Abstract
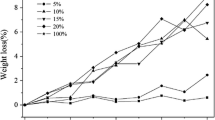
The poly(para-dioxanone) (PPDO) was blended with various contents of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) (10wt%, 20wt%, 30wt%) by solution co-precipitation in this study. The advantage of PLGA is derived from its safety and low cost. The hydrolytic degradation of PPDO / PLGA blends in vitro was studied by weight loss, water absorption, thermal properties, surface morphology, and mechanical properties in phosphate-buffered saline (pH = 7.44) at 37 ℃ for 8 weeks. After degradation, the weight loss and water absorption of all blends increased significantly. PPDO/PLGA (70/30) showed the largest weight loss during the whole degradation period. With the prolongation of hydrolysis degradation time, higher crystallinity of the PPDO was attributed to the chain breakage of unstable ester bonds. A fenestral structure with defects was formed on the surface of the blend bars with degradation. Besides, the glass transition temperature (Tg), the melting temperature (Tm), tensile strength, and breaking elongation of the blends decreased with the hydrolysis rate varying with the blend composition. Compared with pure PLGA and pure PPDO, the PPDO/PLGA blends exhibited a higher hydrolysis rate because of poor miscibility. Therefore, PPDO/PLGA blends with tailored degradation times have a lot of potential as a biomaterial for biomedical applications, such as high-performance absorbable sutures or a filler for ameliorating facial wrinkles.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu XL, Feng SM, Wang X, Qi J, Lei D, Li YD, Bai W (2020) Tuning the mechanical properties and degradation properties of polydioxanone isothermal annealing. Turk J Chem 44(5):1430–1444
Mei FF, Peng Y, Lu ST, Sun F, Zhang Y, Ge C, Zhang Y, Gu HL, Wang YD, Zhao XW, Wang GY (2015) Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid). J Macromol Sci Part B Phys 54(5):562–570
Xie XL, Bai W, Wu A, Chen DL, Xiong CD, Tang CM, Pang XB (2015) Increasing the compatibility of poly(L-lactide)/poly(para-dioxanone) blends through the addition of poly(para-dioxanone-co-L-lactide). J Appl Polym Sci 132(4):1029–1035
Xie XL, Bai W, Tang CM, Chen DL, Xiong CD (2015) Effects of poly(para-dioxanone-co-L-lactide) on the in-vitro hydrolytic degradation behaviors of poly(L-lactide)/poly(para-dioxanone) blends. J Mater Res 30(6):860–868
Bai W, Zhang LF, Li Q, Chen DL, Xiong CD (2010) In-vitro hydrolytic degradation of poly(para-dioxanone)/poly(D, L-lactide) blends. Mater Chem Phys 122(1):79–86
Bai W, Zhang ZP, Li Q, Chen DL, Chen HC, Zhao N, Xiong CD (2009) Miscibility, morphology and thermal properties of poly(para-dioxanone)/poly(D, L-lactide) blends. Polym Int 58(2):183–189
Li Q, Zhang YL, Li JB, Wang H, Lu H, Fan HH, Zheng G (2019) Stimulatory effects of poly-para-dioxanone, poly L-lactic acid, polycaprolactone, and poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/PLLA in rats. Mater Express 9(8):962–969
Kim J, Van Abel D (2015) Neocollagenesis in human tissue injected with a polycaprolactone-based dermal filler. J Cosmet Laser Ther 17(2):99–101
Heidari BS, Chen PL, Ruan R, Davachi SM, Al-Salami H, Pardo EDJ, Zheng M, Doyle B (2021) A novel biocompatible polymeric blend for applications requiring high toughness and tailored degradation rate. J Mater Chem B 9(10):2532–2546
Xu ZY, Liu JL, Chen JW, Lin JR, Chen QH (2020) Design of Janus particles based on silica@polystyrene and their compatibilization on poly(p-dioxanone)/poly(lactic acid) composites. J Appl Polym Sci 138(16):11
Sun J, Sun K, Bai K, Chen S, Zhao F, Wang FJ, Hong NC, Hu HB (2020) Oversized composite braided biodegradable stents with post-dilatation for pediatric applications: mid-term results of a porcine study. Biomater Sci 8(18):5183–5195
Yuan Y, Ding SD, Zhao YQ, Wang YZ (2016) Influences of Bis-(2,6-Diisopropylphenyl) carbodiimide on the thermal stability and crystallization of poly(p-Dioxanone). J Macromol Sci Part B Phys 55(5):532–546
Wang ZC, Li Q, Xiong CD (2015) Crystallization and mechanical properties of biodegradable poly(para-dioxanone)/octamethyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes nanocomposites via simple solution casting method. Bull Mater Sci 38(6):1589–1596
Dang HC, Luo YK, Xu C, Song F, Wang XL, Wang YZ (2015) Contribution of hemispheric CaCO3 to improving crystalline, physical properties and biocompatibility of poly(p-dioxanone). Ind Eng Chem Res 54(24):6269–6281
Gu PF, Wusiman A, Wang SY, Zhang Y, Liu ZG, Hu YL, Liu JG, Wang DY (2019) Polyethylenimine-coated PLGA nanoparticles-encapsulated Angelica sinensis polysaccharide as an adjuvant to enhance immune responses. Carbohyd Polym 223:115–128
Makadia HK, Siegel SJ (2011) Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers 3(3):1377–1397
Bai Y, Wang PQ, Bai W, Zhang LF, Li Q, Xiong CD (2105) Miscibility, thermal and mechanical properties of poly(para-dioxanone)/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) blends. J Polym Environ 23(3):367–373
Zhang XJ, Ma C, Bai W, Xiong CD, Chen DL (2014) Miscibility and isothermal crystallization behavior of poly-(L-lactide-co-glycolide)/poly(para-dioxanone) blends. Polym Polym Compos 22(8):705–712
Grizzi I, Garreau H, Li S, Vert M (1995) Hydrolytic degradation of devices based on poly(DL-Lactic Acid) size-dependence. Biomaterials 16(4):305–311
Zhang XJ, Bai W, Xiong CD, Chen DL, Pang XB (2015) Nonisothermal crystallization behaviour of poly(para-dioxanone) and poly(L-lactic acid) blends. Bull Mater Sci 38(2):517–523
Zhu GQ, Wang FG, Gao QC, Liu YY (2013) Physicochemical properties of poly(lactic acid-co-glycolic acid) film modified via blending with poly(butyl acrylate-co-methyl methacrylate). Polímeros 23(5):619–623
Liao L, Dong JT, Shi L, Fan ZY, Li SM, Lu ZQ (2015) In-vitro degradation behavior of L-lactide/trimethylene carbonate/glycolide terpolymers and a composite with poly(l-lactide-co-glycolide) fibers. Polym Degrad Stab 111:203–210
Cai Q, Wang Y, Yang F, Shen H, Yang XP, Wang SG (2011) Phase separation of polyphosphazene/poly(lactide-co-glycolide) blends prepared under different conditions. Polym Adv Technol 22(12):2448–2457
Oka M, Mandke R, Lakkadwala S, Lipp L, Singh J (2015) Effect of molar mass and water solubility of incorporated molecules on the degradation profile of the triblock copolymer delivery system. Polymers 7(8):1510–1521
Haghighat F, Abdolkarim S, Ravandi H (2014) Mechanical properties and in-vitro degradation of PLGA suture manufactured via electrospinning. Fiber Polym 15(1):71–77
Zhang LL, Xiong CD, Deng XM (1996) Miscibility, crystallization and morphology of poly(beta-hydroxybutyrate)/poly(d, l-lactide) blends. Polymer 37(2):235–241
Ishikiriyama K, Pyda M, Zhang G, Forschner T, Grebowicz J, Wunderlich B (1998) Heat capacity of poly-p-dioxanone. J Macromol Sci Part B Phy B37(1):27–44
Xie XL, Bai W, Chen DL, Xiong CD, Pang XB (2015) Effect of poly(para-dioxanone) on the hydrolytic degradation of poly(l-lactide). J Polym Environ 23(2):156–164
Sabino MA, Albuerne J, Müller AJ, Brisson J, Prud’homme RE, (2004) Influence of in-vitro hydrolytic degradation on the morphology and crystallization behavior of poly(p-dioxanone). Biomacromol 5(2):358–370
Sun JH, Li L, Li J (2019) Effects of furan-phosphamide derivative on flame retardancy and crystallization behaviors of poly(lactic acid). Chem Eng J 369:150–160
Chu CC, Browning A (1988) The study of thermal and gross morphologic properties of polyglycolic acid upon annealing and degradation treatments. J Biomed Mater Res 22(8):699–712
Yuan XY, Mak AFT, Yao KD (2002) Comparative observation of accelerated degradation of poly(L-lactic acid) fibres in phosphate buffered saline and a dilute alkaline solution. Polym Degrad Stab 75(1):45–53
Yang KK, Wang XL, Wan YZ, Huang HX (2006) Effects of molecular weights of bioabsorbable poly(p-dioxanone) on its crystallization behaviors. J Appl Polym Sci 100(3):2331–2335
Bai W, Chen DL, Li Q, Zhang SL, Huang XC, Xiong CD (2009) In-vitro hydrolytic degradation of poly(p-dioxanone) with high molecular weight. J Polym Res 16:471–480
Im JN, Kim JK, Kim HK, In CH, Lee KY, Park WH (2007) In-vitro and in vivo degradation behaviors of synthetic absorbable bicomponent monofilament suture prepared with poly(p-dioxanone) and its copolymer. Polym Degrad Stab 92(4):667–674
Keles H, Naylor A, Clegg F, Sammon C (2015) Investigation of factors influencing the hydrolytic degradation of single PLGA microparticles. Polym Degrad Stab 119:228–241
Hong KH, Woo SH, Kang TJ (2012) In-vitro degradation and drug-release behavior of electrospun, fibrous webs of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid). J Appl Polym Sci 124(1):209–214
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81974153).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Hou, P., Liu, S. et al. Effect of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) blend ratios on the hydrolytic degradation of poly(para-dioxanone). J Polym Res 28, 166 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02529-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02529-7