Abstract
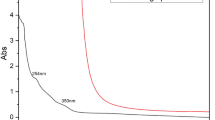
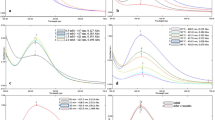
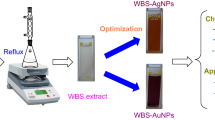
This work presents an environmentally friendly approach to synthesizing silver-zinc oxide (Ag-Zn) bimetallic nanoparticles using domestic waste of kiwi (Actinidia chinensis var. deliciosa) peel extract that acts as a reducing and stabilizing agent. The fabricated nanoparticles were characterized using various techniques such as UV–Vis spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). The antimicrobial and catalytic activity of the fabricated Ag–Zn were investigated. The antimicrobial activity against gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (SA), Bacillus subtilis (BS), and gram-negative Klebsiella pneumonia (KP) strains were evaluated and it was found that KP showed higher zone of inhibition i.e.12 mm, then followed by 11 mm, and 9 mm for SA and BS respectively. For the catalytic activity, more than 85% of methyl red, 93% of phenol red, and 78% of eosin yellow dyes were degraded in 1 h. The green synthesis method presented in this study provides a sustainable and non-toxic synthesis route while simultaneously remediating the environment.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Ramesh, K. Saravanan, P. Manogar, J. Johnson, E. Vinoth, M. Mayakannan, Green synthesis and characterization of biocompatible zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of its antibacterial potential. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 31, 100399 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2021.100399
M. Hosny, M. Fawzy, A.S. Eltaweil, Green synthesis of bimetallic Ag/ZnO@Biohar nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline, antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Sci. Rep. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-11014-0
X. Xie et al., Ag nanoparticles cluster with pH-Triggered reassembly in targeting antimicrobial applications. Adv. Func. Mater. 30(17), 2000511 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202000511
S. Nayak, L.C. Goveas, C. Vaman Rao, Biosynthesis of Silver nanoparticles using turmeric extract and evaluation of its anti-bacterial activity and catalytic reduction of methylene blue, in Materials, Energy and Environment Engineering. ed. by R.B. Mohan, G. Srinikethan, B.C. Meikap (Springer, Singapore, 2017), pp.257–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2675-1_31
V. Kanikireddy, K. Varaprasad, M.S. Rani, P. Venkataswamy, B.J. Mohan Reddy, M. Vithal, Biosynthesis of CMC-Guar gum-Ag0 nanocomposites for inactivation of food pathogenic microbes and its effect on the shelf life of strawberries. Carbohydr. Polym. 236, 116053 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116053
Z. Luksiene, N. Rasiukeviciute, B. Zudyte, N. Uselis, Innovative approach to sunlight activated biofungicides for strawberry crop protection: ZnO nanoparticles. J. Photochem. Photobiol., B 203, 111656 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111656
A. Farahi, M. Achak, L. El Gaini, M.A. El Mhammedi, M. Bakasse, Silver particles-modified carbon paste electrodes for differential pulse voltammetric determination of paraquat in ambient water samples. J. Assoc. Arab Univ. Basic Appl. Sci. 19(1), 37–43 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaubas.2014.06.011
S. Nayak, M.K.B. Dr, L. Goveas, C.V. Rao, S. Sajankila, Investigation of nonlinear optical properties of AgNPs synthesized using Cyclea peltata leaf extract post OVAT optimization. BioNanoScience (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-021-00875-w
V.B. Patil, D. Ilager, S.M. Tuwar, K. Mondal, N.P. Shetti, Nanostructured ZnO-based electrochemical sensor with anionic surfactant for the electroanalysis of trimethoprim. Bioengineering (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100521
H. Kumar, N. Venkatesh, H. Bhowmik, A. Kuila, Metallic nanoparticle: a review. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res 4(2), 3765–3775 (2018)
D.S. Idris et al., Polymer-based nanocarriers for biomedical and environmental applications. e-Polymers (2023). https://doi.org/10.1515/epoly-2023-0049
T. Mazhar, V. Shrivastava, R.S. Tomar, Green synthesis of bimetallic nanoparticles and its applications: a review. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 9(2), 102 (2017)
M.C. Jobe, D.M. Mthiyane, M. Mwanza, D.C. Onwudiwe, Biosynthesis of zinc oxide and silver/zinc oxide nanoparticles from Urginea epigea for antibacterial and antioxidant applications. Heliyon 8(12), e12243 (2022)
S. Nayak, C.V. Rao, S. Mutalik, Exploring bimetallic Au–Ag core shell nanoparticles reduced using leaf extract of Ocimum tenuiflorum as a potential antibacterial and nanocatalytic agent. Chem. Pap. 76(10), 6487–6497 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02299-6
M. Barwant et al., Eco-friendly synthesis and characterizations of Ag/AgO/Ag2O nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Solanum elaeagnifolium for antioxidant, anticancer, and DNA cleavage activities. Chem. Pap. 76(7), 4309–4321 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02178-0
E. Tilahun, Y. Adimasu, Y. Dessie, Biosynthesis and optimization of ZnO nanoparticles using Ocimum lamifolium leaf extract for electrochemical sensor and antibacterial activity. ACS Omega 8(30), 27344–27354 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.3c02709
A. Velidandi, N.P.P. Pabbathi, S. Dahariya, R.R. Baadhe, Green synthesis of novel Ag–Cu and Ag–Znbimetallic nanoparticles and their in vitro biological, eco-toxicity and catalytic studies. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 26, 100687 (2021)
D.S. Idris, A. Roy, Synthesis of Bimetallic nanoparticles and applications—an updated review. Crystals (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13040637
W.P. Wicaksono et al., A green synthesis of gold–palladium core–shell nanoparticles using orange peel extract through two-step reduction method and its formaldehyde colorimetric sensing performance. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 24, 100535 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2020.100535
D.S. Idris, A. Roy, Biogenic synthesis of Ag–CuO nanoparticles and its antibacterial, antioxidant, and catalytic activity. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02873-9
K.V.G. Ravikumar, S.V. Sudakaran, K. Ravichandran, M. Pulimi, C. Natarajan, A. Mukherjee, Green synthesis of NiFe nano particles using Punica granatum peel extract for tetracycline removal. J. Clean. Prod. 210, 767–776 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.108
A.E. Adebayo et al., Biosynthesis of silver, gold and silver–gold alloy nanoparticles using Persea americana fruit peel aqueous extract for their biomedical properties. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 4(1), 13 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41204-019-0060-8
S. PrashannaSuvaitha, P. Sridhar, T. Divya, P. Palani, K. Venkatachalam, Bio-waste eggshell membrane assisted synthesis of NiO/ZnO nanocomposite and its characterization: evaluation of antibacterial and antifungal activity”. Inorganica Chim. Acta 536, 120892 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2022.120892
S.R. Dhruval et al., Rapid synthesis of antimicrobial Fe/Cu alloy nanoparticles using Waste Silkworm Cocoon extract for cement mortar applications. Adv. Nat. Sci: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11(2), 025006 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6254/ab8790
J. Zhang, J. Tian, N. Gao, E.S. Gong, G. Xin, C. Liu, B. Li, Assessment of the phytochemical profile and antioxidant activities of eight kiwi berry (Actinidia arguta (Siebold & Zuccarini) Miquel) varieties in China. Food. Sci. Nutr. 9(10), 5616–5625 (2021)
X. He et al., “Actinidia chinensis Planch.: A Review of Chemistry and Pharmacology,” Frontiers in Pharmacology, vol. 10, 2019, [Online]. Available: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01236. Accessed 04 Jul 2023
X. Sun et al., Sodium alginate-based nanocomposite films with strong antioxidant and antibacterial properties enhanced by polyphenol-rich kiwi peel extracts bio-reduced silver nanoparticles. Food Packag. Shelf Life 29, 100741 (2021)
J. Li, Y. Li, H. Wu, S. Naraginti, Y. Wu, Facile synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by Actinidia deliciosa fruit peel extract: bactericidal, anticancer and detoxification properties. Environ. Res. 200, 111433 (2021)
N. Ajmal, K. Saraswat, M.A. Bakht, Y. Riadi, M.J. Ahsan, M. Noushad, Cost-effective and eco-friendly synthesis of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles using fruit’s peel agro-waste extracts: characterization, in vitro antibacterial, antioxidant activities. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 12(3), 244–254 (2019)
E. Gomathi, M. Jayapriya, M. Arulmozhi, Environmental benign synthesis of tin oxide (SnO2) nanoparticles using Actinidia deliciosa (Kiwi) peel extract with enhanced catalytic properties. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 130, 108670 (2021)
R. Priyadarshi, S. Roy, J.-W. Rhim, Enhanced functionality of green synthesized sulfur nanoparticles using kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa) peel polyphenols as capping agents. J. Nanostruct. Chem. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-021-00422-
Tanuja, A. Lagashetty, Synthesis and characterization of silver doped zinc oxide nanoparticle from beetle leaf extract- evaluation of antimicrobial activity against human pathogenic bacteria and fungi. IJRASET 10(5), 2703–2716 (2022). https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2022.42914
Green synthesis of Ag, Zn and Cu nanoparticles from aqueous extract of Spondias mombin leaves and evaluation of their antibacterial activity, African J. Clin. Exp. 21(2), 106–113 (2020). https://doi.org/10.4314/AJCEM.V21I2.4
S. Kunwar et al., Bio-fabrication of Cu/Ag/Zn Nanoparticles and their antioxidant and dye degradation activities. Catalysts (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13050891
M. Pudukudy, Z. Yaakob, Facile synthesis of quasi spherical ZnO nanoparticles with excellent photocatalytic activity. J. Clust. Sci. 26(4), 1187–1201 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-014-0806-1
S.S. Patil et al., Nanostructured microspheres of silver @ zinc oxide: an excellent impeder of bacterial growth and biofilm. J. Nanopart. Res. 16(11), 2717 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2717-3
D.K. Adeyemi, A.O. Adeluola, M.J. Akinbile, O.O. Johnson, G.A. Ayoola, Green synthesis of Ag, Zn and Cu nanoparticles from aqueous extract of Spondias mombin leaves and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. Afr. J. Clin. Exp. Microbiol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.4314/ajcem.v21i2.4
H. Yousaf, A. Mehmood, K.S. Ahmad, M. Raffi, Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications as an alternative antibacterial and antioxidant agents. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 112, 110901 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.110901
N. Jomehzadeh, Z. Koolivand, E. Dahdouh, A. Akbari, A. Zahedi, N. Chamkouri, Investigating in-vitro antimicrobial activity, biosynthesis, and characterization of silver nanoparticles, zinc oxide nanoparticles, and silver-zinc oxide nanocomposites using Pistacia Atlantica Resin. Mater. Today Commun. 27, 102457 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102457
S.M. Mousavi-Kouhi, A. Beyk-Khormizi, M.S. Amiri, M. Mashreghi, M.E. TaghavizadehYazdi, Silver-zinc oxide nanocomposite: from synthesis to antimicrobial and anticancer properties. Ceram. Int. 47(15), 21490–21497 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.04.160
A. Kadam et al., Facile synthesis of Ag–ZnO core–shell nanostructures with enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 61, 78–86 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.12.003
A. Jayachandran, T.R. Aswathy, A.S. Nair, Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Cayratia pedata leaf extract. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports 26, 100995 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.100995
A. Daphedar, T.C. Taranath, Green synthesis of zinc nanoparticles using leaf extract of Albizia saman (Jacq.) Merr. and their effect on root meristems of Drimia indica (Roxb.) Jessop. Caryologia 71(2), 93–102 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.2018.1437980
A. Velidandi, M. Sarvepalli, N.P.P. Pabbathi, R.R. Baadhe, Biogenic synthesis of novel platinum-palladium bimetallic nanoparticles from aqueous Annona muricata leaf extract for catalytic activity. 3 Biotech 11(8), 385 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02935-0
R. Vijayan, S. Joseph, B. Mathew, Eco-friendly synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles with enhanced antimicrobial, antioxidant, and catalytic activities. IET Nanobiotechnol. 12(6), 850–856 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2017.0311
P. Kumar, M. Govindaraju, S. Senthamilselvi, K. Premkumar, Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange dye using silver (Ag) nanoparticles synthesized from Ulva lactuca. Colloids Surf. B 103, 658–661 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.11.022
S. Nayak, L.C. Goveas, R. Selvaraj, S. Mutalik, S.P. Sajankila, Use of Cyclea peltata mediated gold nanospheres for adsorptive degradation of methyl green dye. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 20, 101261 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2022.101261
A.R. Suvarna, A. Shetty, S. Anchan, N. Kabeer, S. Nayak, Cyclea peltata leaf mediated green synthesized bimetallic nanoparticles exhibits methyl green dye degradation capability. BioNanoScience 10(3), 606–617 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-020-00739-9
S. Nayak, S.P. Sajankila, C.V. Rao, A.R. Hegde, S. Mutalik, Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Jatropha curcas seed cake extract and characterization: evaluation of its antibacterial activity. Energy Sour. Part A: Recovery, Util. Environ. Eff. 43(24), 3415–3423 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2019.1632394
S. Zhang, L. Lin, X. Huang, Y.-G. Lu, D.-L. Zheng, Y. Feng, Antimicrobial properties of metal nanoparticles and their oxide materials and their applications in oral biology. J. Nanomater. 2022, e2063265 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2063265
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through the Small Group Research Project under grant number (RGP1/71/44).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AR planned the overall content of the paper. DSI perform all the experimentation work. AR and DSI wrote the manuscript. AS, SA, KC and NFQ review the manuscript and provide suggestions to improve it. All the authors approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Idris, D.S., Roy, A., Subramanian, A. et al. Bio-fabrication of Silver–Zinc Bimetallic Nanoparticles and Its Antibacterial and Dye Degradation Activity. J Inorg Organomet Polym (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02936-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02936-x