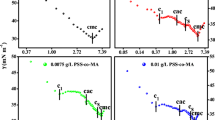
Abstract
UV absorption spectroscopy, electrical conductivity and density experiments have been used to investigate the interactions of some small biomolecules (amino acids/dipeptides) with an active pharmaceutical ingredient in ionic liquid form (API-IL), benzalkonium salicylate (BaSal), in aqueous solution. A number of useful parameters, such as critical micellar concentration (cmc), aggregation number (Nagg) and limiting molar conductivity (Λ0) of BaSal, standard partial molar volumes (\(V_{2,\phi }^{ \circ }\)), corresponding volumes of transfer from water to aqueous BaSal solutions (ΔtrVo), standard partial molar expansibilities (\(E_{\phi }^{ \circ }\)), hydration number (nH) of small biomolecules, as well as the binding constants (Kb) for small biomolecule–BaSal complexes have been evaluated. The dependence of the properties on concentration, temperature and alkyl chain length of amino acids/dipeptides is examined. The results are used to identify the solute–solvent physicochemical interactions occurring in the studied systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei, D., Ivaska, A.: Applications of ionic liquids in electrochemical sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 607, 126–135 (2008)
Sowmiah, S., Srinivasadesikan, V., Tseng, M.C., Chu, Y.H.: On the chemical stabilities of ionic liquids. Molecules 14, 3780–3813 (2009)
Hallet, J.P., Welton, T.: Room-temperature ionic liquids: solvents for synthesis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 111, 3508–3576 (2011)
Wang, T., Kaper, H., Antonietti, M., Smarsly, B.: Templating behavior of a long-chain ionic liquid in the hydrothermal synthesis of mesoporous silica. Langmuir 23, 1489–1495 (2007)
Liu, H.T., Liu, Y., Li, J.H.: Ionic liquids in surface electrochemistry. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 12, 1685–1697 (2010)
Ren, J., Li, Z.Y., Liu, J., Pei, Y.C., Wang, H.Y., Wang, J.J.: Choline derivative ionic liquids-based aqueous two-phase systems: phase diagrams and partition of purine alkaloids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 118, 51–57 (2018)
Zhao, Y.L., Tian, L., Qiu, J.K., Li, Z.Y., Wang, H.Y., Cui, G.K., Zhang, S.J., Wang, J.J.: Remarkable synergistic effect between copper(I) and ionic liquids for promoting chemical fixation of CO2. J. CO2 Util. 22, 374–381 (2017)
Bica, K., Rijksen, C., Nieuwenhuyzen, M., Rogers, R.D.: In search of pure liquid salt forms of aspirin: ionic liquid approaches with acetylsalicylic acid and salicylic acid. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 12, 2011–2017 (2010)
Stoimenovski, J., MacFarlane, D.R., Bica, K., Rogers, R.D.: Crystalline vs. ionic liquid salt forms of active pharmaceutical ingredients: a position paper. Pharm. Res. 27, 521–526 (2010)
Malhotra, S.V., Kumar, V.: A profile of the in vitro antitumor activity of imidazolium-based ionic liquids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20, 581–585 (2010)
Maddali, K., Kumar, V., Marchand, C., Pommier, Y., Malhotra, S.V.: Biological evaluation of imidazolium- and ammonium-based salts as HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. Med. Chem. Comm. 2, 143–150 (2011)
Pernak, J., Sobaszkiewicz, K., Mirska, I.: Anti-microbial activities of ionic liquids. Green Chem. 5, 52–56 (2003)
Pinto, P.C.A.G., Ribeiro, D.M.G.P., Azevedo, A.M.O., Dela-Justina, V., Cunha, E., Bica, K., Vasiloiu, M., Reis, S.: Saraiva, M.L.M.F.S.: Active pharmaceutical ingredients based on salicylate ionic liquids: insights into the evaluation of pharmaceutical profiles. New J. Chem. 37, 4095–4102 (2013)
Fei, Z., Geldbach, T.J., Zhao, D., Dyson, P.J.: From dysfunction to bis-function: on the design and applications of functionalised ionic liquids. Chem. A Eur. J. 12, 2122–2130 (2006)
Shekaari, H., Zafarani-Moattar, M.T., Mirheydari, S.N.: Conductometric analysis of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium ibuprofenate as an active pharmaceutical ingredient ionic liquid (API-IL) in the aqueous amino acids solutions. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 103, 165–175 (2016)
Shekaari, H., Zafarani-Moattar, M.T., Mirheydari, S.N.: Thermodynamic properties of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium salicylate as an active pharmaceutical ingredient ionic liquid (API-IL) in aqueous solutions of glycine and l-alanine at T = (288.15–318.15) K. Thermochim. Acta 637, 51–68 (2016)
Yan, Z.N., Wen, X.L., Kang, Y.X., Chu, W.W.: Intermolecular interactions of α-amino acids and glycyl dipeptides with the drug domiphen bromide in Aqueous solutions analyzed by volumetric and UV–Vis spectroscopy methods. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 101, 300–307 (2016)
Boutti, S., Graillat, C., McKenna, T.: A look at surfactant partitioning in polymeric latexes using conductivity measurements. Eur. Polym. J. 40, 2671–2677 (2004)
Sová, J.O., Vitková, Z., Vitko, A.: Study of micelle properties and thermodynamics of micellization of the benzethonium chloride. Tenside Surf. Det. 49, 322–329 (2012)
Chauhan, S., Singh, R., Sharma, K., Kumar, K.: Interaction study of anionic surfactant with aqueous non-ionic polymers from conductivity, density and speed of sound measurements. J. Surfactants Deterg. 18, 225–232 (2015)
Carpena, P., Aguiar, J., Bernaola-Galvan, P., Ruiz, C.C.: Problems associated with the treatment of conductivity–concentration data in surfactant solutions: simulations and experiments. Langmuir 18, 6054–6058 (2002)
Aguiar, J., Carpena, P., Molina-Bolivar, J.A., Ruiz, C.C.: On the determination of the critical micelle concentration by the pyrene 1:3 ratio method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 258, 116–122 (2003)
Mukhim, T., Dey, J., Das, S., Ismail, K.: Aggregation and adsorption behavior of cetylpyridinium chloride in aqueous sodium salicylate and sodium benzoate solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 350, 511–515 (2010)
Wang, H.Y., Feng, Q.Q., Wang, J.J., Zhang, H.C.: Salt effect on the aggregation behavior of 1-decyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide in aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 114, 1380–1387 (2010)
Rutyunyan, N.G., Arutyunyan, L.R., Grigoryan, V.V., Arutyunyan, R.S.: Effect of amino acids on the critical micellization concentration of different surfactants. Colloid J. 70, 666–668 (2008)
Scott, R.L.: Some comments on the Benesi–Hildebrand equation. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas 75, 787–789 (1956)
Yan, Z.N., Liu, R.L., Wu, S.Y., Bai, X.R., Wang, J.J.: Effect of temperature on the interactions of glycyl dipeptides with sodium perfluorooctanoate in aqueous solution: volumetric, conductometric, and spectroscopic study. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 57, 360–366 (2013)
Harned, H.S., Owen, B.B.: The Physical Chemistry of Electrolytic Solutions, Monograph Series, 3rd edn. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC (1950)
Kimizuka, H., Satake, L.: Estimation of micellar charge from conductivity data of aqueous detergent solutions. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn 35, 251–253 (1962)
Redlich, O., Meyer, D.M.: The molal volumes of electrolytes. Chem. Rev. 64, 221–227 (1964)
Zhang, J., Zhu, C.Y., Ma, Y.G.: Volumetric and viscometric properties of amino acids in aqueous maltitol solutions at T = (293.15–323.15) K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 111, 52–64 (2017)
Wen, X.L., Yan, Z.N., Kang, Y.X., Zhang, S.Y.: Apparent molar volume, conductivity, and fluorescence studies of ternary systems of dipeptides + ionic liquids ([C(n)Mim]Br, n = 10, 14) + water at different temperatures. Colloid Polym. Sci. 293, 2485–2495 (2015)
Yan, Z.N., Wang, J.J., Liu, W.B., Lu, J.S.: Apparent molar volumes and viscosity B-coefficients of some amino acids in aqueous solutions from 278.15 to 308.15 K. Thermochim. Acta 334, 17–27 (1999)
Pal, A., Chauhan, N.: Volumetric behaviour of amino acids and their group contributions in aqueous lactose solutions at different temperatures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 43, 140–146 (2011)
Mishra, A.K., Ahluwalia, J.C.: Apparent molal volumes of amino acids, N-acetylamino acids, and peptides in aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 88, 86–92 (1984)
Millero, F.J., Surdo, A.L., Shin, C.: The apparent molal volumes and adiabatic compressibilities of aqueous amino acids at 25 °C. J. Phys. Chem. 82, 784–792 (1978)
Berlin, E., Pallansch, M.J.: Densities of several proteins and l-amino acids in the dry state. J. Phys. Chem. 72, 1887–1889 (1968)
Yan, Z.N., Zhao, Y., Xing, R.H., Wang, X.G., Wang, J.J.: Volumetric and conductometric behavior at T = 298.15 K of 2-[(2-aminoacetyl)amino]acetic acid, 2-[(2-aminoacetyl)amino]-3-methylbutanoic acid, and (2S)-2-[(2-aminoacetyl)amino]-4-methylpentanoic acid with sodium hexanoate. J. Chem. Eng. Data 55, 759–764 (2010)
Gaba, R., Pal, A., Sharma, D.: Solvation behavior of glycine and glycyl dipeptide in aqueous 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide ionic liquid solutions at different temperatures. J. Mol. Liq. 233, 38–44 (2017)
Hepler, L.: Thermal expansion and structure in water and aqueous solutions. Can. J. Chem. 47, 4613–4617 (1969)
Acknowledgement
The project was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21573199).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Z., Shen, S., Ma, L. et al. Interaction Between an Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient Ionic Liquid Benzalkonium Salicylate and Small Biomolecules in Aqueous Solution: UV Absorption, Conductivity, and Volumetric Study. J Solution Chem 47, 1514–1528 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-018-0810-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-018-0810-4