Abstract
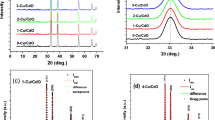
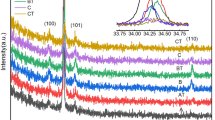
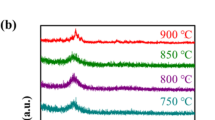
Strontium ferrite (SrFe\(_{12}\)O\(_{19}\)) films on alumina substrate were prepared using DC sputtering technique. The SrFe\(_{12}\)O\(_{19}\) hexaferrite target was sputtered at 100-watt power at a 24 sccm flow rate of argon gas on the alumina substrates. A series of films were prepared with different sputtering times and calcination temperature durations in the form of Series B, and Series E. The structural, morphological, optical, and magnetic properties of prepared SrM films were investigated at room temperature using FTIR, XRD, SEM, EDS, UV–Vis, Raman, and VSM measurements, respectively. The XRD analysis revealed the formation of the M-phase (hexagonal) along with the peaks corresponding to the alumina substrate. The film samples exhibited morphology with interconnected grains, which have a structure similar to porous fiber. The UV–VIS spectra show a sharp rise from 400 nm giving rise to bandgap, a red shift is observed with calcination duration. Raman spectra of all film samples showed nine Raman-active modes: \(4A_{1\text {g}}\) and \(3E_{1\text {g}}\) and \(2E_{2\text {g}}\). M–H loops analysis was carried out of the films for both in-plane and out-of-plane orientation of the films. M\(_s\) and H\(_c\) values varied for both the series B and E with thickness and calcination time. The resulting films show good magnetic properties, which makes them appropriate for utilisation in various applications like data storage, EMI shielding, and optoelectronic applications, etc.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
G.D. Soria, J.F. Marco, A. Mandziak, S. Sánchez-Cortés, M. Sánchez-Arenillas, J.E. Prieto, J. Dávalos, M. Foerster, L. Aballe, J. López-Sánchez, J.C. Guzmán-Mínguez, C. Granados-Miralles, J. Figuera, A. Quesada, Influence of the growth conditions on the magnetism of SrFe\(_{12}\)O\(_{19}\) thin films and the behavior of Co/SrFe\(_{12}\)O\(_{19}\) bilayers. J. Phys. D 53(34), 344002 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ab8d70
K. Strnat, G. Hoffer, J. Olson, W. Ostertag, J.J. Becker, A family of new cobalt-base permanent magnet materials. J. Appl. Phys. 38(3), 1001–1002 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1709459
K.J. Strnat, Chapter 2 rare earth-cobalt permanent magnets, in Handbook of Ferromagnetic Materials (Elsevier, 1988), pp. 131–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1574-9304(05)80077-x
B. Sprecher, Y. Xiao, A. Walton, J. Speight, R. Harris, R. Kleijn, G. Visser, G.J. Kramer, Life cycle inventory of the production of rare earths and the subsequent production of NdFeB rare earth permanent magnets. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48(7), 3951–3958 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/es404596q
T.-S. Chin, Permanent magnet films for applications in microelectromechanical systems. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 209(1–3), 75–79 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-8853(99)00649-6
E.W. Gorter, Saturation magnetization of some ferrimagnetic oxides with hexagonal crystal structures. Proc. IEE B Radio Electron. Eng. 104(5S), 255–260 (1957). https://doi.org/10.1049/pi-b-1.1957.0042
R.C. Pullar, Hexagonal ferrites: a review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 57(7), 1191–1334 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2012.04.001. (cited By 1696)
M.M. Hessien, M.M. Rashad, K. El-Barawy, Controlling the composition and magnetic properties of strontium hexaferrite synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320(3–4), 336–343 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2007.06.009
G.D. Soria, P. Jenus, J.F. Marco, A. Mandziak, M. Sanchez-Arenillas, F. Moutinho, J.E. Prieto, P. Prieto, J. Cerda, C. Tejera-Centeno, S. Gallego, M. Foerster, L. Aballe, M. Valvidares, H.B. Vasili, E. Pereiro, A. Quesada, J. Figuera, Strontium hexaferrite platelets: a comprehensive soft X-ray absorption and Mossbauer spectroscopy study. Sci. Rep. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-48010-w
A. Ghasemi, A. Morisako, Static and high frequency magnetic properties of Mn-Co-Zr substituted Ba-ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 456(1–2), 485–491 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.02.101
S.M. Masoudpanah, S.A.S. Ebrahimi, Synthesis and characterization of nanostructured strontium hexaferrite thin films by the sol-gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324(14), 2239–2244 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.02.109
N. Matsushita, M. Ichinose, S. Nakagawa, M. Naoe, Preparation and characteristics of Co-Zn ferrite rigid disks without protective layers for high density recording. IEEE Trans. Magn. 34(4), 1639–1641 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1109/20.706641
Y. Slimani, M.A. Almessiere, D.S. Klygach, A. Baykal, T.I. Zubar, S.V. Trukhanov, S. Caliskan, A.V. Trukhanov, M. Amir, Structural, magnetic, and microwave features of Sc3+ ions substituted Sr0.5Ba0.5Fe12O19 nanohexaferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 976, 173138 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.173138
M.S. Yuan, H.L. Glass, L.R. Adkins, Epitaxial barium hexaferrite on sapphire by sputter deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 53(4), 340–341 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.100601
J.D. Adam, S.V. Krishnaswamy, S.H. Talisa, K.C. Yoo, Thin-film ferrites for microwave and millimeter-wave applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 83(1–3), 419–424 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-8853(90)90570-g
M. Matsumoto, A. Morisako, T. Haeiwa, K. Naruse, T. Karasawa, Ba-ferrite films prepared by sol-gel pyrolysis method. IEEE Transl. J. Magn. Jpn. 6(8), 648–653 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1109/tjmj.1991.4565229
E. Fujii, H. Torii, M. Aoki, Preparation of spinel ferrite thin films by plasma assisted MO-CVD. IEEE Transl. J. Magn. Jpn. 4(8), 512–517 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1109/tjmj.1989.4564041
C.A. Carosella, D.B. Chrisey, P. Lubitz, J.S. Horwitz, P. Dorsey, R. Seed, C. Vittoria, Pulsed laser deposition of epitaxial BaFe\(_{12}\)O\(_{19}\) thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 71(10), 5107–5110 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.350614
P.C. Dorsey, S.E. Bushnell, R.G. Seed, C. Vittoria, Epitaxial yttrium iron garnet films grown by pulsed laser deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 74(2), 1242–1246 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.354927
A. Lisfi, M. Guyot, R. Krishnan, M. Porte, P. Rougier, V. Cagan, Microstructure and magnetic properties of spinel and hexagonal ferrimagnetic films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 157–158, 258–259 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-8853(95)01246-x
M. Mohebbi, K. Ebnabbasi, C. Vittoria, First observation of magnetoelectric effect in M-type hexaferrite thin films. J. Appl. Phys. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4795721
S. Anjum, M.S. Rafique, M. Khaleeq-ur-Rahman, K. Siraj, A. Usman, S.I. Hussain, S. Naseem, Investigation of induced parallel magnetic anisotropy at low deposition temperature in Ba-hexaferrites thin films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324(5), 711–716 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.08.059
J. Liu, Z. Dong, Z. Zhang, R. Sun, M. Chen, H. Wang, Z. Zhang, M. Zhang, X. Jia, C. Zhi, The SiO2 on the surface of BaFe12O19 to prepare flexible films with excellent microwave absorption properties. J. Market. Res. 21, 4674–4687 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.11.019
F. Wang, D. Zhang, Y. Zhang, H. Li, S. Yang, Q. Yang, H. Zhang, Effect of annealing temperature on the properties of BaFe12O19 thin films deposited on GGG (111) substrates by pulsed laser deposition. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 580, 170915 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2023.170915
L.V. Saraf, S.E. Lofland, A.V. Cresce, S.M. Bhagat, R. Ramesh, Structural and ferromagnetic resonance characteristics of BaFe12O19 films with minimal linewidths. Appl. Phys. Lett. 79(3), 385–387 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1385348
H. Köçkar, N. Kaplan, Single crystal martensitic phase of structural properties-related magnetic behaviour of FeCrNi thin films: in-plane magnetic anisotropy under different substrate rotation speeds. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31(15), 12823–12829 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03835-4
M.M. Haque, M. Huq, M.A. Hakim, Densification, magnetic and dielectric behaviour of Cu-substituted Mg-Zn ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 112(2), 580–586 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.05.097. (cited By 129)
Coates, J. (2006). Interpretation of infrared spectra, a practical approach. in Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry, ed. by R.A. Meyers, M.L. McKelvy. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470027318.a5606J
H. Kojima, Chapter 5 fundamental properties of hexagonal ferrites with magnetoplumbite structure, in Handbook of Ferromagnetic Materials, vol. 3 (Elsevier, 1982), pp. 305–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1574-9304(05)80091-4
S.K. Godara, Ravleen, B. Kaur, V. Kaur, A. Kumar Sood, P. Singh Malhi, G. Ram Bhadu, I. Pushkarna, M. Singh, Characterization of M-type barium hexaferrite synthesized using potatoes as natural fuel. Mater. Today Proc. 28, 1–3 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.12.056. (Cited by 9)
R.D. Waldron, Infrared spectra of ferrites. Phys. Rev. 99(6), 1727–1735 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.99.1727. (cited By 1965)
T. Gupta, C.C. Chauhan, A.R. Kagdi, S.S. Meena, R.B. Jotania, C. Singh, C.B. Basak, Investigation on structural, hysteresis, Mössbauer properties and electrical parameters of lightly erbium substituted X-type Ba\(_2\)Co\(_2\)Er\(_x\)Fe\(_{28-x}\)O\(_{46}\) hexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 46(6), 8209–8226 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.12.049. (cited By 14)
Y. Zhu, A. Chen, H. Zhou, W. Zhang, J. Narayan, J.L. MacManus-Driscoll, Q. Jia, H. Wang, Research updates: epitaxial strain relaxation and associated interfacial reconstructions: the driving force for creating new structures with integrated functionality. APL Mater. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4828936
R.S. Alam, M. Moradi, H. Nikmanesh, J. Ventura, M. Rostami, Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of BaMg\(_{x/2}\)Mn\(_{x/2}\)Co\(_x\)Ti\(_2x\)Fe\(_{12-4x}\)O\(_{19}\) hexaferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 402, 20–27 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.11.038
P. Kaur, S.K. Chawla, S.S. Meena, S.M. Yusuf, S.B. Narang, Synthesis of Co-Zr doped nanocrystalline strontium hexaferrites by sol-gel auto-combustion route using sucrose as fuel and study of their structural, magnetic and electrical properties. Ceram. Int. 42(13), 14475–14489 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.06.053
P.A. Prashanth, R.S. Raveendra, R.H. Krishna, S. Ananda, N.P. Bhagya, B.M. Nagabhushana, K. Lingaraju, H.R. Naika, Synthesis, characterizations, antibacterial and photoluminescence studies of solution combustion-derived \(\alpha \)-Al\(_2\)O\(_3\) nanoparticles. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 3(3), 345–351 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jascer.2015.07.001
R. Dom, P.H. Borse, C.R. Cho, J.S. Lee, S.M. Yu, J.H. Yoon, T.E. Hong, E.D. Jeong, H.G. Kim, Synthesis of SrFe\(_{12}\)O\(_{19}\) and Sr\(_7\)Fe\(_{10}\)O\(_{22}\) systems for visible light photocatalytic studies. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 13(4), 451–456 (2012). (cited By 16)
J. Tauc, R. Grigorovici, A. Vancu, Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Physica Status Solidi (b) 15(2), 627–637 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.19660150224. (cited By 7992)
M. Khojaste khoo, P. Kameli, Structure and magnetization of strontium hexaferrite (SrFe\(_{12}\)O\(_{19}\)) films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Front. Mater. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2021.717251
D. Anadkat, C. Badampudi, A. Gor, A.V. Sanchela, Investigation of frequency dependent dielectric properties of La-doped BaSnO3-ZnSnO3 solid-solutions. J. Alloys Compd. 958, 170350 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.170350
J. Kreisel, G. Lucazeau, H. Vincent, Raman spectra and vibrational analysis of BaFe\(_{12}\)O\(_{19}\) hexagonal ferrite. J. Solid State Chem. 137(1), 127–137 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1006/jssc.1997.7737
X. Zhang, X.-F. Qiao, W. Shi, J.-B. Wu, D.-S. Jiang, P.-H. Tan, Phonon and Raman scattering of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides from monolayer, multilayer to bulk material. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44(9), 2757–2785 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cs00282b
Q. Wu, Z. Yu, H. Hao, Y. Chu, H. Xie, The effect of pH value on strontium hexaferrites: microstructure and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28(17), 12768–12775 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7104-2
M. Sivakumar, A. Gedanken, W. Zhong, Y.W. Du, D. Bhattacharya, Y. Yeshurun, I. Felner, Nanophase formation of strontium hexaferrite fine powder by the sonochemical method using Fe(Co)\(_5\). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 268(1–2), 95–104 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-8853(03)00479-7
M. Farid, I. Ahmad, G. Murtaza, M. Kanwal, I. Ali, Electric modulus properties of praseodymium substituted copper ferrites. J. Ovonic Res. 12(3), 137–146 (2016)
P.R. Graves, C. Johnston, J.J. Campaniello, Raman scattering in spinel structure ferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 23(11), 1651–1660 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-5408(88)90255-3
D. Bersani, P.P. Lottici, A. Montenero, Micro-Raman investigation of iron oxide films and powders produced by sol-gel syntheses. J. Raman Spectrosc. 30(5), 355–360 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-4555(199905)30:5<355::aid-jrs398>3.0.co;2-c}
A. Ataie, I.R. Harris, C.B. Ponton, Magnetic properties of hydrothermally synthesized strontium hexaferrite as a function of synthesis conditions. J. Mater. Sci. 30(6), 1429–1433 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00375243
Y. Wang, Q. Li, C. Zhang, B. Li, Effect of Fe/Sr mole ratios on the formation and magnetic properties of SrFe\(_{12}\)O\(_{19}\) microtubules prepared by solgel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321(19), 3368–3372 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.05.066
J. Burk, I. Drbohlav, Z. Frait, K. Knizek, R. Kuzel, K. Kouril, Oriented SrFe\(_{12}\)O\(_{19}\) thin films prepared by chemical solution deposition. J. Solid State Chem. 184(11), 3085–3094 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2011.09.024
H. Kojima, Fundamental properties of hexagonal ferrites with magnetoplumbite. Structure 3, 305–391 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1574-9304(05)80091-4
S.R. Shinde, A.S. Ogale, S.B. Ogale, S. Aggarwal, V. Novikov, E.D. Williams, R. Ramesh, Self-organized pattern formation in the oxidation of supported iron thin films. I. An experimental study. Phys. Rev. B (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.64.035408
E.C. Stoner, E. Wohlfarth, A mechanism of magnetic hysteresis in heterogeneous alloys. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 240(826), 599–642 (1948)
A.R. Abuzir, S.A. Salman, Fabrication and micromagnetic modeling of barium hexaferrite thin films by RF magnetron sputtering. Results Phys. 8, 587–591 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.01.003
A.V. Singh, B. Khodadadi, J.B. Mohammadi, S. Keshavarz, T. Mewes, D.S. Negi, R. Datta, Z. Galazka, R. Uecker, A. Gupta, Bulk single crystal-like structural and magnetic characteristics of epitaxial spinel ferrite thin films with elimination of antiphase boundaries. Adv. Mater. 29(30), 1701222 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201701222
Acknowledgements
C. C. Chauhan is thankful to GUJCOST (GUJCOST/2020-21/879 dated 13th August 2020), Gandhinagar, India for the financial support. R. B. Jotania is grateful to UGC, New Delhi, India for DRS-SAP-Phase-II (F.530/10/DRS/2018 (SAP-I) dated 17th April 2018) and DST, India for DST-FIST (level-I, No. SR/FST/PSI-198/2014) grants.
Funding
Chetna C. Chauhan reports financial support was provided by GUJCOST, Gandhinagar, Gujarat, India. Rajshree B. Jotania reports partial financial support was provided by University Grants Commission, New Delhi, India and department of Science and Technology, India under DRS-SAP (Phase-II) and DST-FIST (level-I) project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Abhishek A. Gor: graphical abstract preparation, samples preparation, characterization, data curation and analysis, software, graphics, original draft preparation, conceptualization. Ankita Singh: characterization, data curation, analysis, graphics, draft reading and modification. Niranjan M. Devashrayee: draft reading, modification, graphics, supervision. Chetna C. Chauhan: samples characterizations, supervisions, graphs modifications, data curation and analysis, draft modifications, conceptualization. Rajshree B. Jotania: data curation, samples characterization, draft reading, writing and modification, final manuscript checking.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in present paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gor, A.A., Singh, A., Devashrayee, N.M. et al. Effect of sputtering time and calcination temperature duration on the structural, optical, and magnetic properties of DC sputtered SrM films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 584 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12298-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12298-w