Abstract
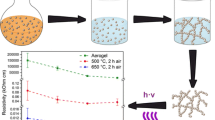
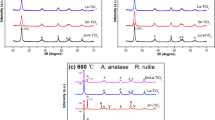
High purity antimony doped tin oxide (ATO) aerogel nanoparticles with various concentrations of Sb have been successfully synthesized using modified sol–gel method. In this process, hydrolysis was slowly released and followed by a thermal drying in supercritical conditions of ethanol. The aim of this study is to enhance the properties of nanoparticles with low doping concentration and low cost. The structural, morphological, optical and electrical properties were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Raman spectroscopy, UV–Vis–IR spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and impedance spectroscopy, respectively. We show that ATO aerogels have a polycrystalline tetragonal rutile structure with a highly (110) plane preferred orientation. The grain sizes are in the range of 13–23 nm, dependending on the elaboration conditions. Raman spectra reveals fundamental peaks at 483, 633, and 770 cm− 1, corresponding to the Eg, A1g and B2g vibration modes, respectively, in a good agreement with those for the rutile bulk SnO2. The optical band gap of tin oxide increases slightly from 3.88 to 3.94 eV with the increase of Sb content. Impedance spectroscopy results indicate that the electrical properties are strongly dependent on temperature and doping rate. All results suggested that the as-prepared ATO nanoparticles were good quality material for thin film solar cell applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Tan, L. Wang, Y. Wang, J. Nanomater. 10 (2011)
D.S. Ginley, Handbook of Transparent Conductors. (Springer, New York, 2010)
Ç. Kılıç, A. Zunger, Phys. Rev. lett. 88, 095501 (2002)
R.D. Sakhare, G.D. Khuspe, S.T. Navale, R.N. Mulik, M.A. Chougule, R.C. Pawar, C.S. Lee, S. Sen, V.B. Patil, J. Alloys Compd. 563, 300 (2013)
A.A. Zhukova, M.N. Rumyantseva, V.B. Zaytsev, A.V. Zaytseva, A.M. Abaku-mov, A.M. Gaskov, J. Alloys Compd. 565, 6 (2013)
S. Balaji, R. Vasuki, D. Mutharasu, J. Alloys Compd. 554, 25 (2013)
C. Karunakaran, S. Sakthi Raadha, P. Gomathisankar, J. Alloys Compd. 549, 269 (2013)
E. Elangovan, K. Ramamurthi, Appl. Surf. Sci. 249, 183 (2005)
C. Karunakaran, S. Sakthi Raadha, P. Gomathisankar, J. Alloys Compd. 549, 269 (2011)
N. Talebian, F. Jafarinezhad, Ceram. int. 39, p. 8311 (2013)
X. Zhong, B. Yang, X. Zhang, J. Jia, G. Yi, Particuology 10, 365 (2012)
F. Bai, Y. He, P. He, Y. Tang, Z. Jia, Mater. Lett. 60, 3126 (2006)
Y. Li, J. Wang, B. Feng, K. Duan, J. Weng, J. Alloys Compd. 634, 37 (2015)
L. Lili, M. Liming, D. Xuechen, Mater. Res. Bull. 41, 541 (2006)
H. Huang, M. Ng, Y. Wu, L. Kong, Mater. Design. 88, p. 384 (2015)
M. Seo, Y. Akutsu, H. Kagemoto, Ceram. Int. 33, 625 (2007)
J. Kong, H.M. Deng, P.X. Yang, J.H. Chu, Mater. Chem. Phys. 114, 854 (2009)
C. Terrier, J.P. Chatelon, J.A. Roger, R. Berjoan, C. Dubois, J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 10, 75 (1997)
T. Krishnakumar, R. Jayaprakash, N. Pinna, A.R. Phani, M. Passacantando, S. Santucci, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 70, 993 (2009)
E. Abdelkader, L. Nadjia, B. Naceur, B. Noureddine, J. Alloys Compd. 679, 408 (2016)
V.G. Kravets, Opt Spectrosc. 103, 766 (2007)
G.K. Williamson, W.K. Hall, Acta Metall. 1, 22 (1953)
A.S. Riad, S.A. Mahmoud, A.A. Ibrahim, Physica B 296, 319 (2001)
Y. Li, J. Wang, B. Feng, K. Duan, J. Weng, J. Alloys Compd. 634, 37 (2015)
B. Zhang, Y. Tian, J.X. Zhang, W. Cai, Mater. Lett. 65, 1204 (2011)
Q.-P. Tran, J.-S. Fang, T.-S. Chin, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process 40, 664 (2015)
Z.Y. Banyamin, P.J. Kelly, G. West, J. Boardman, Coatings 4, 732 (2014)
J.M. Xu, L. Li, S. Wang, H.L. Ding, Y.X. Zhang, G.H. Li, Cryst. Eng. Comm. 15, 3296 (2013)
M.L. Singla, M.M. Shafeeq, M. Kumar, J. Lumin. 129, 434 (2009)
F. López Morales, T. Zayas, O.E. Contreras, L. Salgado, Front. Mater. Sci. 7, 387 (2013)
A.P. Alivisatos, Science 271, 933 (1996)
E. Burstein, Phys. Rev. 93, 632 (1954)
W. Ben Haj Othmen, N. Sdiri, H.Elhouichet, M. Férid, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process 52, 46 (2016)
A.R. West, D.C. Sinclair, N. Hirose, J. Electro Ceram. 1, 65 (1997)
A.K. Jonscher, Nature 276, 673 (1977)
N. Haddad, Z. Ben Ayadi, H. Mahdhi, K. Djessas, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 15457 (2017)
H. Bottger, U.V. Bryskin, Hopping Conduction in Solids. (Verlag Akademie, Berlin, 1985)
H. Rahmouni, A. Dhahri, K. Khirouni, J.Alloys Compds 591, 259–262 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haddad, N., Ayadi, Z.B. & Djessas, K. Synthesis and characterization of antimony doped tin oxide aerogel nanoparticles using a facile sol–gel method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 721–729 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7965-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7965-4