Abstract
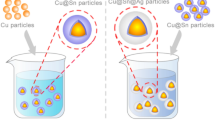
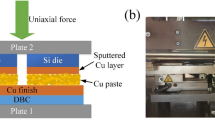
This paper presents a high-temperature-resistant preform based on Cu@In@Ag particles that can be used as a die attach material for high-power devices, using an electroless method to achieve the preparation of core–shell structure particles. Indium has a lower melting point of 156.6 °C and can be completely consumed to form intermetallic compounds of Cu2In, Ag9In4, and Ag3In, which will raise the melting point of the solder joint to over 400 °C. The silver coating is intended to enhance the oxidation resistance of the Cu@In particles and to improve the service reliability of the solder joint. It was demonstrated that high-temperature-resistant solder joints could be obtained by reflowing at 200 °C for 15 min under a pressure of 10 MPa. The shear strengths of solder joints were 29.70 MPa and 21.85 MPa at 25 °C and 300 °C, respectively. The thermal and electrical properties of the solder joints after reflow composed of Cu@In@Ag core–shell particles were tested and the thermal conductivity was 79.02 W/m K and 58.64 W/m K at 30 °C and 250 °C, respectively. Great electrical and thermal conductivity and high shear strength at high temperatures result in high-temperature reliability. As a high-temperature-resistant die attachment material, it has the potential to be used in die attachment in high-power equipment modules.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors are in agreement with the research data policy. The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
R.W. Johnson, J.L. Evans, P. Jacobsen, J.R.R. Thompson, M. Christopher, IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 27, 164–176 (2004)
J. Hornberger et al., IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings (IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, 2004), pp. 2538–2555
T. Nomura, M. Masuda, N. Ikeda, S. Yoshida, IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 23, 692–697 (2008)
H.S. Chin, K.Y. Cheong, A.B. Ismail, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 41, 824–832 (2010)
M.D. Mathew, H. Yang, S. Movva, K.L. Murty, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36A, 99–105 (2005)
J.B. Nysaether, Z.H. Lai, J.H. Liu, IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 23, 743–749 (2000)
J. Wang, S. Xue, P. Zhang, P. Zhai, Y. Tao, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 9065–9086 (2019)
N. Jiang et al., Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 20, 876–901 (2019)
D.G. Ivey, Micron 29, 281–287 (1998)
J.M. Song, H.Y. Chuang, Z.M. Wu, J. Electron. Mater. 35, 1041–1049 (2006)
H.J. Jiang, K.S. Moon, J.X. Lu, C.P. Wong, J. Electron. Mater. 34, 1432–1439 (2005)
Q. Wang, S. Zhang, T. Lin, P. Zhang, P. He, K.W. Paik, Prog. Nat. Sci.: Mater. Int. 31, 129–140 (2021)
S. Zhang et al., J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 9171–9183 (2019)
R. Khazaka, L. Mendizabal, D. Henry, J. Electron. Mater. 43, 2459–2466 (2014)
K.S. Siow, J. Alloys Compd. 514, 6–19 (2012)
T. Wang, X. Chen, G.Q. Lu, G.Y. Lei, J. Electron. Mater. 36, 1333–1340 (2007)
Y. Li, H. Jing, Y. Han, L. Xu, G. Lu, J. Electron. Mater. 45, 3003–3012 (2016)
C. Chen, C. Choe, Z. Zhang, D. Kim, K. Suganuma, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 14335–14346 (2018)
M. Cherrington, T.C. Claypole, D. Deganello, I. Mabbett, T. Watson, D. Worsley, J. Mater. Chem. 21, 7562–7564 (2011)
Y. Mei, Y. Cao, G. Chen, X. Li, G.Q. Lu, X. Chen, IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 13, 258–265 (2013)
Q. Wang, S. Zhang, G. Liu, T. Lin, P. He, J. Alloys Compd. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153184
S. Zhang, Q. Wang, T. Lin, P. Zhang, P. He, K.W. Paik, J. Manuf. Processes 62, 546–554 (2021)
B.M. Amoli, S. Gumfekar, A. Hu, Y.N. Zhou, B. Zhao, J. Mater. Chem. 22, 20048–20056 (2012)
J. Bultitude, J. McConnell, C. Shearer, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 9236–9242 (2015)
N.S. Bosco, F.W. Zok, Acta Mater. 53, 2019–2027 (2005)
B.S. Lee, S.K. Hyun, J.W. Yoon, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 7827–7833 (2017)
X. Xie et al., J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 18302–18310 (2018)
T. Hu, H. Chen, M. Li, Mater. Des. 108, 383–390 (2016)
J. Liu et al., J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 14703–14714 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2019A1515011844), and the Opening Project of Science and Technology on Reliability Physics and Application Technology of Electronic Component Laboratory (No. ZHD201801), and Preliminary Research Project of Equipment Development Department of the Central Military Commission (No.31512050201).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, XM; Writing—review and editing, XM; Conceptualization, JL; Investigation, FY; Data curation, XF; Visualization, CH; Supervision, HC; Project administration, ML.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
We declare that the study follows accepted principles of ethical and professional conduct.
Research involving human and animal participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, X., Liu, J., Yu, F. et al. A high-temperature-resistant die attach material based on Cu@In@Ag particles for high-power devices. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 5599–5612 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07747-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07747-3