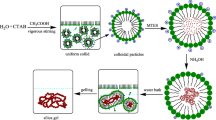
Abstract
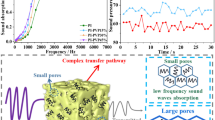
In this paper, PI-reinforced polymethylsiloxane aerogels composites were prepared by using methyltriethoxysilane (MTES) as precursor and polyimide fibers as reinforcement phase in the aqueous solvent system through acid-base two-step method and CO2 supercritical drying method. The effects of changes in the length and content of PI fibers on the thermal, mechanical, and sound insulation properties of the aerogel composites were systematically studied. The PI fiber is tightly bonded with the flexible aerogel substrate, showing good thermal properties. The density of the prepared samples is between 0.05 and 0.20 g/cm3, and the thermal conductivity is between 0.021 and 0.026 W/(m K). The thermal conductivity of samples decreases with the increase of fiber length and increases with the increase of PI fiber content, and the initial thermal decomposition temperature reaches 522.1 °C. During the compression test, PI-reinforced polymethylsiloxane aerogels did not crack in the 20% deformation compression process, and the rebound rate was between 44 and 46%, which was little affected by the reinforcing phase. The maximum compressive strength was 0.023 MPa, which was 1.4 times that of the polymethylsiloxane aerogel without adding reinforcing phase. The sound insulation property of PI simple with density around 52 mg/cm3 is mainly affected by fiber content and length change in low-frequency region, and the sound transmission loss of the sample with 3 mm and 2 wt% PI fibers reaches 18 dB at 500 Hz.

Graphical abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dorcheh AS, Abbasi MH (2008) Silica aerogel, synthesis, properties and characterization. J Mater Process Technol 199(1-3):10–26
Maleki H, Durães L, Portugal A (2014) An overview on silica aerogels synthesis and different mechanical reinforcing strategies. J Non-Crystalline Solids 385:55–74
Kistler SS (1931) Coherent expanded-aerogels. J Chem Phys 36(1):52–64
Othman AM, Ghobashy MM, Abd El-Sattar NEA (2021) Radiation synthesis of porous calcium silicate aerogel derived from polyacrylamide hydrogel as thermal insulator. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 98(3):593–604
Wei G, Liu Y, Zhang X (2011) Thermal conductivities study on silica aerogel and its composite insulation materials. Int J Heat Mass Transf 54(11-12):2355–2366
Mazrouei-Sebdani Z, Begum H, Schoenwald S (2021) A review on silica aerogel-based materials for acoustic applications. J Non-Crystalline Solids 562:120770
Cao L, Yu X, Yin X (2021) Hierarchically maze-like structured nanofiber aerogels for effective low-frequency sound absorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 597:21–28
Gu H, Zhou X, Lyu S (2020) Magnetic nanocellulose-magnetite aerogel for easy oil adsorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 560:849–856
Yu Y, Wu X, Guo D, Fang J (2014) Preparation of flexible, hydrophobic, and oleophilic silica aerogels based on a methyltriethoxysilane precursor. J Mater Sci 49:7715–7722
Rao AV, Kulkarni MM, Amalnerkar DP (2003) Superhydrophobic silica aerogels based on methyltrimethoxysilane precursor. J Non-Crystalline Solids 330(1-3):187–195
Nadargi DY, Rao AV (2009) Methyltriethoxysilane: new precursor for synthesizing silica aerogels. J Alloy Compd 467(1-2):0–404
Cui S, Liu Y, Fan MH (2011) Temperature dependent microstructure of MTES modified hydrophobic silica aerogels. Mater Lett 65(4):606–609
Kanamori K (2014) Monolithic silsesquioxane materials with well-defined pore structure. J Mater Res 29(23):2773–2786
Hayase G, Kanamori K, Maeno A (2016) Dynamic spring-back behavior in evaporative drying of polymethylsilsesquioxane monolithic gels for low-density transparent thermal superinsulators. J Non-Crystalline Solids 434:115–119
Kanamori K, Aizawa M, Nakanishi K (2007) New transparent methylsilsesquioxane aerogels and xerogels with improved mechanical properties. Adv Mater 19(12):1589–1593
Xiaohua L, Zichun Y, Kunfeng L (2019) A flexible silica aerogel with good thermal and acoustic insulation prepared via water solvent system. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 92(3):652–661
Xiaohua L, Zichun Y, Kunfeng L (2020) Preparation and characterization of transparent and compressible methylsilsesquioxane aerogels using MTES as precursor. Chem Ind Eng Prog 039(003):1115–1121
Chonghai W, Haiming C, Changqing H (2018) Lightweight chopped carbon fiber reinforced silica-phenolic resin aerogel nanocomposite: Facile preparation, properties and application to thermal protection. Compos Part A: Appl Sci Manuf 112:81–90
Yuan B, Ding S, Wang D (2012) Heat insulation properties of silica aerogel/glass fiber composites fabricated by press forming. Mater Lett 75:204–206
Yanfei W, Changrui Z, Jian F (2008) Fabrication and properties of SiO2-aerogel loading chopped mullite fiber porous skeleton composite. J Natl Univ Def Technol 030(006):24–28
Jiang S, Uch B, Agarwal S (2017) Ultralight, thermally insulating, compressible polyimide fiber assembled sponges. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(37):32308–32315
Liu H, Chen X, Zheng Y (2021) Lightweight, superelastic, and hydrophobic polyimide nanofiber/MXene composite aerogel for wearable piezoresistive sensor and oil/water separation applications. Adv Funct Mater 31(13):2008006
Wenjie G, Zichun Y, Kunfeng L (2019) Preparation and characterization of polyimide fiber reinforced silica aerogel. Mater Rev 33(04):714–718
Cao L, Fu Q, Si Y (2018) Porous materials for sound absorption. Compos Commun 10:25–35
Kuczmarski MA, Johnston JC (2011) Acoustic absorption in porous materials. NASA Center for Aerospace Information (CASI), United States, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022309321001290
Rahimabady M, Statharas EC, Yao K (2017) Hybrid local piezoelectric and conductive functions for high performance airborne sound absorption. Appl Phys Lett 111(24):241601
Stumpf C, Von Gässler K, Reichenauer G (1992) Dynamic gas flow measurements on aerogels. J Non-crystalline Solids 145:180–184
Jichao W, Jun S, Xingyuan N (2010) Acoustic properties of nanoporous silica aerogel. Rare Met Mater Eng 39:14–17
He J, Zhao H, Li X, Su D, Zhang F, Ji H, Liu R (2018) Superelastic and superhydrophobic bacterial cellulose/silica aerogels with hierarchical cellular structure for oil absorption and recovery. J Hazard Mater 346:199–207
Shi M, Tang C, Yang X (2017) Superhydrophobic silica aerogels reinforced with polyacrylonitrile fibers for adsorbing oil from water and oil mixtures. RSC Adv 7:4039–4045
Lei Y, Chen X, Song H (2017) The influence of thermal treatment on the microstructure and thermal insulation performance of silica aerogels. J Non-Crystalline Solids 470:178–183
Kanamori K, Aizawa M, Nakanishi K, Hanada T (2008) Elastic organic-inorganic hybrid aerogels and xerogels. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 48:172–181
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Yang, Z., Shao, H. et al. The influence of chopped PI fibers on thermal, mechanical and sound insulation properties of methylsilsesquioxane aerogels. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 101, 519–528 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05701-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05701-z