Abstract
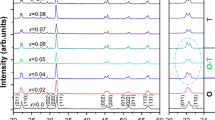
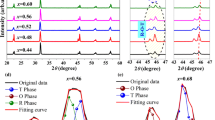
In this work, (Ba0.96Ca0.04)(Ti0.92Sn0.08)O3–xmol MnO (BCTS–xMn) lead-free piezoelectric ceramics were fabricated by the conventional solid-state technique. The composition dependence (0 ≤ x ≤ 3.0 %) of the microstructure, phase structure, and electrical properties was systematically investigated. An O–T phase structure was obtained in all ceramics, and the sintering behavior of the BCTS ceramics was gradually improved by doping MnO content. In addition, the relationship between poling temperature and piezoelectric activity was discussed. The ceramics with x = 1.5 % sintering at temperature of 1330 °C demonstrated an optimum electrical behavior: d 33 ~ 475 pC/N, k p ~ 50 %, ε r ~ 4060, tanδ ~ 0.4 %, P r ~ 10.3 μC/cm2, E c ~ 1.35 kV/mm, T C ~ 82 °C, strain ~0.114 % and \(d_{33}^{*}\) ~ 525 pm/V. As a result, we achieved a preferable electric performance in BaTiO3-based ceramics with lower sintering temperature, suggesting that the BCTS–xMn material system is a promising candidate for lead-free piezoelectric ceramics.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Jaffe, W.R. Cook, H. Jaffe, Piezoelectric Ceramics (Academic, New York, 1971)
J. RÖdel, W. Jo, K.T.P. Seifert, E.M. Anton, T. Granzow, D. Damjanovic, Perspective on the development of lead-free piezoceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 1153–1177 (2009)
W.F. Liu, X.B. Ren, Large piezoelectric effect in Pb-free ceramics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 257602 (2009)
B. Wu, C. Han, D. Xiao et al., Investigation of a new lead-free (0.89 − x)(Bi0.5 Na0.5)TiO3–0.11(Bi0.5K0.5)TiO3–xBa0.85Ca0.15Ti0.90Zr0.10O3 ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 47(11), 3937–3940 (2012)
J. Wu, D. Xiao, J. Zhu, Potassium–sodium niobate lead-free piezoelectric materials: past, present, and future of phase boundaries. Chem. Rev. 115(7), 2559–2595 (2015)
J. Wu, D. Xiao, J. Zhu, Potassium-sodium niobate lead-free piezoelectric ceramics: recent advances and perspectives. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26(12), 9297–9308 (2015)
J.F. Li, K. Wang, F.Y. Zhu, L.Q. Cheng, F.Z. Yao, (K, Na)NbO3-Based Lead-Free piezoceramics: fundamental aspects, processing technologies, and remaining challenges. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96(12), 3677–3696 (2013)
B. Wu, D. Xiao, J. Wu et al., Microstructure and electrical properties of (Ba0.98Ca0.02)(Ti0.94Sn0.06)O3–x wt% ZnO lead-free piezoelectric ceramics sintered at lower temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26(4), 2323–2328 (2015)
B. Wu, D. Xiao, J. Wu et al., Microstructures and piezoelectric properties of CuO-doped (Ba0.98Ca0.02)(Ti0.94Sn0.06)O3 ceramics. J. Electroceram. 33(1–2), 117–120 (2014)
B. Wu, D. Xiao, J. Wu et al., Effect of sintering parameters on microstructure and electrical properties of (Ba0.98Ca0.02)(Ti0.94Sn0.06)O3 lead-free piezo-ceramics. Ferroelectrics 489(1), 129–134 (2015)
B. Wu, D. Xiao, J. Wu et al., Modification of both d 33 and T C in a potassium–sodium niobate ternary system. Dalton Trans. 44(48), 21141 (2015)
Y. Saito, H. Takao, T. Tani, T. Nonoyama et al., Lead-free piezoceramics. Nature 432, 84 (2004)
R. Bechmann, Elastic, piezoelectric, and dielectric constants of polarized barium titanate ceramics and some applications of the piezoelectric equations. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 28, 347 (1956)
J. Wu, D. Xiao, B. Wu, W. Wu et al., Sintering temperature-induced elecrical properties of (Ba0.90Ca0.10)(Ti0.85Zr0.15)O3 lead-free ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 1281 (2012)
D. Liang, X. Zhu, Y. Zhang et al., Large piezoelectric effect in (1 − x)Ba(Zr0.15Ti0.85)O3–x(Ba0.8Sr0.2)TiO3 lead-free ceramics. Ceram. Int. 41(6), 8261–8266 (2015)
D. Xue, Y. Zhou, H. Bao et al., Large piezoelectric effect in Pb-free Ba (Ti, Sn) O3–x(Ba, Ca) TiO3 ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99(12), 122901 (2011)
M. Chen, Z. Xu, R. Chu et al., Polymorphic phase transition and enhanced piezoelectric properties in (Ba0.9Ca0.1)(Ti1−x Sn x )O3 lead-free ceramics. Mater. Lett. 97, 86–89 (2013)
W. Li, Z. Xu, R. Chu, P. Fu, G. Zang, High piezoelectric d 33 coefficient in (Ba1−x Ca x )(Ti0.98Zr0.02)O3 lead-free ceramics with relative high Curie temperature. Mater. Lett. 64, 2325 (2010)
S.W. Zhang, H.L. Zhang, B.P. Zhang, S. Yang, Phase-transition behavior and piezoelectric properties of lead-free (Ba0.95Ca0.05)(Ti1−x Zr x )O3 ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 506, 131 (2010)
P. Wang, Y. Li, Y. Lu, Enhanced piezoelectric properties of (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti 0.9Zr0.1)O3 lead-free ceramics by optimizing calcination and sintering temperature. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 31, 2005 (2011)
J. Wu, D. Xiao, W. Wu et al., Effect of dwell time during sintering on piezoelectric properties of Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1)O3 lead-free ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 509, L359 (2011)
S. Su, R.Z. Zuo, S.B. Lu, Z.K. Xu et al., Poling dependence and stability of piezoelectric properties of Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3–(Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3 ceramics with huge piezoelectric coefficients. Curr. Appl. Phys. 11, 120 (2011)
C. Zhao, W. Wu, H. Wang et al., Site engineering and polarization characteristics in (Ba1−y Ca y )(Ti1−x Hf x ) O3 lead-free ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 119(2), 024108 (2016)
Y. Yu, J. Wu, T.L. Zhao, S.X. Dong et al., MnO2 doped PSN–PZN–PZT piezoelectric ceramics for resonant actuator application. J. Alloys Compd. 615, 676 (2014)
T.H. Lee, S.G. Lee, J.H. Yeo, D.Y. Kim, Piezoelectric properties of (Na0.465K0.465Bi0.07)(Nb0.93Ti0.07)O3 ceramics with MnO2 addition. J. Electroceram. 30, 213 (2013)
Y. Li, D.W. Wang, W.Q. Cao, B. Li, J. Yuan, D.Q. Zhang, S.J. Zhang, M.S. Cao, Effect of MnO2 addition on relaxor behavior and electrical properties of PMNST ferroelectric ceramics. Ceram. Int. 41, 9647 (2015)
Y.C. Guo, H.Q. Fan, C.B. Long, J. Shi, L. Yang, S.H. Lei, Electromechanical and electrical properties of Bi0.5Na0.5Ti1−x Mn x O3−δ ceramics with high remnant polarization. J. Alloys Compd. 610, 189 (2014)
M. Jiang, Q. Lin, D. Lin et al., Effects of MnO and sintering temperature on microstructure, ferroelectric, and piezoelectric properties of Ba0.85Ca0.15Ti0.90Zr0.10O3 lead-free ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 48(3), 2013 (1035)
C. Han, J. Wu, C. Pu et al., High piezoelectric coefficient of Pr2O3-doped Ba0.85Ca0.15Ti0.90Zr0.10O3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 38(8), 6359–6636 (2012)
G.R. Li, L.Y. Zheng, Q.R. Yin, B. Jiang, W.W. Cao, Microstructure and ferroelectric properties of MnO2-doped bismuth-layer (Ca, Sr)Bi4Ti4O15 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 064108 (2005)
E. Buixaderas, V. Bovtun, M. Kempa, M. Savinov et al., Broadband dielectric response and grain-size effect in K0.5Na0.5NbO3 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 107, 014111 (2010)
Y. Park, W.J. Lee, H.G. Kim, Particle-size-induced diffuse phase transition in the fine-particle barium titanate porcelains. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 9, 9445 (1997)
S. Chattopadhyay, P. Ayyub, V.R. Palkar, M. Multani, Size-induced diffuse phase transition in the nanocrystalline ferroelectric PbTiO3. Phys. Rev. B 52, 13177 (1995)
C.S. Yu, H.L. Hsieh, Piezoelectric properties of Pb(Ni1/3, Sb2/3)O3–PbTiO3–PbZrO3 ceramics modified with MnO2 additive. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 25, 2425 (2005)
S.M. Li, S.H. Lee, C.B. Yoon, H.E. Kim, K.W. Lee, Low-temperature sintering of MnO2-doped PZT–PZN Piezoelectric ceramics. J. Electroceram. 18, 311 (2007)
T. Chen, T. Zhang, G.C. Wang, J.F. Zhou, J.W. Zhang, Y.H. Liu, Effect of CuO on the microstructure and electrical properties of Ba0.85Ca0.15Ti0.90Zr0.10O3 piezoceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 47, 4612 (2012)
M. Jiang, X. Li, J. Zhu, X. Zhu, W. Shi, L. Li, D. Xiao, J. Zhu, Double hysteresis loops induced by Mn doping in Pb0.99Nb0.02(Zr0.95Ti0.05)0.98O3 ferroelectric ceramics. Curr. Appl. Phys. 10, 526–530 (2010)
S. Wongsaenmai, K. Kanchiang, S. Chandarak et al., Crystal structure and ferroelectric properties of Mn-doped ((Ka0.5Na0.5)0.935Li0.065)NbO3 lead-free ceramics. Curr. Appl. Phys. 12(2), 418 (2012)
X. Ren, Large electric-field-induced strain in ferroelectric crystals by reversible domain switching. Nat. Mater. 3, 91–94 (2004)
X.L. Huang, D.Q. Xiao, X.H. Li, W.J. Wu, W.F. Liang et al., Effects of CuO on the electrical properties of CaTiO3-modified [(Na0.52K0.48)0.955Li0.045](Nb0.955Sb0.045)O3 lead-free piezoceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 2563–2566 (2010)
Z. Feng, X. Ren, Aging effect and large recoverable electrostrain in Mn-doped KNbO3-based ferroelectrics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 032904 (2007)
L.X. Zhang, X. Ren, Aging behavior in single-domain Mn-doped BaTiO3 crystals: implicationfor a unified microscopic explanation of ferroelectric aging. Phys. Rev. B 73, 094121 (2006)
B. Zhang, J. Wu, B. Wu et al., Effects of sintering temperature and poling conditions on the electrical properties of Bi0.50(Na0.70K0.20Li0.10)0.50TiO3 piezoelectric ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 525, 53–57 (2012)
J. Wu, D. Xiao, B. Wu et al., Sintering temperature-induced electrical properties of (Ba0.90Ca0.10)(Ti0.85Zr0.15)O3 lead-free ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 47(5), 1281–1284 (2012)
B.K. Lee, S.Y. Chung, S.J. Kang, Grain boundary faceting and abnormal grain growth in BaTiO3. Acta Mater. 48(7), 1575–1580 (2000)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Project (Grant Nos. KYTZ201312 and J201220) Supported by the Scientific Research Foundation of CUIT, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Southwest University for Nationalities (No. 2014NZYQN11), The Foundation of Sichuan province science and technology support program, China (Grant No. GZ0198) and Scientific Research Project of Sichuan Provincial Department of Education (Grant No.16ZA0216).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, B., Ma, J., Wu, W. et al. Structure and electrical properties of MnO doped (Ba0.96Ca0.04)(Ti0.92Sn0.08)O3 lead free ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 2358–2365 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5804-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5804-7