Abstract
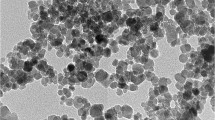
Magnetic nanoparticles occupy a significant class of inorganic nanoparticles with its very promising application in biosensors and bio-imaging. Physical and chemical methods have been used conventionally to prepare magnetic nanoparticles. However, these methods have its own limitations, which redirected recent research towards safe, clean and eco-friendly green synthesis approach. In our study, green magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (FeNP DG) were prepared by using aqueous Desmodium gangeticum root extract as a reducing as well as a capping agent. Nanoparticles used in different biological milieu has to be explored for their toxicity before its application. Thus prepared nanoparticles were evaluated for its nephrotoxicity in Wistar rats (100 mg/kg b.wt), in renal epithelial cells, LLC PK1 (1 mg/ml) and isolated mitochondria (0.25, 0.5, 1 mg/ml) and compared it with the conventionally prepared iron oxide nanoparticles (FeNP Chem). Our study demonstrate that chemically prepared FeNPs are toxic to kidney and its epithelial cells.On the other hand, when the same nanoparticles were prepared by green route (FeNP DG) exhibited minimum toxicity measured via the renal markers in blood and urine along with cytotoxicity assay in LLC PK1 cells. But at mitochondrial level, both FeNP Chem and FeNP DG were found to be toxic to the organelle.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Andreas, R. Georgieva, M. Ladwig, S. Mueller, M. Notter, M. Sittinger, and J. Ringe (2012). Biomaterials 33, (18), 4515.
S. C. McBain, H. H. Yiu, and J. Dobson (2008). Int. J. Nanomed. 3, (2), 169.
M. K. Yu, Y. Y. Jeong, J. Park, S. Park, J. W. Kim, J. J. Min, K. Kim, and S. Jon (2008). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 47, (29), 5362.
N. A. Frey, S. Peng, K. Cheng, and S. Sun (2009). Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, (9), 2532.
M. Mohapatra and S. Anand (2010). Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2, (8), 127.
A. Afkhami and R. Moosavi (2010). J. Hazard. Mater. 174, (1), 398.
M. Tarantash, H. Nosrati, H. Kheiri Manjili, and A. Baradar Khoshfetrat (2018). Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 44, (11), 1895–1903.
H. Nosrati, M. Salehiabar, H. Kheiri Manjili, S. Davaran, and H. Danafar (2018). Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 44, (10), 1668–1678.
M. Salehiabar, H. Nosrati, E. Javani, F. Aliakbarzadeh, H. K. Manjili, S. Davaran, and H. Danafar (2018). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 115, 83–89.
H. Nosrati, A. Mojtahedi, H. Danafar, and H. Kheiri Manjili (2018). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 106, (6), 1646–1654.
H. Nosrati, M. Salehiabar, E. Attari, S. Davaran, H. Danafar, and H. K. Manjili (2018). Appl. Organomet. Chem. 32, (2), e4069.
M. Mahmoudi, S. Laurent, M. A. Shokrgozar, and M. Hosseinkhani (2011). ACS Nano 5, (9), 7263.
N. Singh, G. J. Jenkins, B. C. Nelson, B. J. Marquis, T. G. Maffeis, A. P. Brown, P. M. Williams, C. J. Wright, and S. H. Doak (2012). Biomaterials 33, (1), 163.
M. Sundrarajan and S. Gowri (2011). Chalcogenide Lett. 8, (8), 447.
G. Scarano and E. Morelli (2002). Biometals 15, (2), 145.
A. Meyyappan, A. Shakila Banu, and G. A. Kurian (2015). Int. J Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 7, (13), 70.
C. G. Fraga, B. E. Leibovitz, and A. L. Tappel (1988). Free Rad. Biol. Med. 4, 155.
J. T. Rotruck, A. L. Pope, H. E. Ganther, A. B. Swanson, D. G. Hafeman, and W. G. Hoekstra (1973). Science 179, 588.
B. Chance and N. Oshino (1971). Biochem. J. 122, 225.
C. W. Cheng, L. Y. Chen, C. W. Chou, and J. Y. Liang (2015). J. Photochem. Photobiol., B 148, 262.
S. Morgenstern, R. Flor, G. Kessler, and B. Klein (1965). Anal. Biochem. 13, (1), 149.
T. Mosmann (1983). J. Immunol. Methods 65, 55.
G. A. Kurian, N. Yagnesh, R. S. Kishan, and J. Paddikkala (2008). J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 60, (4), 523.
W. P. Zeijlemaker, D. V. Dervartanian, C. Veeger, and E. C. Slater (1969). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 178, 213.
M. J. Wimmer and J. H. Harrison (1975). J. Biol. Chem. 250, 8768.
M. E. Cerdan, M. A. Serra, N. Lopez-Moratalla, and E. Santiago (1987). Rev. Esp. Fisiol. 43, 13.
M. Alagumira, A. Shakila Banu, and K. A. Gino (2015). Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 7, (1), 70.
M. I. Khan, A. Mohammad, G. Patil, S. A. Naqvi, L. K. Chauhan, and I. Ahmad (2012). Biomaterials 33, (5), 1477.
G. A. Kurian and J. Paddikkala (2009). Indian J. Exp. Biol. 47, (2), 129.
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank Vice Chancellor, SASTRA University. This study was partly supported by grants from the Department of Science and Technology (INSPIRE), New Delhi, India (No: DST/INSPIRE Fellowship/2013/326). We would like to thank Dr. C David Raj for his assistance during animal experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahalakshmi, A., Kurian, G.A. Evaluation of Chemical and Green Synthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles’ Associated Renal Toxicity in Different Experimental Models: A Comparative Study. J Clust Sci 30, 343–350 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-018-01492-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-018-01492-6