Abstract
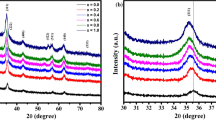
Cadmium ferrites belong to normal spinel ferrites, and they exhibit interesting electrical, magnetic, and optical properties. The pure and cerium-doped cadmium ferrites CdFe2−xCexO4 (x = 0.0, 0.125, 0.250, 0.375, 0.5) were synthesized by a chemical co-precipitating technique using sodium hydroxide as a co-precipitating agent. The structures and phase purity of fabricated nanomaterials were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The crystallite size for all the prepared nanomaterials was in the range of 28–46 nm. The lattice constant and unit cell volume were found to decrease with the increasing concentration of Cerium, which was confirmed by the peak shift in the XRD pattern. The X-ray density for all nano ferrites increased with the enhancement of cerium composition. The resistivity of the nanomaterials has random behavior with the enhancement of cerium composition for a temperature, but the value of resistivity at x = 0.125 has the lowest value and at x = 0.375 has the highest value for almost all temperatures. For specific concentrations, a decreasing trend of resistivity of fabricated materials was found with an increment of temperature. The activation energies were also calculated, and it increased for x = 0.125 and then decreased for all the nanomaterials. For the confirmation of the M–O bonds, FTIR analysis of all the nano ferrites was also performed. The analysis shows a higher frequency absorption band in the range of 531.24–534.84 cm−1. This absorption band confirms that metal oxides are formed in all the synthesized nanoparticles.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patange, S., Shirsath, S.E., Toksha, B., Jadhav, S.S., Jadhav, K.: Electrical and magnetic properties of Cr3+ substituted nanocrystalline nickel ferrite, J. Appl. Phys. 106, 023914 (2009)
Nejati, K., Zabihi, R.: Preparation and magnetic properties of nano size nickel ferrite particles using hydrothermal method. Chem. Cent. J. 6, 1–6 (2012)
ALIa, I., Amin, N., Rehman, A., Akhtar, M., Fatima, M., Mahmood, K., ALIa, A., Mustafa, G., Hasan, M.S., Bibi, A.: Electrical and magnetic properties of BaCoxCd2xFe16O27 W-type hexaferrites (0≤ x≤ 0.5). Digest J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 15, (2020)
Amin, N., Akhtar, M., Sabir, M., Mahmood, K., ALIa, A., Mustafa, G., Hasan, M.S., Bibi, A., Iqbal, M.Z., Iqbal, F.: Synthesis, structural and optical properties of Zn-substituted Co W-ferrites by coprecipitation method. J. Ovonic Res. 16, 11–19 (2020)
Amin, N., Hasan, M.S.U., Majeed, Z., Latif, Z., un Nabi, M.A., Mahmood, K., Ali, A., Mehmood, K., Fatima, M., Akhtar, M.: Structural, electrical, optical and dielectric properties of yttrium substituted cadmium ferrites prepared by Co-Precipitation method. Ceram. Int. 46, 20798–20809 (2020)
Aslam, A., Rehman, A.U., Amin, N., un Nabi, M.A., ul ain Abdullah, Q., Morley, N.A., Arshad, M.I., Ali, H.T., Yusuf, M., Latif, Z.: Lanthanum doped Zn0.5Co0.5LaxFe2− xO4 spinel ferrites synthesized via co-precipitation route to evaluate structural, vibrational, electrical, optical, dielectric, and thermoelectric properties. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 154, 110080 (2021)
Nejati, K., Zabihi, R.: Preparation and magnetic properties of nano size nickel ferrite particles using hydrothermal method. Chem. Cent. J. 6, 23 (2012)
Goswami, P.P., Choudhury, H.A., Chakma, S., Moholkar, V.S.: Sonochemical synthesis and characterization of manganese ferrite nanoparticles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52, 17848–17855 (2013)
Atassi, Y., Tally, M.: Low sintering temperature of Mg-Cu-Zn ferrite prepared by the citrate precursor method. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 3, 242–246 (2006)
Shirsath, S.E., Kadam, R., Gaikwad, A.S., Ghasemi, A., Morisako, A.: Effect of sintering temperature and the particle size on the structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Li0.5Fe2.5O4. J. Magnet. Magnet. Mater. 323, 3104–3108 (2011)
Rehman, A.U., Morley, N.A., Amin, N., Arshad, M.I., un Nabi, M.A., Mahmood, K., Ali, A., Aslam, A., Bibi, A., Iqbal, M.Z.: Controllable synthesis of La3+ doped Zn0.5Co0.25Cu0.25Fe2− xLaxO4 (x = 0.0, 0.0125, 0.025, 0.0375, 0.05) nano-ferrites by sol-gel auto-combustion route. Ceram. Int. 46, 29297–29308 (2020)
Aslam, A., Morley, N.A., Amin, N., Arshad, M.I., un Nabi, M.A., Ali, A., Mahmood, K., Bibi, A., Iqbal, F., Hussain, S.: Study of structural, optical and electrical properties of La3+ doped Mg0. 25 Ni0.15Cu0.25Co0.35Fe2-xLaxO4 spinel ferrites. Phys. B: Condens. Matter. 602, 412565 (2021)
Karanjkar, M., Tarwal, N., Vaigankar, A., Patil, P.: Structural, Mössbauer and electrical properties of nickel cadmium ferrites. Ceram. Int. 39, 1757–1764 (2013)
Zamani, F., Taghvaei A.H.: Synthesis of nanocrystalline Mg0.6Cd0.4Fe2O4 ferrite by glycine-nitrate auto-combustion method and investigation of its microstructure and magnetic properties. Ceram. Int. 43, 16693–16702 (2017)
Kumar, S., Kumar, R., Sharma, S., Reddy, V., Banerjee, A.: Temperature-dependent Mössbauer and dielectric studies of Mg0.95Mn0.05Fe1.0Ti1.0O4. Solid State Commun. 142, 706–709 (2007)
Sharma, R., Singhal, S.: Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of zinc doped nickel ferrite and their application in photo catalytic degradation of methylene blue. Phys. B 414, 83–90 (2013)
Akhtar, M.N., Sulong, A., Akhtar, M., Khan, M.A.: Systematic study of Ce3+ on the structural and magnetic properties of Cu nanosized ferrites for potential applications. J. Rare Earths 36, 156–164 (2018)
Lohar, K., Patange, S., Mane, M., Shirsath, S.E.: Cation distribution investigation and characterizations of Ni1− xCdxFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by citrate gel process. J. Mol. Struct. 1032, 105–110 (2013)
Ali, H.T., Ramzan, M., Arshad, M.I., Morley, N.A., Abbas, M.H., Yusuf, M., Rehman, A.U., Mahmood, K., Ali, A., Amin, N.: Tailoring the optical, and magnetic properties of La-BaM hexaferrites by Ni substitution. Chin. Phys. B (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/ac1412
Mustafa, G., Islam, M.U., Zhang, W., Jamil, Y., Iqbal, M.A., Hussain, M., Ahmad, M.: Temperature dependent structural and magnetic properties of Cerium substituted Co–Cr ferrite prepared by auto-combustion method, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 378, 409–416 (2015)
Akhtar, M.N., Khan, M.A.: Effect of rare earth doping on the structural and magnetic features of nanocrystalline spinel ferrites prepared via sol gel route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 460, 268–277 (2018)
Vasanthi, V., Shanmugavani, A., Sanjeeviraja, C., KalaiSelvan, R.: Microwave assisted combustion synthesis of CdFe2O4: magnetic and electrical properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 2100–2107 (2012)
Dasan, Y., Guan, B., Zahari, M., Chuan, L.: Influence of La3+ substitution on structure, morphology and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Ni-Zn ferrite. PloS One. 12, e0170075 (2017)
Thakur, P., Sharma, R., Kumar, M., Katyal, S.C., Negi, N.S., Thakur, N., Sharma, V., Sharma, P.: Superparamagnetic La doped Mn–Zn nano ferrites: dependence on dopant content and crystallite size. Mater. Res. Express. 3, 075001 (2016)
Aslam, A., Razzaq, A., Naz, S., Amin, N., Arshad, M.I., Nabi, M.A.U., Nawaz, A., Mahmood, K., Bibi, A., Iqbal, F.: Impact of lanthanum-doping on the physical and electrical properties of cobalt ferrites. J. Supercond. Novel Magnet. 1–10 (2021)
Miao, F., Deng, Z., Lv, X., Gu, G., Wan, S., Fang, X., Zhang, Q., Yin, S.: Fundamental properties of CdFe2O4 semiconductor thin film. Solid State Commun. 150, 2036–2039 (2010)
Iqbal, M.J., Ahmad, Z., Melikhov, Y., Nlebedim, I.C.: Effect of Cu–Cr co-substitution on magnetic properties of nanocrystalline magnesium ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 1088–1094 (2012)
JavedIqbal, M., ZahoorAhmad, Y., Melikhov, I.C.: Nlebedim, Effect of Cu–Cr co-substitution on magnetic properties of nano crystalline magnesium ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 1088–1094 (2012)
Zakir, R., Iqbal, S.S., Rehman, A.U., Nosheen, S., Ahmad, T.S., Ehsan, N., Inam, F.: Spectral, electrical, and dielectric characterization of Ce-doped Co-Mg-Cd spinel nano-ferrites synthesized by the sol-gel auto combustion method, (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.07.016
Hussain, K., Amin, N., Ajaz-Un-Nabi, M., Ali, A., Mahmood, K., Mustafa, G., sharif, M., Hassan, M.S., Sabir, N., Ali, S., Jabeen, F., Asif, M., Arshad, M.I.: Investigation of structural and electrical properties of Ce3+ ions substituted Cd-Co ferrites. Digest J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 14, 85–92 (2019)
Belavia, P.B., Chavana, G.N., Naika, L.R., Somashekarb, R., Kotnala, R.K.: Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of cadmium substituted nickel–copper ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 132, 138– 144 (2012)
Al-Hilli, M.F., Li, S., Kassim, K.S.: Microstructure, electrical properties and Hall coefficient of europium-doped Li–Ni ferrites. Mater. Sci. Eng., B 158, 1–6 (2009)
Manzoor, A., Khan, M.A., Khan, M.Y., Akhtar, M.N., Hussain, A.: Tuning magnetic and high frequency dielectric behavior in Li-Zn ferrites by Ho doping. Ceram. Int. 44, 6321–6329 (2018)
Padalia, D., Johri, U.C., Zaidi, M.G.H.: Study of cerium doped magnetite (Fe3O4:Ce)/PMMA nano composites. Phys. B 407, 838–843 (2012)
Raghasudha, M., Ravinder, D., Veerasomaiah, P.: Electrical resistivity studies of Cr doped Mg nano-ferrites, Materials. Discovery 2, 50–54 (2015)
Malana, M.A., Qureshi, R.B., Ashiq, M.N., Zafar, Z.I.: Synthesis, electrical and dielectric characterization of cerium doped nano copper ferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 4775–4779 (2013)
Yousuf, M.A., Jabeen, S., Shahi, M.N., Khan, M.A., Shakir, I., Warsi, M.F.: Magnetic and electrical properties of yttrium substituted manganese ferrite nanoparticles prepared via micro-emulsion route. Results Phys. 16, 102973 (2020)
Naeem, M., Shah, N.A., Gul, I.H., Maqsood, A.: Structural, electrical and magnetic characterization of Ni–Mg spinel ferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 487, 739–743 (2009)
Hussain, K., Amin, N., Arshad, M.I.: Evaluation of structural, optical, dielectric, electrical, and magnetic properties of Ce3+ doped Cu0.5Cd0.25Co0.25Fe2-xO4 spinel nano-ferrites. Ceram. Int. 47, 3401–3410 (2021)
Gul, I., Ahmed, W., Maqsood, A.: Electrical and magnetic characterization of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrite synthesis by co-precipitation route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 270–275 (2008)
Hussain, K., Bibi, A., Jabeen, F., Amin, N., Mahmood, K., Ali, A., Iqbal, M.Z., Arshad, M.: Study of structural, optical, electrical and magnetic properties of Cu2+ doped Zn0.4Co0.6xCe0.1Fe1.9O4 spinel ferrites. Phys. B: Condens. Matter. 584, 412078 (2020)
Wagner, K.W.: Zur theorie der unvollkommenen dielektrika. Ann. Phys. 345, 817–855 (1913)
Maxwell, J.C.: Electricity and magnetism, Dover New York (1954)
Fawzi, A.S., Sheikh, A., Mathe, V.: Structural, dielectric properties and AC conductivity of Ni(1–x)ZnxFe2O4 spinel ferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 502, 231–237 (2010)
Funding
The current research is supported by Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP—2020/293), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia. The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research (DRS), king Khalid University, Abha, Saudi Aribia for funding this work through General Reseach Project, under grant no.G.R.P. 30/42. Khalid Husain also received support from the HEC, Pakistan, through IRSIP, PIN: IRSIP 46 PSc.45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the special issue “Selected articles based on 4th International Conference on Materials Science & Nanotechnology”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amin, N., Razaq, A., Rehman, A.U. et al. Transport Properties of Ce-Doped Cd Ferrites CdFe2−xCexO4. J Supercond Nov Magn 34, 2945–2955 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-06053-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-06053-z