Abstract
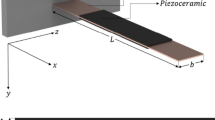
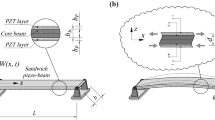
The properties of several configurations of piezoelectric bending actuators were investigated at high vibration amplitude both theoretically and experimentally. It was found that under high amplitude vibration conditions, the failure of the actuator was mainly caused by the maximum stress and domain reorientation. The actuator tends to fracture or crack at the location of maximum stress, which is indicated by the sudden drop of the displacement during frequency scan. The dimension, boundary condition and vibration order influence the distribution and magnitude of the stress. Domain reorientation may also occur during the frequency scan, which results in the distortion of the current profile. And meanwhile the magnitude of the current, admittance and temperature of the actuator will increase significantly and abruptly. The temperature was found to be increase with the increase of frequency, electric field or vibration amplitude due to the higher mechanical and electrical losses. The un-even stress distribution has also resulted in a high-to-low gradient temperature rise from the clamped end to the free end of the actuator under the Clamped-Free boundary condition. A linear model based on Euler–Benoulli theory has been derived and it provides reasonable explanations on the phenomena observed experimentally in this paper.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Niezrechi, D. Brei, A. Moskalik, Shock Vibr. Dig. 33, 269 (2001)
G.H. Haertling, J. Am. Cram. Soc. 82, 797 (1999)
A.J. Moulson, J.M. Herbert, Electroceramics. (Wiley, England, 2003), Chapter 2 & 6
J.G. Smits, S.I. Dalke, T.K. Cooney, Sens. Actuators 28, 41 (1991)
M. Besell, S. Johansson, Journal of Electroceramics 3, 73 (1999)
J.H. Yoo, J.I. Hong, W. Cao, Sens. Actuators 79, 8 (2000)
Y.H. Chen, T. Li, J. Ma, in Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Materials-Smart/Intelligent Materials and Nanotechnology (Chiang Mai University, Thailand, 2004), p. 70
T. Li, Y.H. Chen, J. Ma, J. Mater. Sci. 40, 3601 (2005)
T. Kanda, Y. Kobayashi, T. Higuchi, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42, 3014 (2003)
M. Umeda, K. Nakamura, S. Ueha, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 38, 5581 (1999)
S. Tashiro, M. Ikehiro, H. Igarashi, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 36, 3004 (1997)
W.P. Chen, C.P. Chong, P.C.K. Liu, Mat. Sci., Eng. B99, 203 (2003)
C.H. Xu, J.H. Hu, H.L.W. Chan, Ultrasonics 39, 735 (2002)
J.M. Calderon-Moreno, M. Popa, Mat. Sci. Eng. A336, 124 (2002)
T. Fett, D. Munz, G. Thun, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 19, 1921 (2000)
K. Uchino, J.H. Zheng, J.W.C. DE Vries, Journal of Electroceramics 2, 33–40 (1998)
S. Takahashi, Y. Sasaki, K. Uchino, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 34, 5328 (1995)
K. Uchino, S. Hirose, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 48, 307 (2001)
S. Takahashi, S. Hirose, K. Uchino, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 77, 2429 (1994)
Q.M. Wang, Q.M. Zhang, L.E. Cross, J. Appl. Phys. 86, 3352 (1999)
Y. Sasaki, M. Umeda, M. Yamamoto, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 40, 5743 (2001)
C.W. de Silva, Vibration: Fundamentals and Practice. (CRC, Boca Raton, 1999), p. 352
P. Lu, K.H. Lee, J. Sound Vib. 266, 723 (2003)
S. Sherrit, X. Bao, Y. Bar-Cohen, in Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium. (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., Atlanta, 2001), P. 1097
J. Hu, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 50, 594 (2003)
J. Zheng, S. Takahashi, K. Uchino, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79, 3193 (1996)
K. Yao, K. Uchino, L.C. Lim, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 47,819 (2000)
P. Kielczynski, W. Pajewski, Sens. Actuators 36, 97 (1993)
P. Gerthsen, K.H. Hardtl, N. A. Schmidt, J. Appl. Phys. 51, 1131 (1980)
D. Damjanovic, Rep. Prog. Phys. 61, 1267 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Chen, Y.H., Boey, F.Y.C. et al. High amplitude vibration of piezoelectric bending actuators. J Electroceram 18, 231–242 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-007-9039-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-007-9039-0