin grain boundaries and the presence of all element’s constituent for the synthesis of the samples, respectively. Dielectric properties were evaluated at various frequencies and temperatures and found to follow space charge polarization with significantly reduced dielectric losses at all frequency ranges investigated. Impedance study on the samples aids in understanding the contributions of electrical conductivity and interfacial polarization, and the results verify the claims explained during the dielectric property investigation. Magnetic studies on the samples reveal that among all the samples, Cr/Mn co-doped (BCrFMO) sample shows significant enhancement in the value of saturation magnetization (3.718 emu/g) while Ni/Mn co-doped (BNiFMO) sample demonstrates higher coercivity (259.734 Oe) at room temperature. With all enhanced structural, microstructural, dielectric and magnetic order through the influence of co-doing, these materials are highly recommended for spintronic, multifunctional memories, sensors, and actuators.
Graphical Abstract

Highlights
-
Wet chemical synthesis of sol-gel autocombustion produced Bi(1-x)TrxFe(1-y)MnyO3 (where x & y = 0, 0.05 and Tr = Cr, Ni, Zn, Cu) multiferroic samples with co-doping effect were studied for the first time.
-
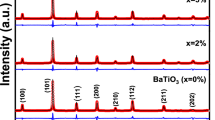
XRD and FTIR data shows that all samples have rhombohedral-symmetric single-phase perovskite structures.
-
Co-doping boosts magnetic order in all Cr, Ni, Zn, Cu and Mn co-doped samples.
-
Highest magnetization value of 3.718 emu/g was evident in Cr-Mn co-doped bismuth ferrite (BCrFMO) sample.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eerenstein W, Mathur ND, Scott JF (2006) Nature 442:759
Khomskii D (2009) Physics 2:20
Catalan G, Scott JF (2009) Adv Mater 21:2463
Marzouk M, Hashem HM, Soltan S, Ramadan AA (2020) J Mat Sci: Mat Elect 31:5599
Rhaman MM, Matin MA, Al Mamun MA et al. (2020) J Mat Sci Mat Electro 31:8727–8736
Dhanalakshmi B, Kollu P, Sekhar BC, Rao BP, Rao PSVS (2017) Ceram Int 43:9272
Vivekananda KV, Dhanalakshmi B, Rao BP, Rao PSVS (2021) Appl Phys A 127(3):1–9
Das R, Khan GG, Varma S, Dev Mukherjee G, Mandal K (2013) J Phys Chem C 117(39):20209–20216
Rana S, Karimunnesa S, Alam F, Chandra Das B, Khan FA (2022) Heliyon 8(12):e12530
Dung NQ, Lam NH, Dien LX et al. (2023) Appl Phys A 129:547
Dhanalakshmi B, Pratap K, Parvatheeswara Rao B, Subba Rao PSV (2016) J Alloy Compd 676:193
Dhanalakshmi B, Sekhar BC, Vivekananda KV, Rao BS, Rao BP, Rao PSVS (2020) Appl Phys A 126(7):1–9
Sravani GM, Murali N, Sekhar BC, Dhanalakshmi B, Parajuli D, Naidu TG (2022) J Indian Chem Soc 99(6):100465
Dhanalakshmi B, Sravani GM, Suresh J, Reddy PVSSSN, Rao KE, Jyothula S, Beera CS (2023) Appl Phys A 129(6):452
Sreekanth K, Dhanalakshmi B, Madhavaprasad D (2022) J Ind Chem Soc 99(9):100649
Shannon RD (1976) Acta Cryst A32:751–767
Ladgaonkar BP, Kolekar CB, Vaingankar AS (2002) Bull Mater Sci 25:351–354
Rao GVS, Rao CNR, Ferraro JR (1970) Appl Spectrosc 24:436–445R.IR-1
Som KK, Molla S, Bose K, Chaudhury BK (1992) Phys Rev B 45(4):1655–1659
Pradeep A, Chandrasekaran G (2006) Mater Lett 60:371–374
Dhanalakshmi B, Pratap K, ParvatheeswaraRao B, Rao PSVS (2016) J Mag Mag Mat 404:119–125
Kanth MR, Dhanalakshmi, Rao PSVS, Parvatheeswara B (2022) J Mater Eng Perform 32:1–12
Dhanalakshmi B, Subba Rao PSV, Rao BP, Kim C (2016) J Nanosci Nanotech 16:11089–11093
Panda B, Routray KL, Behera D (2020) Phys B: Condens Matter 583:411967
Routray KL, Saha S, Dhrubananda B (2020) J Electron Mater 49:7244–7258
Dhanalakshmi B, Kollu P, Rao BP, Rao PSVS (2016) Ceram Int 42(2):2186–2197
Routray KL, Sanyal D, Behera D (2017) J Appl Phys 122:224104
Macdonald JR (1987) Chemistry 223:25–50
Pattanayak S, Choudhary RNP et al. (2014) Ceram Int 40:7983–7991
Tirupathi P, Kumar N et al. (2015) J Appl Phys 117(0-8):074105
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dhanalakshmi, B., Madhusudanacharyulu, A.S., Madhuri Sailaja, J. et al. Effect of co-doping on structural, microstructural, dielectric, impedance and magnetic properties of sol-gel synthesized Bi(1-x)TrxFe(1-y)MnyO3 (Tr = Cr, Ni, Zn, Cu) multiferroic nanoceramics. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 109, 97–109 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06255-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06255-y