Abstract
This study explored the microstructural and magnetic features of NiFe2−xDyxO4 (x ≤ 0.10) NPs (nanoparticles) that were synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion method. The single phase of spinel ferrite has been verified for all samples without any impurity. The cubic morphology of the products was also showed by SEM. Room temperature (300 K) and 10 K magnetization curves were recorded applying a dc magnetic field up to ±50 kOe and it was observed that magnetic features of NiFe2O4 NPs significantly changed by the substitution of Dy3+ ion. Magnetization measurements showed low order of 300 and 10 K magnetic parameters (such as Keff, coercivity and anisotropy field values), revealing soft ferrimagnetic behaviors of all pristine and doped NiDyxFe2−xO4 (0.00 ≤ x ≤ 0.10) NPs at both 300 and 10 K. Pristine NiFe2O4 has maximum magnetic moment and saturation magnetization values among all samples. Dy3+ substitution showed a slight decrement in magnetization values compared with pristine sample. A slight increase in coercivity was noticed with Dy3+ substitution. Squareness ratios (SQRs) have a range between 0.144 and 0.324. These values are smaller than the theoretical limit of 0.50, implying the multi-domain nature for NPs. Blocking temperature (TB) was calculated as 28 K for NiFe2O4 NPs.

Pure phase of NiDyxFe2−xO4 (0.00 ≤ x ≤ 0.10) nanoparticles were prepared via sol–gel auto-combustion process. The structure, morphology, and magnetic properties were investigated.
Highlights
-
NiFe2−xDyxO4 (x ≤ 0.10) NPs were prepared via sol–gel auto-combustion method.
-
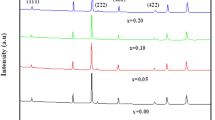
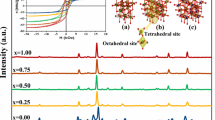
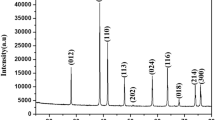
XRD analysis indicates the formation of pure single phase of spinel ferrites.
-
NiFe2−xDyxO4 (x ≤ 0.10) NPs exhibit soft ferrimagnetic nature.
-
All prepared NiFe2−xDyxO4 (x ≤ 0.10) NPs displayed a multi-domain nature.
-
Blocking temperature (TB) was calculated as 28 K for NiFe2O4 NPs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurtan U, Amir M, Yildiz A, Baykal A (2016) Synthesis of magnetically recyclable MnFe2O4@SiO2@Ag nanocatalyst: its high catalytic performances for azo dyes and nitro compounds reduction. Appl Surf Sci 376:16–25
Raghasudha M, Ravinder D, Veerasomaiah P (2014) Thermoelectric power studies of Co–Cr nano ferrites. J Alloy Compd 604:276–280
Nikumbh A, Pawar R, Nighot D, Gugale G, Sangale M, Khanvilkar M, Nagawade A (2014) Structural, electrical, magnetic and dielectric properties of rare-earth substituted cobalt ferrites nanoparticles synthesized by the co-precipitation method. J Magn Magn Mater 355:201–209
Sadaqat A, Almessiere M, Slimani Y, Guner S, Sertkol M, Albetran H, Baykal A, Shirsath SE, Ozcelik B, Ercan I (2019) Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Tb3+ substituted Co nanoferrites prepared via sonochemical approach. Ceram Int 45:22538–22546
Almessiere M, Slimani Y, Guner S, Nawaz M, Baykal A, Aldakheel F, Sadaqat A, Ercan I (2019) Effect of Nb substitution on magneto-optical properties of Co0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles. J Mol Struct 1195:269–279
Almessiere M, Slimani Y, Kurtan U, Guner S, Sertkol M, Shirsath SE, Akhtar S, Baykal A, Ercan I (2019) Structural, magnetic, optical properties and cation distribution of nanosized Co0.7Zn0.3TmxFe2-xO4 (0.0≤ x≤ 0.04) spinel ferrites synthesized by ultrasonic irradiation. Ultrasonics Sonochem:104638
Heiba ZK, Mohamed MB, Arda L, Dogan N (2015) Cation distribution correlated with magnetic properties of nanocrystalline gadolinium substituted nickel ferrite. J Magn Magn Mater 391:195–202
Naik S, Salker A (2012) Change in the magnetostructural properties of rare earth doped cobalt ferrites relative to the magnetic anisotropy. J Mater Chem 22:2740–2750
Eltabey M, Agami W, Mohsen H (2014) Improvement of the magnetic properties for Mn–Ni–Zn ferrites by rare earth Nd3+ ion substitution. J Adv Res 5:601–605
Ahmed M, Okasha N, El-Sayed M (2007) Enhancement of the physical properties of rare-earth-substituted Mn–Zn ferrites prepared by flash method. Ceram Int 33:49–58
Karimi Z, Mohammadifar Y, Shokrollahi H, Asl SK, Yousefi G, Karimi L (2014) Magnetic and structural properties of nano sized Dy-doped cobalt ferrite synthesized by co-precipitation. J Magn Magn Mater 361:150–156
Murugesan C, Sathyamoorthy B, Chandrasekaran G (2015) Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of Gd substituted manganese ferrite nanoparticles. Phys Scr 90:085809
Naik PP, Tangsali R, Meena S, Yusuf S (2017) Influence of rare earth (Nd+3) doping on structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline manganese-zinc ferrite. Mater Chem Phys 191:215–224
Kadam A, Shinde S, Yadav S, Patil P, Rajpure K (2013) Structural, morphological, electrical and magnetic properties of Dy doped Ni–Co substitutional spinel ferrite. J Magn Magn Mater 329:59–64
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, Güngüneş H, Ali S, Manikandan A, Ercan I, Baykal A, Trukhanov A (2019) Magnetic attributes of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles: influence of dysprosium ions (Dy3+) substitution. Nanomaterials 9:820
Shirsath SE, Mane ML, Yasukawa Y, Liu X, Morisako A (2013) Chemical tuning of structure formation and combustion process in CoDy0.1Fe1.9O4 nanoparticles: influence@pH. J Nanopart Res 15:1976
Shirsath SE, Mane ML, Yasukawa Y, Liu X, Morisakoa A (2014) Self-ignited high temperature synthesis and enhanced super-exchange interactions of Ho3+–Mn2+–Fe3+–O2− ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:2347–2357
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, Baykal A (2018) Exchange spring magnetic behavior of Sr0.3Ba0.4Pb0.3Fe12O19/(CuFe2O4)x nanocomposites fabricated by a one-pot citrate sol–gel combustion method. J Alloy Compd 762:389–397
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, El Sayed HS, Baykal A (2019) Morphology and magnetic traits of strontium nanohexaferrites: effects of manganese/yttrium co-substitution. J Rare Earths 37:732–740
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, El Sayed HS, Baykal A, Ercan I (2019) Microstructural and magnetic investigation of vanadium-substituted Sr-nanohexaferrite. J Magn Magn Mater 471:124–132
Zi ZF, Ma XH, Wie YY, Liu QC, Zhang M, Zhu XB (2018) Influence of La-Mn substitutions on magnetic properties of M-type strontium hexaferrites. AIP Adv 8:056235
Qui J, Gu M, Shen H (2005) Microwave absorption properties of Al and Cr-substituted M-type barium hexaferrite. J Magn Magn Mater 295:263–268
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, Baykal A (2018) Structural, morphological and magnetic properties of hard/soft SrFe12-xVxO19/(Ni0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4)y nanocomposites: effect of vanadium substitution. J Alloy Compd 767:966–975
Baiga MM, Yousufa MA, Warsia MF, Agboola PO, Sher M, Shakir I (2019) Surfactant assisted synthesis of rare earth Dy3+ substituted MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram Int 45:18014–18022
Poudel TP, Rai BK, Yoon S, Guragain D, Neupane D, Mishra SR (2019) The effect of gadolinium substitution in inverse spinel nickel ferrite: structural, magnetic, and Mossbauer study. J Alloy Compd 802:609–619
Akhtar MN, Khan MAzhar (2018) Effect of rare earth doping on the structural and magnetic features of nanocrystalline spinel ferrites prepared via sol gel route. J Magn Magn Mater 460:268–277
Tijerina-Rosaa A, Greneche JM, Fuentes AF, Rodriguez-Hernandez J, Menéndez JL, Rodríguez-González FJ, Montemayor SagrarioM (2019) Partial substitution of cobalt by rare-earths (Gd or Sm) in cobalt ferrite: effect on its microstructure and magnetic properties. Cer Int 45:22920–22929
Match! software version 3.9.0.158. (2019) https://www.crystalimpact.com/match/download.htm
Shirsath SE, Wang D, Jadhav SS, Mane ML, Li S (2018) Ferrites obtained by sol–gel method. In: Klein L, Aparicio M, Jitianu A (Eds.) Handbook of sol–gel science and technology. Springer, Cham, p 695–735
Kabbur SM, Ghodake UR, Nadargi DY, Kambale RC, Suryavanshi SS (2018) Effect of Dy3+ substitution on structural and magnetic properties of nanocrsytalline Ni-Cu-Zn ferrites. J Magn Magn Mater 451:665–675
Cullity BD, Graham CD (2008) Introduction to magnetic materials. Wiley, Hoboken, NJ
Stoner EC, Wohlfarth EP (1948) A mechanism of magnetic hysteresis in heterogeneous alloys. Philos Trans R Soc A 240(826):599–642
George M, John AM, Nair SS, Joy PA, Ananatharaman MR (2006) Finite size effects on the structural and magnetic properties of sol–gel synthesized NiFe2O4 powders. J Magn Magn Mater 302:190–195
Pulisova P, Kovac J, Voigt A, Raschman P (2013) Structure and magnetic properties of Co and Ni nano-ferrites prepared by a two-step direct microemulsions synthesis. J Magn Magn Mater 341:93–99
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, El Sayed HS, Baykal A, Ali S, Ercan I (2019) J Supercond Nov Magn 32:1437–1445
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, Sertkol M, Khan FA, Nawaz M, Tombuloglu H, Baykal A (2019) Ce–Nd Co-substituted nanospinel cobalt ferrites: an investigation of their structural, magnetic, optical, and apoptotic properties. Ceram Int 45:16147–16156
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This material has not been published in whole or in part elsewhere; the paper is not currently being considered for publication in another journal; all authors have been personally and actively involved in substantive work leading to the paper and will hold themselves jointly and individually responsible for its content.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slimani, Y., Almessiere, M.A., Güner, S. et al. Magnetic and microstructural features of Dy3+ substituted NiFe2O4 nanoparticles derived by sol–gel approach. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 95, 202–210 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05292-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05292-1