Abstract
In this study, cubic bixbyite FeMnO3 oxide nanoparticles were synthesized via a one-pot co-precipitation method. The effects of calcination temperature on the nanoparticles structural, optical, and morphological properties were investigated by calcining them at 700, 900, and 1100 °C in air for 2 h, which resulted in significant changes in their structural and optical properties. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy confirmed the presence of Fe–O and Mn–O stretching vibrations and X-ray diffraction analysis showed that the nanoparticles transformed from an amorphous to a crystalline phase upon calcination. Moreover, when the nanoparticles were calcined at higher temperatures, they displayed strong absorption in the visible and near-infrared regions, which resulted in a notable redshift in the optical band gap from 2.41 to 1.53 eV. Photocatalytic experiments demonstrated the nanoparticles excellent degradation capability in removing methylene blue from water under solar light irradiation. Specifically, the nanoparticles calcined at 1100 °C exhibited the highest photocatalytic efficiency with a maximum photo-degradation rate of 91%. Additionally, the nanoparticles displayed good antibacterial activity against Bacillus meurellus, Acetobactor rhizospherensis, Escherichia coli but were less effective against Bacillus subtilis.
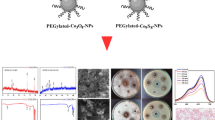
Graphical abstract

The XRD patterns of Fe-Mn binary oxide (FeMnO3) nanoparticles (left side of figure) indicate a transformation from an amorphous to a crystalline structure. In the middle figure, the photodegradation of methylene blue is depicted at various time intervals using FeMnO3 photocatalyst under sunlight irradiation. Additionally, the proposed mechanism for the degradation of methylene blue is also illustrated on the right side figure.
Highlights
-
Fe-Mn binary oxide with cubic bixbyite structure was successfully prepared via co-precipitation method.
-
Nanoparticles displays strong absorption in visible and near IR regions.
-
Optical bandgap significantly reduces with calcination temperature.
-
Fe-Mn binary oxide exhibits excellent multifunctional properties as solar light photocatalyst and antibacterial agent.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Muneer I, Farrukh MA, Ali D, Bashir F (2021) Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes by highly efficient GdCoSnO3. Mater Sci Eng B 265:115028
Muneer I, Farrukh MA (2022) Structural, optical, photoluminescence, photocatalytic and antifungal features of Gd/Mn2SnO4 nanocomposite annealed at different temperatures. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33:1263–1279
Ebrahimi M, Akhavan O (2022) Nanomaterials for photocatalytic degradations of analgesic, mucolytic and anti-biotic/viral/inflammatory drugs widely used in controlling SARS-CoV-2. Catalysts 12(6):667
ShilpaAmulya MA, Nagaswarupa HP, AnilKumar MR, Ravikumar CR, Kusuma KB (2020) Enhanced photocatalytic and electrochemical properties of Cu doped NiMnFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized via probe sonication method. Appl Surf Sci Adv 2:100038
Ahmed MA, El-Katori EE, Gharni ZH (2013) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye using Fe2O3/TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. J Alloy Compd 553:19–29
Gao M, Liu G, Gao Y, Chen G, Huang X, Xu X, Wang J, Yang X, Xu D (2021) Recent advances in metal-organic frameworks/membranes for adsorption and removal of metal ions. Trends Anal Chem 137:116226
Chehhat K, Mecif A, Mahdjoub AH, Nazir R, Pandit MA, Salhi F, Noua A (2023) Sol-gel synthesis of porous cobalt-doped ZnO thin films leading to rapid and large scale Orange-II photocatalysis. J Sol Gel Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06060-7
Masoumbeigi H, Rezaee A (2015) Removal of methylene blue (MB) dye from synthetic wastewater using UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation process. J Health Policy Sustain Health 2:160–166
Wang N, Wu L, Li J, Mo J, Peng Q, Li X (2020) Construction of hierarchical Fe2O3@MnO2 core/shell nanocube supported C3N4 for dual Z-scheme photocatalytic water splitting. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 215:110624
Buccolieri A, Serra A, Maruccio G, Monteduro AG, Padmanabhan SK, Licciulli A, Bonfrate V, Salvatore L, Manno D, Calcagnile L, Giancane G (2017) Synthesis and characterization of mixed iron-manganese oxide nanoparticles and their application for efficient nickel ion removal from aqueous samples. J Anal Methods Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9476065
Yan G, Wang P, Li Y, Qin Z, Lan S, Yan Y, Zhang Q, Cheng X (2021) Adsorption-oxidation mechanism of δ-MnO2 to remove methylene blue adsorption science and technology. Adsorp Sci Technol 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3069392
Ali D, Butt MZ, Muneer I, Farrukh MA, Aftab M, Saleem M, Bashir F, Khan AU (2019) Synthesis and characterization of sol-gel derived La and Sm doped ZnO thin films: a solar light photo catalyst for methylene blue. Thin Solid Films 679:86–98
Xiao J, Lv J, Lu Q (2022) Building Fe2O3/MoO3 nanorod heterojunction enables better tetracycline photocatalysis. Mater Lett 311:131580
Akhavan O, Ghaderi E (2009) Photocatalytic reduction of graphene oxide nanosheets on TiO2 thin film for photoinactivation of bacteria in solar light irradiation. J Phys Chem C 113:20214–20220
Dong L, Li Y, Chen D, Chen X, Zhang D (2021) Facilitated activation of peroxymonosulfate by loading ZIF-8 on Fe3O4-MnO2 for deep mineralization of bisphenol A. ACS EST Water 2:417–429
Yan J, Khoo E, Sumboja A, Lee PS (2010) Facile coating of manganese oxide on tin oxide nanowires with high-performance capacitive behavior. ACS Nano 4:4247–4255
Dai D, Liang H, He D, Potgieter H, Li M (2021) Mn-doped Fe2O3/diatomite granular composite as an efficient Fenton catalyst for rapid degradation of an organic dye in solution. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 97:329–339
Lai J, Shafi KVPM, Ulman A, Loos K, Yang N-L, Cui M-H, Vogt T, Estournès C, Locke DC (2004) Mixed iron−manganese oxide nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 108:14876–14883
Ghosh D, Dutta U, Haque A, Mordvinova NE, Lebedev OI, Pal K, Gayen A, Mahata P, Kundu AK, Seikh MM (2017) Evidence of low temperature spin glass transition in bixbyite type FeMnO3. Mater Sci Eng: B 226:206–210
Ma Q, Dong R, Liu H, Zhu A, Qiao L, Ma Y, Wang J, Xie J, Pan J (2020) Prussian blue analogue-derived Mn–Fe oxide nanocubes with controllable crystal structure and crystallinity as highly efficient OER electrocatalysts. J Alloy Compd 820:153438
Amulya MAS, Nagaswarupa HP, Kumar MRA, Ravikumar CR, Kusuma KB (2021) Sonochemical synthesis of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles and their electrochemical and photocatalytic properties. J Phys Chem Solids 148:109661
Huang X, Liu L, Xi Z, Zheng H, Dong W, Wang G (2019) One-pot solvothermal synthesis of magnetically separable rGO/MnFe2O4 hybrids as efficient photocatalysts for degradation of MB under visible light. Mater Chem Phys 231:68–74
Mandal B, Panda J, Paul PK, Sarkar R, Tudu B (2020) MnFe2O4 decorated reduced graphene oxide heterostructures: nanophotocatalyst for methylene blue dye degradation. Vacuum 173:109150
Luciano AJR, de Soletti LS, Ferreira MEC, Cusioli LF, de Andrade MB, Bergamasco R, Yamaguchi NU (2020) Manganese ferrite dispersed over graphene sand composite for methylene blue photocatalytic degradation. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104191
Balarabe BY, Bowmik S, Ghosh A, Maity P (2022) Photocatalytic dye degradation by magnetic XFe2O3 (X: Co, Zn, Cr, Sr, Ni, Cu, Ba, Bi, and Mn) nanocomposites under visible light: a cost efficiency comparison. J Magn Magn Mater 562:169823
Vasiljevic ZZ, Dojcinovic MP, Krstic JB, Ribic V, Tadic NB, Ognjanovic M, Auger S, Vidic J, Nikolic MV (2020) Synthesis and antibacterial activity of iron manganite (FeMnO3) particles against the environmental bacterium Bacillus subtilis. RSC Adv 10:13879
Siddiqui SI, Chaudhry SA (2018) Nigella sativa plant based nanocomposite-MnFe2O4/BC: An antibacterial material for water purification. J Clean Prod 200:996–1008
Rahmayeni R, Oktavia Y, Stiadi Y, Arief S, Zulhadjri Z (2020) Spinel ferrite of MnFe2O4 synthesized in Piper betle Linn extract media and its application as photocatalysts and antibacterial. J Dispers Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2020.1721011
Liu X, Qiu G, Zhao Y, Zhang N, Yi R (2007) Gallium oxide nanorods by the conversion of gallium oxide hydroxide nanorods. J Alloy Compd 439:275–278
Lee I, Kwak J, Haam S, Lee S-Y (2010) Dipeptide-assisted growth of uniform gallium oxohydroxide spindles. J Cryst Growth 312:2107–2112
Yang C, Ju T, Wang X, Ji Y, Yang C, Lv H, Wang Y, Dong W, Dang F, Shi X, Wang W, Fan Y (2020) The preparation of a novel iron/manganese binary oxide for the efficient removal of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv 10:10612–10623
Wang Y, Gao Y, Zhu Z, Zhang L, Zhao N, Fang Y, Zhu Y, Liu G (2021) Enhanced arsenic removal from aqueous solution by Fe/Mn-C layered double hydroxide composite. Adsorp Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8891643
Ali D, Butt MZ, Muneer I, Bashir F, Hanif M, Khan TM, Abbasi SA (2021) Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial performance of transparent c-axis oriented Al doped ZnO thin films. Surf Interfaces 27:101452
Ali D, Butt MZ, Arif B, Al-Ghamdi AA, Yakuphanoglu F (2017) The role of Al, Ba, and Cd dopant elements in tailoring the properties of c-axis oriented ZnO thin films. Phys B: Condens Matter 506:83–93
Ali D, Butt MZ, Arif B, Al-Sehemi AG, Al-Ghamdi AA, Yakuphanoglu F (2017) Li induced enhancement in c-axis orientation and its effect on structural, optical, and electrical properties of ZnO thin films. Mater Res Express 4:026405
Ali D, Butt MZ, Coughlan C, Caffrey D, Shvets IV, Fleischer K (2018) Nitrogen grain-boundary passivation of In-doped ZnO transparent conducting oxide. Phys Rev Mater 2:043402
Williamson GK, Hall WH (1953) X-ray line broadening from filed aluminium and wolfram. Acta Metall 1:22–31
Ishtiaq M, Ali D, Ahmad R, Muneer I, Bashir F, Hanif M, Khan TM, Abbasi SA (2023) A comparison of antibacterial activity in dark-UV light in perspective ofsurface and structural properties of spray pyrolysis grown Cu doped Cr2O3 thin films. Surf Interfaces 37:102741
Ali D, Butt MZ, Muneer I, Bashir F, Saleem M (2017) Correlation between structural and optoelectronic properties of tin doped indium oxide thin films. Optik 128:235–246
Ali D, Butt MZ (2014) Structural characteristics and inverse Hall–Petch relation in high-purity nickel irradiated with nanosecond infrared laser pulses. Phys B: Condens Matter 444:77–84
Aftab M, Butt MZ, Ali D, Bashir F, Aftab ZH (2021) Impact of copper doping in NiO thin films on their structure, morphology, and antibacterial activity against Escherichia Coli. Ceram Int 46:5037–5049
Aftab M, Aftab A, Butt MZ, Ali D, Bashir F, Iqbal SS (2023) Surface hardness of pristine and laser-treated zinc as a function of indentation load and its correlation with crystallite size valued by Williamson-Hall analysis, size-strain plot, Halder-Wagner and Wagner-Aqua models. Mater Chem Phys 295:127117
Habibi MH, Mosavi V (2017) Urea combustion synthesis of nano-structure bimetallic perovskite FeMnO3 and mixed monometallic iron manganese oxides: effects of preparation parameters on structural, opto-electronic and photocatalytic activity for photo-degradation of Basic Blue 12. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28:8473–8479
Habibi MH, Mosavi V (2017) Wet coprecipitation preparation of perovskite-type iron manganite nano powder pure phase using nitrate precursors: structural, opto-electronic, morphological and photocatalytic activity for degradation of Nile blue dye. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28:10270–10276
Bin H, Yao Z, Zhu S, Zhu C, Pan H, Chen Z, Wolverton C, Zhang D (2017) A high-performance anode material based on FeMnO3/graphene composite. J Alloy Compd 695:1223–1230
Sun P, Shen G, Tan Q, Chen Q, Song R, Hu J (2021) Degradation of BTEXS with stable and pH-insensitive iron-manganese modified biochar from post pyrolysis. Chemosphere 263:128092
Akhavan O, Ghaderi E (2010) Toxicity of graphene and graphene oxide nanowalls against bacteria. ACS Nano 4:5731–5736
Dutta T, Sarkar R, Pakhira B, Ghosh S, Sarkar R, Barui A, Sarkar S (2015) ROS generation by reduced graphene oxide (rGO) induced by visible light showing antibacterial activity: comparison with graphene oxide (GO). RSC Adv 5:80192–80195
Prasanna VL, Vijayaraghavan R (2015) Insight into the mechanism of antibacterial activity of ZnO—surface defects mediated reactive oxygen species even in dark. Langmuir 31:9155–9162
Akhavan O, Ghaderi E, Esfandiar A (2011) Wrapping bacteria by graphene nanosheets for isolation from environment, reactivation by sonication, and inactivation by near-infrared irradiation. J Phys Chem B 115:6279–6288
Liu S, Zeng TH, Hofmann M, Burcombe E, Wei J, Jiang R, Kong J, Chen Y (2011) Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: membrane and oxidative stress. ACS Nano 5:6971–6980
Akhavan O, Ghaderi E (2012) Escherichia coli bacteria reduce graphene oxide to bactericidal graphene in a self-limiting manner. Carbon 50:1853–1860
Kumar A, Pandey AK, Singh SS, Shanker R, Dhawan A (2011) Engineered ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and DNA damage leading to reduced viability of Escherichia coli. Free Radic Biol Med 51:1872–1881
Wang YW, Cao A, Jiang Y, Zhang X, Liu JH, Liu Y, Wang H (2014) Superior antibacterial activity of zinc oxide/graphene oxide composites originating from high zinc concentration localized around bacteria. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:2791–2798
Jannesari M, Akhavan O, Hosseini HRM, Bakhshi B (2023) Oxygen-rich graphene/ZnO2-Ag nanoframeworks with pH-switchable catalase/peroxidase activity as O2 nanobubble-self generator for bacterial inactivation. J Colloid Interface Sci 637:237–250
Manojkumar U, Kaliannan D, Srinivasan V, Balasubramanian B, Kamyab H, Mussa ZH, Palaniyappan J, Mesbah M, Chelliapan S, Palaninaicker S (2023) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Brassica oleracea var. botrytis leaf extract: photocatalytic, antimicrobial and larvicidal activity. Chemosphere 323:138263
Kalaimurugan D, Lalitha K, Durairaj K, Sivasankar P, Park S, Nithya K, Shivakumar MS, Liu WC, Balamuralikrishnan B, Venkatesan S (2022) Biogenic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles mediated from Borassus flabellifer (Linn): antioxidant, antimicrobial activity against clinical pathogens, and photocatalytic degradation activity with molecular modeling. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:86308–86319
Arokiyaraj S, Saravanan M, Prakash NKU, Arasu MV, Vijayakumar B, Vincent S (2013) Enhanced antibacterial activity of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles treated with Argemone mexicana L. leaf extract: an in vitro study. Mater Res Bull 48:3323–3327
Behera SS, Patra JK, Pramanik K, Panda N, Thatoi H (2012) Characterization and evaluation of antibacterial activities of chemically synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles. World J Nano Sci Eng 2:196–200
Arakha M, Pal S, Samantarrai D, Panigrahi TK, Mallick BC, Pramanik K, Mallick B, Jha S (2015) Antimicrobial activity of iron oxide nanoparticle upon modulation of nanoparticle-bacteria interface. Sci Rep 5:14813
Saod WM, Hamid LL, Alaallah NJ, Ramizy A (2022) Biosynthesis and antibacterial activity of manganese oxide nanoparticles prepared by green tea extract. Biotechnol Rep 34:00729
Lu H, Zhang X, Khan SA, Li W, Wan L (2021) Biogenic synthesis of MnO2 nanoparticles with leaf extract of viola betonicifolia for enhanced antioxidant, antimicrobial, cytotoxic, and biocompatible applications. Front Microbiol 12:761084
Yan Y, Jiang N, Liu X, Pan J, Li M, Wang C, Camargo PHC, Wang J (2022) Enhanced Spontaneous Antibacterial Activity of δ-MnO2 by Alkali Metals Doping. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 9:788574
Li Y, Yang D, Wang S, Li C, Xue B, Yang L, Shen Z, Jin M, Wang J, Qiu Z (2018) The detailed bactericidal process of ferric oxide nanoparticles on E. coli. Molecules 23:606
Armijo LM, Wawrzyniec SJ, Kopciuch M, Brandt YI, Rivera AC, Withers NJ, Cook NC, Huber DL, Monson TC, Smyth HDC, Osiński M (2020) Antibacterial activity of iron oxide, iron nitride, and tobramycin conjugated nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. J Nanobiotechnol 18:35
Ezealigo US, Ezealigo BN, Aisida SO, Ezema FI (2021) Iron oxide nanoparticles in biological systems: antibacterial and toxicology perspective. JCIS Open 4:100027
Patra JK, Baek K-H (2017) Green biosynthesis of magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using the aqueous extracts of food processing wastes under photo-catalyzed condition and investigation of their antimicrobial and antioxidant activity. J Photochem Photobiol B: Biol 173:291–300
Jagathesan G, Rajiv P (2018) Biosynthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles using Eichhornia crassipes leaf extract and assessing their antibacterial activity. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 13:90–94
Sharma AK, Pawar CA, Prasad NR, Yewale MA, Kamble DB (2018) Antimicrobial efficacy of green synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles. Mater Res Express 5:075402
Vasantharaj S, Sathiyavimal S, Senthilkumar P, Oscar FL, Pugazhendhi A (2019) Biosynthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Ruellia tuberosa: antimicrobial properties and their applications in photocatalytic degradation. J Photochem Photobiol B: Biol 192:74–82
Haneefa MM, Jayandran M, Balasubramanian V (2017) Evaluation of antimicrobial activity of green-synthesized manganese oxide nanoparticles and comparative studies with curcuminaniline functionalized nanoform. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 10:347–352
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have participated in the research activities of this paper. DA, IM, FB, MZB, AW, MH, MFMRW performed material preparation, data collection and analysis. The first draft of the manuscript was written by DA and IM, and all authors have commented on previous editions. MZB, MFMRW revised the English grammar of the original manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, D., Muneer, I., Bashir, F. et al. Sol–gel derived iron-manganese oxide nanoparticles: a promising dual-functional material for solar photocatalysis and antimicrobial applications. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 107, 452–466 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06123-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06123-9