Abstract
In this paper, yttria-magnesia composite nanopowders with high specific surface area were synthesized by the sol–gel method. The crystallization kinetics of MgO–Y2O3 composite nanopowders were studied by the non-isothermal differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) technique. The crystallization activation energy of MgO–Y2O3 composite nanopowder was obtained 106.41 kJ/mol. The Avrami exponent (n) was 2.96 that corresponded to the three-dimensional growth. As-synthesized MgO–Y2O3 composite nanopowder had the average particle size of 10–15 nm with 140.42 m2/g specific surface area. The FESEM results showed that MgO and Y2O3 phases had a uniform phase distribution in the MgO–Y2O3 composite.
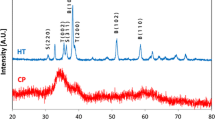
Graphical abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Razavi RS, Ahsanzadeh-Vadeqani M, Barekat M et al. (2016) Effect of sintering temperature on microstructural and optical properties of transparent yttria ceramics fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Ceram Int 42:7819–7823
Jiang D, Mukherjee AK (2008) Synthesis of Y2O3–MgO nanopowder and infrared transmission of the sintered nanocomposite. Nanosci Eng 7030:703007
Harris DC, Cambrea LR, Johnson LF et al. (2013) Properties of an infrared-transparent MgO: Y2O3 nanocomposite. J Am Ceram Soc 96:3828–3835
Jiang D, Mukherjee AK (2010) Spark plasma sintering of an infrared-transparent Y2O3–MgO nanocomposite. J Am Ceram Soc 93:769–773
Stefanik T, Gentilman R, Hogan P (2007) Nanocomposite optical ceramics for infrared windows and domes. In: Def. Secure. Symp. SPIE, USA. p 65450A
Xu S, Li J, Li C et al. (2015) Hot pressing of infrared-transparent Y2O3–MgO nanocomposites using sol–gel combustion synthesized powders. J Am Ceram Soc 98:1019–1026
Xu S, Li J, Li C et al. (2015) Infrared-transparent Y2O3–MgO nanocomposites fabricated by the glucose sol–gel combustion and hot-pressing technique. J Am Ceram Soc 98:2796–2802
Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA, Taheri-Nassaj E (2008) Effects of milling and calcination temperature on the compressibility and sinterability of a nanocrystalline Al2O3—Y3Al5O12 composite powder. J Am Ceram Soc 91:3546–3551
Huang L, Yao W, Liu J et al. (2014) Spark plasma sintering and mechanical behavior of magnesia—yttria (50:50vol.%) nanocomposites. Scr Mater 75:18–21
Chen C-H, Garofano JKM, Muoto CK et al. (2011) A foaming esterification sol—gel route for the synthesis of magnesia—yttria nanocomposites. J Am Ceram Soc 94:367–371
Chaim R, Shlayer A, Estournes C (2009) Densification of nanocrystalline Y2O3 ceramic powder by spark plasma sintering. J Eur Ceram Soc 29:91–98
Chaim R, Shen Z, Nygren M (2004) Erratum: transparent nanocrystalline MgO by rapid and low-temperature spark plasma sintering. J Mater Res 19:2527–2531
Chaonan W, Weiping Z, Min Y (2009) Preparation and spectroscopic properties of Y2O3: Eu 3+nanopowders and ceramics. J Alloys Compd 474:180–184
Mangalaraja RV, Mouzon J, Hedström P et al. (2008) Combustion synthesis of Y2O3 and Yb—Y2O3: part I. Nanopowders and their characterization. J Mater Process Technol 208:415–422
Hajizadeh-Oghaz M, Razavi RS, Ghasemi A (2016) The effect of solution pH value on the morphology of ceria—yttria Co stabilized zirconia particles prepared using the polymerizable complex method. J Clust Sci 27:469–483
Hajizadeh-Oghaz M, Razavi RS, Ghasemi A (2015) Synthesis and characterization of ceria-yttria co-stabilized zirconia (CYSZ) nanoparticles by sol–gel process for thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) applications. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 74:603–612
Oghaz MH, Razavi RS, Loghman-Estark MR, Ghasemi R (2012) Optimization of morphology and particle size of modified sol–gel synthesized YSZ nanopowder using Taguchi method. J Nano Res 21:65–70
Hajizadeh-Oghaz M, Razavi RS, Khajelakzay M (2015) Optimizing sol–gel synthesis of magnesia-stabilized zirconia (MSZ) nanoparticles using Taguchi robust design for thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) applications. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 73:227–241
Suñol JJ, Bonastre J (2010) Crystallization kinetics of metallic glasses. J Therm Anal Calorim 102:447–450
Hasheminezhad SA, Haddad-Sabzevar M, Sahebian S (2012) Non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of Co67Fe4Cr7Si8B14 amorphous alloy. Mater Sci Forum 706:1311–1317
Gao YQ, Wang W (1986) On the activation energy of crystallization in metallic glasses. J Non Cryst Solids 81:129–134
Abu-Sehly AA, Alamri SN, Joraid AA (2009) Measurements of DSC isothermal crystallization kinetics in amorphous selenium bulk samples. J Alloys Compd 476:348–351
Málek J (2000) Kinetic analysis of crystallization processes in amorphous materials. Thermochim Acta 355:239–253
Elabbar AA, El-Oyoun MA, Abu-Sehly AA, Alamri SN (2008) Crystallization kinetics study of Pb 4.3 Se 95.7 chalcogenide glass using DSC technique. J Phys Chem Solids 69:2527–2530
Kissinger HE (1957) Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem 29:1702–1706
Çelikbilek M, Ersundu AE, Ayd/in S (2012) Crystallization kinetics of amorphous materials. INTECH Open Access Publisher
Loghman-Estarki MR, Davar F, Ghorbani S et al. (2016) Synthesis and characterization of aluminum Oxy nitride (AlON) from the nanosized gel precursor. Ceram Int 42:16861–16866
Ghaderi M, Logman-Estarki MR, Razavi RS, Ghorbani S (2016) Spark plasma sintering of transparent Y2O3 ceramic using hydrothermal synthesized nanopowders. Ceram Int 42:14403–14410
Shirinparvar S, Razavi RS, Davar F et al. (2016) Synthesis, characterization and optical properties of Zr+ 4/La+ 3/Nd+ 3 tri-doped yttria nanopowder by sol–gel combustion method. Ceram Int 42:10551–10558
Zhang J, An L, Liu M et al. (2009) Sintering of Yb3+: Y2O3 transparent ceramics in hydrogen atmosphere. J Eur Ceram Soc 29:305–309
Beecroft LL, Ober CK (1997) Nanocomposite materials for optical applications. Chem Mater 9:1302–1317
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alhaji, A., Shoja Razavi, R., Ghasemi, A. et al. Study of crystallization behavior and kinetics of yttria-50 vol% magnesia composite nanopowders using a non-isothermal process. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 85, 93–102 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4520-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4520-y