Abstract
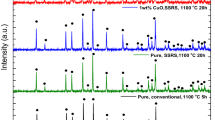
Due to the increasingly urgent safety and energy density concerns of lithium-ion batteries, more and more attention has been attracted by the Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO)-based solid electrolytes with high ion conductivity and chemical stability against Li-metal. However, to prepare the high-quality LLZO ceramic electrolyte with high-ion conductivity and density, there is still a big challenge of the serious “Li-loss” and the abnormal grain growth during the long-time high-temperature sintering process. A novel covered sintering method is put forward to prepare the high-quality Mo-doped LLZO (LLZMO) ceramic electrolyte. The sintering strategy effectively suppresses the Li-loss to obtain the LLZMO dense ceramics with cubic garnet phase and tight grain boundaries. The LLZMO ceramics sintered at lower temperature of 1050 °C for 2 h via the novel covered sintering exhibit high density (ρr = 92.3%) and high-ionic conductivity of 6.08 × 10–4 S cm−1 at 25 °C, which are close to those of LLZO-based ceramics prepared by hot pressing sintering, ultrafast high-temperature sintering (UHS). The novel covered sintering provides an energy-saving, low-cost and high-efficient strategy to prepare the high-quality LLZO-based ceramics electrolyte.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be available on request due to privacy/ethical restrictions.
References
N. Kamaya, K. Homma, Y. Yamakawa, M. Hirayama, R. Kanno, M. Yonemura, T. Kamiyama, Y. Kato, S. Hama, K. Kawamoto, A. Mitsui, A lithium superionic conductor. Nat. Mater. 10, 682–686 (2011)
J.B. Goodenough, K.S. Park, The Li-ion rechargeable battery: a perspective. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 1167–1176 (2013)
L. Ye, X. Li, A dynamic stability design strategy for lithium metal solid state batteries. Nature 593, 218–222 (2021)
N.S. Grundish, J.B. Goodenough, H. Khani, Designing composite polymer electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 30, 100828 (2021)
L. Fan, S.Y. Wei, S.Y. Li, Q. Li, Y.Y. Lu, Recent progress of the solid-state electrolytes for high-energy metal-based batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1702657 (2018)
M.A.T. Marple, T.A. Wynn, D. Cheng, R. Shimizu, H.E. Mason, Y.S. Meng, Local structure of glassy lithium phosphorus oxynitride thin films: a combined experimental and ab initio approach. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 22185–22193 (2020)
S.P. Shao, G. Tang, H.J. Li, L. Zhang, J.C. Zheng, Y. Luo, J.P. Yue, Y. Shi, Z. Chen, Low-temperature fabrication of NASICON-type LATP with superior ionic conductivity. Ceram. Int. 48, 36961–36967 (2022)
J.H.L. Silva, Y.G.S. Alves, A. Almeida, J. Agostinho Moreira, R. Vilarinho, J.C.A. Santos, Y. Leyet, L.M. Jesus, R.S. Silva, Study of the ionic conductivity of Li0.5La0.5TiO3 laser-sintered ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 40, 5619–5625 (2020)
R. Murugan, V. Thangadurai, W. Weppner, Fast lithium-ion conduction in garnet-type Li7La3Zr2O12. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 7778–7781 (2007)
R.S. Chen, Q.H. Li, X.Q. Yu, L.Q. Chen, H. Li, Approaching practically accessible solid-state batteries: stability issues related to solid electrolytes and interfaces. Chem. Rev. 120, 6820–6877 (2020)
H. Zheng, G. Li, J. Liu, S. Wu, X. Zhang, Y. Wu, H. Zhu, X. Huang, H. Liu, H. Duan, A rational design of garnet-type Li7La3Zr2O12 with ultrahigh moisture stability. Energy Storage Mater. 49, 278–290 (2022)
L. Yang, Q. Dai, L. Liu, D. Shao, K. Luo, S. Jamil, H. Liu, Z. Luo, B. Chang, X. Wang, Rapid sintering method for highly conductive Li7La3Zr2O12 ceramic electrolyte. Ceram. Int. 46, 10917–10924 (2020)
H.M. Kasper, Series of rare earth garnets Ln3+3M2Li+3O12(M = Te, W). Inorg. Chem. 8, 1000–1002 (1969)
V. Thangadurai, H. Kaack, W.J.F. Weppner, Novel fast lithium-ion conduction in garnet-type Li5La3M2O12(M = Nb, Ta). J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 86, 437–440 (2003)
Y. Jin, P.J. McGinn, Al-doped Li7La3Zr2O12 synthesized by a polymerized complex method. J. Power Sources 196, 8683–8687 (2011)
J.L. Allen, J. Wolfenstine, E. Rangasamy, J. Sakamoto, Effect of substitution (Ta, Al, Ga) on the conductivity of Li7La3Zr2O12. J. Power Sources 206, 315–319 (2012)
D. Rettenwander, A. Welzl, L. Cheng, J. Fleig, M. Musso, E. Suard, M.M. Doeff, G.J. Redhammer, G. Amthauer, Synthesis, crystal chemistry, and electrochemical properties of Li7−2xLa3Zr2−xMoxO12 (x = 0.1-0.4): stabilization of the cubic garnet polymorph via substitution of Zr4+ by Mo6+. Inorg. Chem. 54, 10440–10449 (2015)
C. Wang, W. Ping, Q. Bai, H. Cui, R. Hensleigh, R. Wang, A.H. Brozena, Z. Xu, J. Dai, Y. Pei, C. Zheng, G. Pastel, J. Gao, X. Wang, H. Wang, J.C. Zhao, B. Yang, X. Zheng, J. Luo, Y. Mo, B. Dunn, L. Hu, A general method to synthesize and sinter bulk ceramics in seconds. Science 368, 521–526 (2020)
X. Zhou, L. Huang, O. Elkedim, Y. Xie, Y. Luo, Q. Chen, Y. Zhang, Y. Chen, Sr2+ and Mo6+ co-doped Li7La3Zr2O12 with superior ionic conductivity. J. Alloys Compd. 891, 161906 (2021)
X. Liu, Y. Li, T. Yang, Z. Cao, W. He, Y. Gao, J. Liu, G. Li, Z. Li, High lithium ionic conductivity in the garnet-type oxide Li7−2xLa3Zr2−xMoxO12 (x = 0-0.3) ceramics by sol-gel method. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100, 1527–1533 (2017)
Y. Li, T. Yang, W. Wu, Z. Cao, W. He, Y. Gao, J. Liu, G. Li, Effect of Al-Mo codoping on the structure and ionic conductivity of sol-gel derived Li7La3Zr2O12 ceramics. Ionics 24, 3305–3315 (2018)
S. Ramakumar, C. Deviannapoorani, L. Dhivya, L.S. Shankar, R. Murugan, Lithium garnets: synthesis, structure, Li+ conductivity, Li+ dynamics and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 88, 325–411 (2017)
R. Murugan, V. Thangadurai, W. Weppner, Fast lithium ion conduction in garnet type Li7La3Zr2O12. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 46, 7778–7781 (2007)
X. Huang, Y. Lu, Z. Song, K. Rui, Q. Wang, T. Xiu, M.E. Badding, Z. Wen, Manipulating Li2O atmosphere for sintering dense Li7La3Zr2O12 solid electrolyte. Energy Storage Mater. 22, 207–217 (2019)
L.C. Zhang, J.F. Yang, Y.X. Gao, X.P. Wang, Q.F. Fang, C.H. Chen, Influence of Li3BO3 additives on the Li+ conductivity and stability of Ca/Ta-substituted Li6.55(La2.95Ca0.05)-(Zr1.5Ta0.5)O12 electrolytes. J. Power Sources 355, 69–73 (2017)
C. Wang, Z.G. Liu, P.P. Lin, X. Xu, F.G. Lu, J.J. Xu, Y.H. Shi, P. He, T.S. Lin, Impacts of 3Li2O-2GeO2 melt on fabrication and electrical performance of novel LLZTO@Li4GeO4/Li2O composite electrolytes. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 42, 2290–2298 (2022)
N.C. Rosero-Navarro, T. Yamashita, A. Miura, M. Higuchi, K. Tadanaga, Effect of sintering additives on relative density and Li-ion conductivity of Nb-doped Li7La3Zr2O12 solid electrolyte. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100, 276–285 (2017)
B. Xu, W. Li, H. Duan, H. Wang, Y. Guo, H. Li, H. Liu, Li3PO4-added garnet-type Li6.5La3Zr1.5Ta0.5O12 for Li-dendrite suppression. J. Power Sources 354, 68–73 (2017)
Z.Y. Huang, K. Liu, L.H. Chen, Y.R. Lu, Y.T. Li, C.A. Wang, Sintering behavior of garnet-type Li6.4La3Zr1.4Ta0.6O12 in Li2CO3 atmosphere and its electrochemical property. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 14, 921–927 (2017)
Y. Wang, W. Lai, Phase transition in lithium garnet oxide ionic conductors Li7La3Zr2O12: the role of Ta substitution and H2O/CO2 exposure. J. Power Sources 275, 612–620 (2015)
H. Huo, J. Luo, V. Thangadurai, Li2CO3: a critical issue for developing solid garnet batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 5, 252–262 (2019)
S. Yu, R.D. Schmidt, R. Garcia-Mendez, E. Herbert, N.J. Dudney, J.B. Wolfenstine, J. Sakamoto, D.J. Siegel, Elastic properties of the solid electrolyte Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO). Chem. Mater. 28, 197–206 (2016)
Y. Zhang, F. Chen, R. Tu, Q. Shen, L. Zhang, Field assisted sintering of dense Al substituted cubic phase Li7La3Zr2O12 solid electrolytes. J. Power Sources 268, 960–964 (2014)
M.M. Ahmad, Enhanced lithium ionic conductivity and study of the relaxation and giant dielectric properties of spark plasma sintered Li5La3Nb2O12 nanomaterials. Ceram. Int. 41, 6398–6408 (2015)
S.W. Baek, J.M. Lee, T.Y. Kim, M.S. Song, Y. Park, Garnet related lithium ion conductor processed by spark plasma sintering for all solid state batteries. J. Power. Sources 249, 197–206 (2014)
W. Zhang, C. Sun, Effects of CuO on the microstructure and electrochemical properties of garnet-type Li6.3La3Zr1.65W0.35O12 solid electrolyte. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 135, 109080–109082 (2019)
X. Liu, Y. Jiang, X. Cheng, R. Yan, X. Zhu, Reduced synthesis temperature and significantly enhanced ionic conductivity for Li6.1Ga0.3La3Zr2O12 electrolyte prepared with sintering aid CuO. Ionics 28, 507105080 (2022)
C. Li, A. Ishii, L. Roy, D. Hitchcock, Y. Meng, K. Brinkman, Solid-state reactive sintering of dense and highly conductive Ta-doped Li7La3Zr2O12 using CuO as a sintering aid. J. Mater. Sci. 55, 16470–16481 (2020)
C. Zheng, J. Su, Z. Song, T. Xiu, J. Jin, M.E. Badding, Z. Wen, Sintering promotion and electrochemical performance of garnet-type electrolyte with Li2CuO2 additive. J. Alloys Compd. 933, 167810 (2023)
X. Zhang, X. Guan, Y. Zhang, W. Zhang, Q. Shen, On the interfacial properties of the garnet-type electrolyte ceramic pellets of cubic Li6.4La3Zr1.4Ta0.6O12: a comprehensive improvement of the sintering additive of Li-ion conducting LiCl. J. Power Sources 556, 232459 (2023)
Y. Tang, Z. Luo, T. Liu, P. Liu, Z. Li, A. Lu, Effects of B2O3 on microstructure and ionic conductivity of Li6.5La3Zr1.5Nb0.5O12 solid electrolyte. Ceram. Int. 43, 11879–11884 (2017)
P. Wakudkar, A.V. Deshpande, Effect of Li4SiO4 addition in Li6.22Al0.16La3Zr1.7Ta0.3O12 garnet type solid electrolyte for lithium ion battery application. Ceram. Int. 45, 20113–20120 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52102126) and Opening Testing Funds for the Valuable Equipment of Fuzhou University (Grant No. 2023T008).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52102126), and Opening Testing Funds for the Valuable Equipment of Fuzhou University (Grant No. 2023T008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zonggui Gong: investigation, writing—original draft. Wang Nanlan: data curation, writing—original draft. Haoxuan Guo: investigation, data curation. Peishu Zhu: data curation, conceptualization. Qijing Wang: investigation. Hang Yu: investigation. Yu Zhang: data curation. Min Gao: funding acquisition, writing—review & editing. Xinghua Zheng, conceptualization, supervision, writing—review & editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, Z., Wang, N., Guo, H. et al. Sintering mechanism and greatly enhanced ionic conductivity of Mo-doped Li7La3Zr2O12 ceramics via a novel covered sintering. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 670 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12430-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12430-w