Abstract
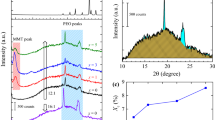
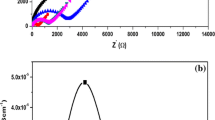
The structure and morphology of the solid nanocomposite polymer electrolytes (SNCPEs) have been studied in the present article. SNCPE systems, consisting of Poly (ethylene oxide) (PEO) host polymer, ammonium iodide (NH4I) salt and Laponite nano-filler, are prepared through the method of ball-milling followed by conventional solution casting technique. Addition of nano-filler in the polymer—salt complex, in general, improves thermal and mechanical stability of the electrolyte films. However, since Laponite possesses (2-d) layered structure, intercalation and/or exfoliation of this nano clay introduces significant variation in the structure and morphology of the host polymer. The present paper investigates the nano clay induced microstructural modifications in polymer/polymer composites and its impact in related properties of PEO-NH4I based SNCPEs. The systematic study on SNCPEs predicts the optimised proportions of the constituents for maximum modifications in dielectric properties and the dc ion conductivity of the system. The main motivation of the work is to understand and analyse the intercalation/exfoliation induced property enhancement of the electrolyte. The structural modifications have been investigated through different techniques like electron microscopy, diffraction analysis and infra-red spectroscopy. The X-ray diffraction analysis along with the calorimetric studies of SNCPE systems confirms the increase in amorphicity of the polymer matrix depending on the concentrations of salt and clay content in the composite. The enhanced amorphicity results in improved ion diffusivity that plays an important role in conductivity enhancement. However, the present work establishes that increased rate of ion dissociation, owing to modified ion – polymer / ion—clay interaction, plays the dominating role in enhancing the dc conductivity of the electrolyte at room temperature. Indication of increased ion dissociation and carrier concentration are confirmed through the FTIR and impedance spectroscopy respectively. Corresponding analysis of dielectric property and relaxation behaviour reveals the structure–property correlation and the contribution of polymer segmental mobility in enhancing the dc ionic conductivity of the clay loaded SNCPEs compared to clay free solid electrolyte systems.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material (data transparency)
Authors have all original data set and can provide for publication if needed.
References
Basu T, Tarafdar S (2016) Influence of gamma irradiation on the electrical properties of LiClO 4-gelatin solid polymer electrolytes: modelling anomalous diffusion through generalized calculus. Radiat Phys Chem 125:180–198
Choudhary S, Bald A, Sengwa R (2013) Dielectric behaviour, ionic conductivity and structure of high energy ball mill blended melt pressed and solution cast solid polymeric nanocomposite electrolytes. Indian J Pure Appl Phys 51:769–779
Agrawal R, Pandey G (2008) Solid polymer electrolytes: materials designing and all-solid-state battery applications: an overview. J Phys D Appl Phys 41(22):223001
Ayesh AS (2009) Dielectric properties of polyethylene oxide doped with NH4I salt. Polym J 41(8):616–621. https://doi.org/10.1295/polymj.PJ2009047
Saha M, Mukhopadhyay M, Ray R, Ballabh TK, Tarafdar S (2014) Influence of gamma irradiation on the molecular weight distribution and related properties of a polymer: study through simulation and experiment. Modell Simul Mater Sci Eng 23(2):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1088/0965-0393/23/2/025003
Hwang B-J, Liu Y-C, Lin H-C (1997) Conductivity of composite solid polymer electrolyte made of PEO-LiClO 4-fiber. J Polym Res 4(3):147–151
Deka M, Kumar A (2013) Dielectric and conductivity studies of 90 MeV O7+ ion irradiated poly(ethylene oxide)/montmorillonite based ion conductor. J Solid State Electrochem 17(4):977–986. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-012-1951-9
Chinnam PR, Wunder SL (2017) Engineered interfaces in hybrid ceramic–polymer electrolytes for use in all-solid-state Li batteries. ACS Energy Lett 2(1):134–138
Zhang J, Zhao J, Yue L, Wang Q, Chai J, Liu Z, Zhou X, Li H, Guo Y, Cui G (2015) Safety-reinforced poly (propylene carbonate)-based All-solid-state polymer electrolyte for ambient-temperature solid polymer lithium batteries. Adv Energy Mater 5(24):1501082
Li Y, Fu KK, Chen C, Luo W, Gao T, Xu S, Dai J, Pastel G, Wang Y, Liu B (2017) Enabling high-areal-capacity lithium–sulfur batteries: designing anisotropic and low-tortuosity porous architectures. ACS Nano 11(5):4801–4807
Raghu S, Archana K, Sharanappa C, Ganesh S, Devendrappa H (2015) The physical and chemical properties of gamma ray irradiated polymer electrolyte films. J Non-Cryst Solids 426:55–62
Raghu S, Archana K, Sharanappa C, Ganesh S, Devendrappa H (2016) Electron beam and gamma ray irradiated polymer electrolyte films: Dielectric properties. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 9(2):117–124
Nanda P, De SK, Manna S, De U, Tarafdar S (2010) Effect of gamma irradiation on a polymer electrolyte: Variation in crystallinity, viscosity and ion-conductivity with dose. Nuc Instrum Methods Phys Res B 268(1):73–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2009.09.063
Wang F, Li L, Yang X, You J, Xu Y, Wang H, Ma Y, Gao G (2018) Influence of additives in a PVDF-based solid polymer electrolyte on conductivity and Li-ion battery performance. Sustainable Energy Fuels
Selvalakshmi S, Mathavan T, Selvasekarapandian S, Premalatha M (2018) Effect of ethylene carbonate plasticizer on agar-agar: NH4Br-based solid polymer electrolytes. Ionics 1–9
Al‐Gunaid MQ, Saeed A (2018) Effects of the electrolyte content on the electrical permittivity, thermal stability, and optical dispersion of poly (vinyl alcohol)–cesium copper oxide–lithium perchlorate nanocomposite solid‐polymer electrolytes. J Appl Polym Sci 135(8)
Dhatarwal P, Sengwa R (2017) Dielectric and electrical characterization of (PEO–PMMA)–LiBF 4–EC plasticized solid polymer electrolyte films. J Polym Res 24(9):1–10
Dhatarwal P, Sengwa R (2019) Impact of PVDF/PEO blend composition on the β-phase crystallization and dielectric properties of silica nanoparticles incorporated polymer nanocomposites. J Polym Res 26(8):1–20
Sun Z, Li Y, Zhang S, Shi L, Wu H, Bu H, Ding S (2019) gC 3 N 4 nanosheets enhanced solid polymer electrolytes with excellent electrochemical performance, mechanical properties, and thermal stability. J Mater Chem A 7(18):11069–11076
Li M, Zhu W, Zhang P, Chao Y, He Q, Yang B, Li H, Borisevich A, Dai S (2016) Graphene-Analogues Boron Nitride Nanosheets Confining Ionic Liquids: A High-Performance Quasi-Liquid Solid Electrolyte. Small 12(26):3535–3542
Shim J, Kim HJ, Kim BG, Kim YS, Kim D-G, Lee J-C (2017) 2D boron nitride nanoflakes as a multifunctional additive in gel polymer electrolytes for safe, long cycle life and high rate lithium metal batteries. Energy Environ Sci 10(9):1911–1916
Tang WJ, Tang S, Zhang CJ, Ma QT, Xiang Q, Yang YW, Luo JY (2018) Adv Energy Mate 8
Aranda P, Ruiz-Hitzky E (1999) Poly (ethylene oxide)/NH 4+-smectite nanocomposites. Appl Clay Sci 15(1):119–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-1317(99)00015-0
Riley M, Fedkiw PS, Khan SA (2002) Transport properties of lithium hectorite-based composite electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 149(6):A667–A674
Nurul M, Mariatti M (2013) Effect of hybrid nanofillers on the thermal, mechanical, and physical properties of polypropylene composites. Polym Bull 70(3):871–884
Rao JK, Raizada A, Ganguly D, Mankad MM, Satyanarayana S, Madhu G (2015) Enhanced mechanical properties of polyvinyl alcohol composite films containing copper oxide nanoparticles as filler. Polym Bull 72(8):2033–2047
Reynaud E, Gauthier C, Perez J (1999) Nanophases in polymers Revue de Metallurgie 96(2):169–176
Young RJ, Kinloch IA, Gong L, Novoselov KS (2012) The mechanics of graphene nanocomposites: a review. Compos Sci Technol 72(12):1459–1476
Byrne N, Efthimiadis J, Macfarlane DR, Forsyth M (2004) The enhancement of lithium ion dissociation in polyelectrolyte gels on the addition of ceramic nano-fillers. J Mater Chem 14(1):127–133
Singh VK, Singh RK (2015) Development of ion conducting polymer gel electrolyte membranes based on polymer PVdF-HFP, BMIMTFSI ionic liquid and the Li-salt with improved electrical, thermal and structural properties. J Mater Chem C 3(28):7305–7318
Manoratne CH, Rajapakse RMG, Dissanayake MAKL (2006) Ionic Conductivity of Poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO)- Montmorillonite (MMT) Nanocomposites Prepared by Intercalation from Aqueous Medium. Int J Electrochem Sci 1(1):32–46
Liu M, Jia Z, Jia D, Zhou C (2014) Recent advance in research on halloysite nanotubes-polymer nanocomposite. Prog Polym Sci 39(8):1498–1525
Albdiry M, Yousif B, Ku H, Lau K (2013) A critical review on the manufacturing processes in relation to the properties of nanoclay/polymer composites. J Compos Mater 47(9):1093–1115
Du J, Cheng HM (2012) The fabrication, properties, and uses of graphene/polymer composites. Macromol Chem Phys 213(10–11):1060–1077
Li X, Wang C, Cao Y, Wang G (2018) Functional MXene materials: progress of their applications. Chem Asian J 13(19):2742–2757
Tu S, Jiang Q, Zhang X, Alshareef HN (2018) Large dielectric constant enhancement in MXene percolative polymer composites. ACS Nano 12(4):3369–3377
Mark J (1996) Ceramic-reinforced polymers and polymer-modified ceramics. Polym Eng Sci 36(24):2905–2920
Herron N, Thorn DL (1998) Nanoparticles: uses and relationships to molecular cluster compounds. Adv Mater 10(15):1173–1184
Huang P, Shi H-Q, Fu S-Y, Xiao H-M, Hu N, Li Y-Q (2016) Greatly decreased redshift and largely enhanced refractive index of mono-dispersed ZnO-QD/silicone nanocomposites. J Mater Chem C 4(37):8663–8669
Sahoo NG, Rana S, Cho JW, Li L, Chan SH (2010) Polymer nanocomposites based on functionalized carbon nanotubes. Prog Polym Sci 35(7):837–867
Han Z, Fina A (2011) Thermal conductivity of carbon nanotubes and their polymer nanocomposites: A review. Prog Polym Sci 36(7):914–944
Roy N, Sengupta R, Bhowmick AK (2012) Modifications of carbon for polymer composites and nanocomposites. Prog Polym Sci 37(6):781–819
Patla SK, Ray R, Karmakar S, Das S, Tarafdar S (2019) Nanofiller-induced ionic conductivity enhancement and relaxation property analysis of the blend polymer electrolyte using non-Debye electric field relaxation function. J Phys Chem C 123(9):5188–5197
Liu F, Hu N, Zhang J, Atobe S, Weng S, Ning H, Liu Y, Wu L, Zhao Y, Mo F (2016) The interfacial mechanical properties of functionalized graphene–polymer nanocomposites. RSC Adv 6(71):66658–66664
Deka M, Kumar A (2011) Electrical and electrochemical studies of poly (vinylidene fluoride)–clay nanocomposite gel polymer electrolytes for Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources 196(3):1358–1364
Scrosati B, Croce F, Panero S (2001) Progress in lithium polymer battery R&D. J Power Sources 100(1–2):93–100
Li Q, Sun H, Takeda Y, Imanishi N, Yang J, Yamamoto O (2001) Interface properties between a lithium metal electrode and a poly (ethylene oxide) based composite polymer electrolyte. J Power Sources 94(2):201–205
Croce F, Sacchetti S, Scrosati B (2006) Advanced, high-performance composite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. J Power Sources 161(1):560–564
Zhang Q, Ding F, Sun W, Sang L (2015) Preparation of LAGP/P (VDF-HFP) polymer electrolytes for Li-ion batteries. RSC Adv 5(80):65395–65401
Kim J-W, Ji K-S, Lee J-P, Park J-W (2003) Electrochemical characteristics of two types of PEO-based composite electrolyte with functional SiO2. J Power Sources 119:415–421
Doeff MM, Reed JS (1998) Li ion conductors based on laponite/poly(ethylene oxide) composites. Solid State Ionics 113:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(98)00367-1
Thomas J, Bohor BF (1968) Surface area of montmorillonite from the dynamic sorption of nitrogen and carbon dioxide. Clays Clay Miner 16(1):83–91
Pálková H, Madejová J, Zimowska M, Serwicka EM (2010) Laponite-derived porous clay heterostructures: 2. FTIR study of the structure evolution. Microporous and Mesoporous Mater 127(3):237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2009.07.012
Aranda P, Mosqueda Y, Pérez-Cappe E, Ruiz-Hitzky E (2003) Electrical characterization of poly (ethylene oxide)–clay nanocomposites prepared by microwave irradiation. J Polym Sci, Part B: Polym Phys 41(24):3249–3263
Stefanescu EA, Schexnailder PJ, Dundigalla A, Negulescu II, Schmidt G (2006) Structure and thermal properties of multilayered Laponite/PEO nanocomposite films. Polymer 47(21):7339–7348
Wang H, Chung T-S, Tong YW, Meier W, Chen Z, Hong M, Jeyaseelan K, Armugam A (2011) Preparation and characterization of pore-suspending biomimetic membranes embedded with Aquaporin Z on carboxylated polyethylene glycol polymer cushion. Soft Matter 7(16):7274–7280
Rahaman MHA, Khandaker MU, Khan ZR, Kufian MZ, Noor ISM, Arof AK (2014) Effect of gamma irradiation on poly (vinyledene difluoride)–lithium bis (oxalato) borate electrolyte. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16(23):11527–11537. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP01233J
Mukhopadhyay M, Saha M, Ray R, Tarafdar S (2016) A study on the effect of gamma irradiation on Poly [-Ethylene Oxide]: structural modification and variation in the kinetics of isoconversional phenomena. Indian J Phys 90(10):1133–1147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-016-0845-6
Bandara T, Mellander B (2011) Evaluation of mobility, diffusion coefficient and density of charge carriers in ionic liquids and novel electrolytes based on a new model for dielectric response. Ionic liquids: theory, properties, new approaches 383–406
Mohan V, Raja V, Bhargav PB, Sharma A, Rao VN (2007) Structural, electrical and optical properties of pure and NaLaF 4 doped PEO polymer electrolyte films. J Polym Res 14(4):283–290
Bruce PG, Vincent C (1993) Polymer electrolytes. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 89(17):3187–3203
Selvasekarapandian S, Hirankumar G, Kawamura J, Kuwata N, Hattori T (2005) 1H solid state NMR studies on the proton conducting polymer electrolytes. Mater Lett 59(22):2741–2745
Manoratne C, Rajapakse R, Dissanayake M (2006) Ionic conductivity of poly (ethylene oxide)(PEO)-montmorillonite (MMT) nanocomposites prepared by intercalation from aqueous medium. Int J Electrochem Sci 1(1):32–46
Dey A, Ghoshal T, Karan S, De S (2011) Size effect of cubic ZrO2 nanoparticles on ionic conductivity of polyethylene oxide-based composite. J Appl Phys 110(4):043707
Wang W, Alexandridis P (2016) Composite Polymer Electrolytes: Nanoparticles Affect Structure and Properties. Polymers 8(11):387
Yang S, Liu Z, Liu Y, Jiao Y (2015) Effect of molecular weight on conformational changes of PEO: an infrared spectroscopic analysis. J Mater Sci 50(4):1544–1552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8714-1
Fan Q, Shan D, Xuea H, He Y, Cosnier S (2007) Amperometric phenol biosensor based on laponite clay–chitosan nanocomposite matrix. Biosens Bioelectron 22(6):816–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2006.03.002
Robert J-L, Beny J-M, Beny C, Volfinger M (1989) Characterization of lepidolites by Raman and infrared spectrometries; I, Relationships between OH-stretching wavenumbers and composition. Can Mineral 27(2):225–235
Saha M, Mukhopadhyay M, Ray R (2017) Impact of gamma irradiation on porosity and pore distribution of poly [ethylene-oxide] films: correlation with dielectric and microstructural properties. Ind J Phys 1–12
Machado JC, Silva GG, Oliveira FCd, Lavall RL, Rieumont J, Licinio P, Windmöller D (2007) Free-volume and crystallinity in low molecular weight poly (ethylene oxide). J Polym Sci, Part B: Polym Phys 45(17):2400–2409
Guan HY, Guo ZB, Ding JJ, Lian F (2016) Ionic conductivity and dielectric behavior of novel poly (vinyl formal)-based single-ion-conductor polymer electrolytes. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43510
Shukur M, Kadir M (2015) Hydrogen ion conducting starch-chitosan blend based electrolyte for application in electrochemical devices. Electrochim Acta 158:152–165
Samui A, Sivaraman P (2010) Solid polymer electrolytes for supercapacitors. In: Polymer Electrolytes. Elsevier, pp 431–470
Awadhia A, Agrawal S (2007) Structural, thermal and electrical characterizations of PVA: DMSO: NH4SCN gel electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 178(13–14):951–958
Ramya C, Selvasekarapandian S, Hirankumar G, Savitha T, Angelo P (2008) Investigation on dielectric relaxations of PVP–NH4SCN polymer electrolyte. J Non-Cryst Solids 354(14):1494–1502
Kumar M, Srivastava N (2015) Conductivity and dielectric investigation of NH4I-doped synthesized polymer electrolyte system. Ionics 21(5):1301–1310
Ramesh S, Yahaya A, Arof A (2002) Dielectric behaviour of PVC-based polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 152:291–294
Sheha E (2009) Ionic conductivity and dielectric properties of plasticized PVA0. 7 (LiBr) 0.3 (H2SO4) 2.7 M solid acid membrane and its performance in a magnesium battery. Solid State Ionics 180(36–39):1575–1579
Sengwa R, Sankhla S, Choudhary S (2009) Dielectric relaxation processes and ionic conduction behaviour in poly (ethylene oxide)–montmorillonite clay nanocomposite aqueous colloidal suspensions. Colloid Polym Sci 287(9):1013–1024
Sengwa R, Choudhary S, Sankhla S (2010) Dielectric properties of montmorillonite clay filled poly (vinyl alcohol)/poly (ethylene oxide) blend nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 70(11):1621–1627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2010.06.003
Vincent CA (1987) Polymer electrolytes. Prog Solid State Chem 17(3):145–261
Mao G, Perea RF, Howells WS, Price DL, Saboungi M-L (2000) Relaxation in polymer electrolytes on the nanosecond timescale. Nature 405(6783):163–165
Othman L, Chew K, Osman Z (2007) Impedance spectroscopy studies of poly (methyl methacrylate)-lithium salts polymer electrolyte systems. Ionics 13(5):337–342
Munshi MZA (1995) Handbook of solid state batteries and capacitors. World Scientific
Kumar JS, Subrahmanyam A, Reddy MJ, Rao US (2006) Preparation and study of properties of polymer electrolyte system (PEO+ NaClO3). Mater Lett 60(28):3346–3349
Reddy MJ, Sreekanth T, Rao US (1999) Study of the plasticizer effect on a (PEO+ NaYF4) polymer electrolyte and its use in an electrochemical cell. Solid State Ionics 126(1–2):55–63
Acknowledgements
RR and PDB wish to acknowledge WBDST for funding (File No. ST/P/S&T/16G-25/2018) the research work. The authors also acknowledge DST, Government of India, for developing and providing instrument facility like LCR meter (Agilent 4294A-Precision Impedance Analyzer) under FIST programme at the Department of Physics, Jadavpur University.
Funding
RR and PDB wish to acknowledge WBDST for funding (File No. ST/P/S&T/16G-25/2018) the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest and financial disclosure
This work is original, has not been published and is not being considered for publication elsewhere. There are no other conflicts of interest for any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, M., Ray, R., Choudhury, A.R. et al. Impact of exfoliation/intercalation of nano-clay on structure, morphology and electrical properties of poly (ethylene oxide) based solid nanocomposite electrolytes. J Polym Res 28, 299 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02622-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02622-x