Abstract
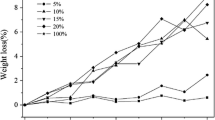
The in vitro hydrolytic degradation of high molecular weight poly (para-dioxanone) was studied by examining the changes of weight retention, water absorption, pH value, tensile strength, break elongation, thermal properties, and morphology of high molecular weight PPDO in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (pH 7.44) at 37°C for 8 weeks. During the degradation, all samples’ weight retention decreased and water absorption increased significantly, whereas hydrolysis rate of PPDO bars varied with molecular weight. Compared with lower molecular weight samples, higher molecular weight PPDO samples exhibited higher hydrolysis rate. The samples’ glass transition temperature (Tg) decreased notably, while the degrees of crystallinity (Dc) increased. The samples almost totally lost their tensile strengths and breaking elongation after 4 weeks of degradation. The results suggested that the stability of PPDO in vitro hydrolytic degradation increased with the increase of molecular weight.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang KK, Wang XL, Wang YZ (2002) J Macromol Sci Polym Rev 42:373–398. doi:10.1081/MC-120006453
Gertzman A, Thompson DR (1986) US 4,591,630
Mattei FV, Doddi N (1984) US 4,440,789
Cachia VV, June MS (1999) US 5,893,850
Forschner TC PCT Int Appl (1997) WO 9,721,753 A1
Yang KK, Wang XL, Wang YZ, Huang HX (2004) Mater Chem Phys 87:218–221. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2004.05.038
Sabino MA, González S, Márquez L, Feijoo JL (2000) Polym Degrad Stabil 69:209–216. doi:10.1016/S0141-3910(00)00062-8
Yang KK, Wang XL, Wang YZ, Huang HX (2006) J Appl Polym Sci 100:2331–2335. doi:10.1002/app.23003
Sabino MA, Feijoo JL, Müller AJ (2001) Polym Degrad Stabil 73:541–547. doi:10.1016/S0141-3910(01)00126-4
Ray JA (1981) Surg Gynecol Obstet 153:497–508
Lin HL, Chu CC, Grubb D (1993) J Biomed Mater Res 27:153–166. doi:10.1002/jbm.820270204
von Fraunhofer JA, Storey RS, Stone IK, Masterson BJ (1985) J Biomed Mater Res 19:595–600. doi:10.1002/jbm.820190511
Boland ED, Coleman BD, Lamellarnes CP, Simpon DG, Wenk GE, Bowlin GL (2005) Acta Biomater 1:115–123. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2004.09.003
Andjelić S, Jamiolkowski D, Mcdivitt J, Fisher J, Zhou J, Vetrecin RJ (2001) Appl Polym Sci 79:742–759. doi:10.1002/1097-4628(20010124)79:4<742::AID-APP190>3.0.CO;2-J
Nishia N, Konno M, Tokiwa Y (2000) Polym Degrad Stabil 68:271–280. doi:10.1016/S0141-3910(00)00010-0
Chen SC, Zhou ZX, Wang XL, Wang YZ, Yang KK (2006) Polymer (Guildf) 47:32–36. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2005.10.008
Sabino MA, Sabater L, Ronca G, Müller AJ (2002) Polym Bull 48:291–298. doi:10.1007/s00289-002-0039-6
Ooi CP, Cameron RE (2002) J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 63:280–290. doi:10.1002/jbm.10180
Chen SC, Wang XL, Wang YZ, Yang KK, Zhou ZX, WG (2007) J Biomed Mater Res Part A 80A:453–465
Chu CC (1981) J Appl Polym Sci 26:1727–1734. doi:10.1002/app.1981.070260527
Ishikiriyama K, Pyda M, Zhang G, Forschner T, Grebowicz J, Wunderlich B (1998) J Macromol Sci Phys B 37:27–44
Sabino MA, Feijoo JL, Müller AJ (2000) Macromol Chem Phys 201:2687–2698. doi:10.1002/1521-3935(20001201)201:18<2687::AID-MACP2687>3.0.CO;2-#
Pezzin APT, Duek EAR (2002) Polym Degrad Stabil 78:405–411. doi:10.1016/S0141-3910(02)00174-X
Sabino MA, Albuerne J, Müller AJ, Brisson J, Prud’homme RE (2004) Biomacromolecules 5:358–370. doi:10.1021/bm034367i
Chu CC, Browning A (1998) J Biomed Mater Res 22:699–712. doi:10.1002/jbm.820220804
Yuan XY, Mak AFT, Yao KD (2002) Polym Degrad Stabil 75:45–53. doi:10.1016/S0141-3910(01)00203-8
Im JN, Kim JK, Kim HK, In CH, Lee KY, Park WH (2007) Polym Degrad Stabil 92:667–674. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2006.12.011
Pezzin APT, Duek EAR (2006) J Appl Polym Sci 101:1899–1912. doi:10.1002/app.23646
Tomilhata M, Suzuki M, Oka T, Ikada Y (1998) Polym Degrad Stabil 59:13–18. doi:10.1016/S0141-3910(97)00183-3
Yu JM, Fu GR, Bian DC, Zhou XF, Liu CY, Yu JL (1996) Acta Polym Sin 6:675–682. in Chinese
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, W., Chen, D., Li, Q. et al. In vitro hydrolytic degradation of poly(para-dioxanone) with high molecular weight. J Polym Res 16, 471–480 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-008-9250-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-008-9250-y