Abstract
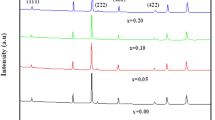
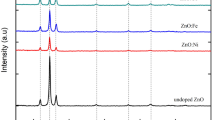
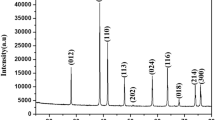
The iron (Fe) and tin (Sn) co-doped indium oxide (In2O3) nanoparticles at different Fe doping concentrations were prepared by solid state reaction and studied for their structural, optical and magnetic properties. The XRD patterns confirmed the cubic structure of all the undoped and co-doped samples. The average crystallite size decreased on increasing from 41 to 32 nm by increase of Fe doping concentration from 5 to 15 at.%. The optical band gap of the samples was found to decrease from 2.89 to 2.77 eV by increasing the Fe dopant concentration. The magnetic properties of the nanoparticles were studied using vibrating sample magnetometer at room temperature and at 100 K by applying the field ±75,000 Oe perpendicular to the sample. The magnetization increased with increase of applied magnetic field and no saturation was observed in all the samples. The similar behavior was observed for the nanoparticles studied at 100 K.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Akaltun, M.A. Yıldırım, A. Ateş, M. Yıldırım, Opt. Commun. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.optcom.2010.12.094
S.H. Babu, S. Kaleemulla, N.M. Rao, C. Krishnamoorthi, J. Electron. Mater. (2016). doi:10.1007/s11664-016-4795-8
S.H. Babu, S. Kaleemulla, N.M. Rao, G.V. Rao, C. Krishnamoorthi, Physica B (2016). doi:10.1016/j.physb.2016.07.037
J.T. McCue, J.Y. Ying, Chem. Mater. (2007). doi:10.1021/cm0617283
H.T. Ng, A. Fang, L. Huang, S.F.Y. Li, Langmuir (2002). doi: 10.1021/la0255828
K. Sreenivas, T.S. Rao, A. Mansingh, S. Chandra, J. Appl. Phys. (1985). doi:10.1063/1.335481
F. Cai, L. Zhu, H. He, J. Li, Y. Yang, X. Chen, Z. Ye, J. Alloys Compd. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.09.016
D. Oh, Y.S. No, S.Y. Kim, W.J. Cho, K.D. Kwack, T.W. Kim, J. Alloys Compd. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.10.180
Y. Wang, Y. Gu, T. Wang, W. Shi, J. Alloys Compd. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.02.175
R.J. Deokate, S.V. Salunkhe, G.L. Agawane, B.S. Pawar, S.M. Pawar, K.Y. Rajpure, A.V. Moholkar, J.H. Kim, J. Alloys Compd. (2010). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.01.150
Z. Deng, X. Fang, R. Tao, W. Dong, D. Li, X. Zhu, J. Alloys Compd. (2008). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.11.064
S. Kaleemulla, N.M. Rao, M.G. Joshi, A.S. Reddy, S. Uthanna, P.S. Reddy, J. Alloys Compd. (2010). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.05.068
D. Kim, J. Alloys Compd. (2010). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.12.056
A.A. Yadav, E.U. Masumdar, A.V. Moholkar, M. Neumann-Spallart, K.Y. Rajpure, C.H. Bhosale, J. Alloys Compd. (2009). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.08.130
V.I. Anisimov, M.A. Korotin, I.A. Nekrasov, A.S. Mylnikova, A.V. Lukoyanov, J.L. Wang, Z. Zeng, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 18, 1695 (2006)
W. Ponhan, V. Amornkitbamrung, S. Maensiri, J. Alloys Compd. (2014). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.03.113
N.S. Krishna, S. Kaleemulla, G. Amarendra, N.M. Rao, C. Krishnamoorthi, M. Kuppan, M.R. Begam, D.S. Reddy, I. Omkaram, Mater. Res. Bull. (2015). doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2014.10.065
M. Kuppan, S. Kaleemulla, N.M. Rao, N.S. Krishna, M.R. Begam, M. Shobana, Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. (2014). doi:10.1155/2014/284237
K. Nomura, C.A. Barrero, J. Sakuma, M. Takeda, Phys. Rev. B (2007). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.75.184411
B.D. Cullity, Introduction to Magnetic Materials. (Addison-Wesley, Reading, 1972)
A. Singhal, S.N. Achary, J. Manjanna, O.D. Jayakumar, R.M. Kadam, A.K. Tyagi, J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 3600–3606 (2009)
J. Tauc, Amorphous and Liquid Semiconductors. (Plenum Press, New York, 1974)
D. Channei, A. Nakaruk, S. Phanichphant, P. Koshy, C.C. Sorrell, J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol. (2016). doi:10.1007/s10971-016-4028-x
Y. Cong, J. Zhang, F. Chen, M. Anpo, D. He, J. Phys. Chem. C (2007). doi:10.1021/jp0727493
S.-C. Ke, T.-C. Wang, M.-S. Wong, N.O. Gopal, J. Phys. Chem. B (2006). doi:10.1021/jp0612578
J. Nowotny, C.C. Sorrell, L.R. Sheppard, T. Bak, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy (2005). doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2004.06.012
X.L. Wang, C.Y. Luan, Q. Shao, A. Pruna, C.W. Leung, R. Lortz, J.A. Zapien, A. Ruotolo, Appl. Phys. Lett. (2013). doi:10.1063/1.4795797
J. Gao, R. Chen, D.H. Li, L. Jiang, J.C. Ye, X.C. Ma, X.D. Chen, Q.H. Xiong, H.D. Sun, T. Wu, Nanotechnology (2011). doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/22/19/195706
B.F. Xin, L.Q. Jing, H.G. Fu, Z.H. Sun, Z.Y. Ren, B.Q. Wang, W.M. Cai, Gaodeng Xuexiao Huaxue Xuebao/Chem. J. Chin. Univ. (2004). doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2004.05.064
J. Gan, X. Lu, J. Wu, S. Xie, T. Zhai, M. Yu, Z. Zhang, Y. Mao, S.C. Ian Wang, Y. Shen, Y. Tong, Sci. Rep. (2013). doi:10.1038/srep01021
S. Dussan, M.K. Singh, A. Kumar, R.S. Katiyar, Integr. Ferroelectr. (2011). doi: 10.1080/10584587.2011.574483
K. Mcguire, Z.W. Pan, Z.L. Wang, D. Milkie, J. Menendez, A.M. Rao, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. (2002). doi:10.1166/jnn.2002.129
B. Santara, B. Pal, P.K. Giri, J. Appl. Phys. (2011). doi:10.1063/1.3665883
N.S. Krishna, S. Kaleemulla, G. Amarendra, N.M. Rao, C. Krishnamoorthi, M.R. Begam, I. Omkaram, D.S. Reddy, J. Alloys Compd. (2015). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.02.167
R.N. Bhowmik, R. Nagarajan, R. Ranganathan, Phys. Rev. B (2004). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.69.054430
M. Kuppan, S. Kaleemulla, N.M. Rao, N.S. Krishna, M.R. Begam, D.S. Reddy, J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 27, 1315–1321 (2014)
S.H. Babu, N.S. Krishna, S. Kaleemulla, N.M. Rao, M. Kuppan, C. Krishnamoorthi, G.M. Joshi, G.A. Basheed, R. Chitra, S. Bhattacharya, N.K. Sahoo, AIP Conf. Proc. 1731, 120003 (2016)
A. Rostamnejadi, P. Kameli, arXiv:0907.2815 (2009). doi: 10.1007/s10948-011-1378-z
R.N. Bhowmik, A. Saravanan, J. Appl. Phys. (2010). doi:10.1063/1.3327433
I. Dzyaloshinsky, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 4, 241–255 (1958)
J. Liu, H. Cao, J. Xiong, Z. Cheng, CrystEngComm (2012). doi: 10.1039/C2CE25578B
C. Frandsen, S. Mørup, Phys. Rev. Lett. (2005). doi:10.1209/epl/i2000-00426-2
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to UGC-DAE-CSR, IGCAR, Kalpakkam, 603102, Tamilnadu, India for providing financial support under Project Sanction number (CSR-KN/CRS-72/2015-2016/809) to carry out the present work. The authors are highly thankful to VIT-SIF for providing, XRD, PL spectrometer and DRS facilities to carry out the present work. The authors are also thankful to UGC-DAE-CSR, IGCAR for providing VSM facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborty, D., Kaleemulla, S., Rao, N.M. et al. Synthesis and magnetic properties of (Fe, Sn) co-doped In2O3 nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 18977–18985 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7851-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7851-0