Abstract
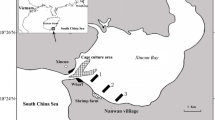
In surface water of the eutrophic Tokyo Bay, the dissolved inorganic phosphorus (DIP) concentration has decreased in recent decades. DIP is generally utilized by phytoplankton; however, under low DIP conditions, phytoplankton utilize dissolved organic phosphorus using alkaline phosphatase, together with bacteria. This study investigated seasonal variation in alkaline phosphatase activity (APA) in the central part of Tokyo Bay during 2013 to understand the P regime in recent years. Water samples were collected monthly from surface (0 m) and bottom (20–25 m) layers at two stations and were filtered through 0.2, 0.7, and 190 μm-pore-sized filters to examine APA in different fractions, approximately corresponding to dissolved components (< 0.2 μm), bacteria (0.2–0.7 μm), and phytoplankton (0.7–190 μm). APA was assayed by a fluorometric method with the addition of 4-methylumbelliferyl-phosphate. Potential maximum APA in total fraction ranged from the undetectable level to 2117 nmol L−1 h−1. The APA in the phytoplankton fraction showed a large contribution to that in the total fraction (69 ± 37%), followed by that in bacterial (17 ± 32%) and dissolved (14 ± 28%) fractions. The total APA was generally higher in the surface layer than in the bottom layer and peaked at the surface in July. Past data on the total APA in the central part of Tokyo Bay also showed peaks at the surface during summer. However, the total APA at the surface in July 2013 was 1–2 orders of magnitude higher than that in July 1973, suggesting that phytoplankton DIP stress has considerably emerged in recent years.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando H, Maki H, Kashiwagi N, Ishii Y (2021) Long-term change in the status of water pollution in Tokyo Bay: recent trend of increasing bottom-water dissolved oxygen concentrations. J Oceanogr 77:843–858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-021-00612-7
Bouman HA, Nakane T, Oka K et al (2010) Environmental controls on phytoplankton production in coastal ecosystems: a case study from Tokyo Bay. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 87:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2009.12.014
Chrost RJ, Siuda W, Albrecht D, Overbeck J (1986) A method for determining enzymatically hydrolyzable phosphate (EHP) in natural waters. Limnol Oceanogr 31:662–667. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1986.31.3.0662
Duhamel S, Björkman KM, Van Wambeke F et al (2011) Characterization of alkaline phosphatase activity in the North and South Pacific Subtropical Gyres: implications for phosphorus cycling. Limnol Oceanogr 55:1414–1425. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2011.56.4.1244
Han M-S, Furuya K, Nemoto T (1992) Species-specific productivity of Skeletonema costatum (Bacillariophyceae) in the inner part of Tokyo Bay. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 79:267–273. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps079267
Hashimoto S, Fujiwara K, Fuwa K (1985) Relationship between alkaline phosphatase activity and orthophosphate in the present Tokyo Bay. J Environ Sci Health 20:781–809. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934528509375258
Hoppe HG (1983) Significance of exoenzymatic activities in the ecology of brackish water: measurements by means of methylumbelliferyl-substrates. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 11:299–308. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps011299
Hoppe HG (2003) Phosphatase activity in the sea. Hydrobiologia 493:187–200. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025453918247
Hoppe HG, Ullrich S (1999) Profiles of ectoenzymes in the Indian Ocean: phenomena of phosphatase activity in the mesopelagic zone. Aquat Microb Ecol 19:139–148. https://doi.org/10.3354/ame019139
Huang B, Hong H (1999) Alkaline phosphatase activity and utilization of dissolved organic phosphorus by algae in subtropical coastal waters. Mar Pollut Bull 39:205–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(99)00006-5
Huber AL, Kidby DK (1984) An examination of the factors involved in determining phosphatase activities in estuarine water. 1: analytical procedures. Hydrobiologia 111:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007374
Ivančić I, Fuks D, Radić T et al (2010) Phytoplankton and bacterial alkaline phosphatase activity in the northern Adriatic Sea. Mar Environ Res 69:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2009.08.004
Kubo A, Hashihama F, Kanda J et al (2019) Long-term variability of nutrient and dissolved organic matter concentrations in Tokyo Bay between 1989 and 2015. Limnol Oceanogr 64:S209–S222. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10796
Kuenzler EJ, Perras JP (1965) Phosphatases of marine algae. Biol Bull 128:271–284. https://doi.org/10.2307/1539555
Kwon HK, Oh SJ, Yang HS (2011) Ecological significance of alkaline phosphatase activity and phosphatase-hydrolyzed phosphorus in the northern part of Gamak Bay, Korea. Mar Pollut Bull 62:2476–2482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.07.027
Labry C, Delmas D, Herbland A (2005) Phytoplankton and bacterial alkaline phosphatase activities in relation to phosphate and DOP availability within the Gironde plume waters (Bay of Biscay). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 318:213–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2004.12.017
Li H, Veldhuis MW, Post AF (1998) Alkaline phosphatase activities among planktonic communities in the northern Red Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 173:107–115. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps173107
Mahaffey C, Reynolds S, Davis CE, Lohan MC (2014) Alkaline phosphatase activity in the subtropical ocean: insights from nutrient, dust and trace metal addition experiments. Front Mar Sci 1:73. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2014.00073
Mather RL, Reynolds SE, Wolff GA et al (2008) Phosphorus cycling in the North and South Atlantic Ocean subtropical gyres. Nat Geosci 1:439–443. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo232
Miyata K, Hattori A (1986) Distribution and seasonal variation of phosphorus in Tokyo Bay. J Oceanogr Soc Jpn 42:241–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02114523
Perry MJ (1972) Alkaline phosphatase activity in subtropical Central North Pacific waters using a sensitive fluorometric method. Mar Biol 15:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00353639
Pettersson K, Jansson M (1978) Determination of phosphatase activity in lake water—a study of methods. Verh Int Verein Limnol 20:1226–1230. https://doi.org/10.1080/03680770.1977.11896677
Sato M, Sakuraba R, Hashihama F (2013) Phosphate monoesterase and diesterase activities in the North and South Pacific Ocean. Biogeosciences 10:7677–7688. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-10-7677-2013
Sebastián M, Niell FX (2004) Alkaline phosphatase activity in marine oligotrophic environments: implications of single-substrate addition assays for potential activity estimations. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 277:285–290. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps277285
Sebastián M, Arístegui J, Montero MF et al (2004a) Alkaline phosphatase activity and its relationship to inorganic phosphorus in the transition zone of the North-western African upwelling system. Prog Oceanogr 62:131–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2004.07.007
Sebastián M, Arístegui J, Montero MF, Niell F (2004b) Kinetics of alkaline phosphatase activity, and effect of phosphate enrichment: a case study in the NW African upwelling region. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 270:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps270001
Strickland JDH, Parsons TR (1972) A practical handbook of seawater analysis, 2nd edn. Bull Fish Res Bd Can, Ottawa, p 310
Suzuki R, Ishimaru T (1990) An improved method for the determination of phytoplankton chlorophyll using N, N-dimethylformamide. J Oceanogr Soc Jpn 46:190–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02125580
Suzumura M, Hashihama F, Yamada N, Kinouchi S (2012) Dissolved phosphorus pools and alkaline phosphatase activity in euphotic zone of the western North Pacific Ocean. Front Microbiol 3:99. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2012.00099
Taga N, Kobori H (1978) Phosphatase activity in eutrophic Tokyo Bay. Mar Biol 49:223–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391134
Yamaguchi H, Nishijima T, Oda A et al (2004) Distribution and variation of alkaline phosphatase activity and phosphatase-hydrolyzable phosphorus in coastal seawaters. Nihon Suisan Gakkaishi 70:333–342. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.70.333[inJapanesewithEnglishabstract]
Yamaguchi T, Sato M, Hashihama F et al (2019) Basin-scale variations in labile dissolved phosphoric monoesters and diesters in the central North Pacific Ocean. J Geophys Res Oceans 124:3058–3072. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JC014763
Yasui-Tamura S, Hashihama F, Ogawa H et al (2020) Automated simultaneous determination of total dissolved nitrogen and phosphorus in seawater by persulfate oxidation method. Talanta Open 2:100016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talo.2020.100016
Yoshimura T, Kudo I (2011) Seasonal phosphorus depletion and microbial responses to the change in phosphorus availability in a subarctic coastal environment. Mar Chem 126:182–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2011.06.003
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the officers, crew, scientists, and students of the Seiyo-Maru cruises for their cooperation at sea. We appreciate the constructive comments of T. Katano, A. Kubo, J. Yoshida, T. Hosaka, and C. Sukigara. This work was financially supported by JSPS KAKENHI Nos. 22710006, 24710004, and 24510009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FH and JK designed the study. SS performed APA assay and P measurements. NH collected Chl a data. FH and SS wrote the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sim, S., Hashihama, F., Horimoto-Miyazaki, N. et al. Seasonal variation in alkaline phosphatase activity in the central part of Tokyo Bay, 2013. J Oceanogr 79, 187–197 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-022-00650-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-022-00650-9