Abstract
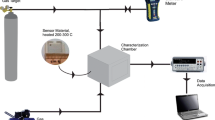
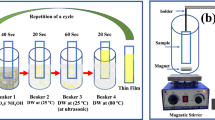
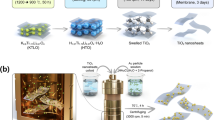
ZnO nanomaterials have been directly grown on Al2O3 ceramic tube by two step seeds-assisted solution method with different ammonia sources. The crystalline phase and morphology of the ZnO nanomaterials are characterized by XRD and SEM. The results of SEM reveal that the ZnO nanomaterials present different morphologies and hierarchical structures where rhombus-shaped nanoprisms, nanorods assembled nanoflowers and nanoleaves constructed nanourchins are obtained in NH4F, hexamethylenetetramine (HMT) and urea, respectively. All of the ZnO nanomaterials show the optimal working temperature at 320 °C and excellent repeatability. Gas sensing experiments demonstrate that the ZnO nanomateirals perform high responses and fast response-recovery to volatile organic compounds, especially for the nanorods assembled nanoflowers prepared in the HMT. It is believed that the enhancement of the gas sensing performances is mainly attributed to the hierarchical structures, exposed deficiencies and excellent ohm contact of the direct grown ZnO nanomaterials.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Menzel, K. Subannajui, F. Güder, D. Moser, O. Paul, M. Zacharias, Multifunctional ZnO-nanowire-based sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 21, 4342–4348 (2011)
M. Chen, Z. Wang, D. Han, F. Gu, G. Guo, High-sensitivity NO2 gas sensors based on flower-like and tube-like ZnO nanomaterials. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 157, 565–574 (2011)
E. Şennik, S. Kerli, Ü. Alver, Z.Z. Öztürk, Effect of fluorine doping on the NO2-sensing properties of ZnO thin films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 216, 49–56 (2015)
R.K. Sonker, S.R. Sabhajeet, S. Singh, B.C. Yadav, Synthesis of ZnO nanopetals and its application as NO2 gas sensor. Mater. Lett. 152, 189–191 (2015)
M. Chen, Z. Wang, D. Han, F. Gu, G. Guo, Porous ZnO polygonal nanoflakes: synthesis, use in high-sensitivity NO2 gas sensor, and proposed mechanism of gas sensing. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 12763–12773 (2011)
H. Gong, J.Q. Hu, J.H. Wang, C.H. Ong, F.R. Zhu, Nano-crystalline Cu-doped ZnO thin film gas sensor for CO. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 115, 247–251 (2006)
M. Hjiri, L. El Mir, S.G. Leonardi, A. Pistone, L. Mavilia, G. Neri, Al-doped ZnO for highly sensitive CO gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 196, 413–420 (2014)
N.D. Khoang, H.S. Hong, D.D. Trung, N.V. Duy, N.D. Hoa, D.D. Thinh, N.V. Hieu, On-chip growth of wafer-scale planar-type ZnO nanorod sensors for effective detection of CO gas. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 181, 529–536 (2013)
V.A. Minh, L.A. Tuan, T.Q. Huy, V.N. Hung, N.V. Quy, Enhanced NH3 gas sensing properties of a QCM sensor by increasing the length of vertically orientated ZnO nanorods. Appl. Surf. Sci. 265, 458–464 (2013)
P. Sundara Venkatesh, P. Dharmaraj, V. Purushothaman, V. Ramakrishnan, K. Jeganathan, Point defects assisted NH3 gas sensing properties in ZnO nanostructures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 212, 10–17 (2015)
K. Diao, M. Zhou, J. Zhang, Y. Tang, S. Wang, X. Cui, High response to H2S gas with facile synthesized hierarchical ZnO microstructures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 219, 30–37 (2015)
Z.S. Hosseini, A. Mortezaali, A. Iraji zad, S. Fardindoost, Sensitive and selective room temperature H2S gas sensor based on Au sensitized vertical ZnO nanorods with flower-like structures. J. Alloys Comp. 628, 222–229 (2015)
Z.S. Hosseini, A.I. Zad, A. Mortezaali, Room temperature H2S gas sensor based on rather aligned ZnO nanorods with flower-like structures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 207A, 865–871 (2015)
A. Mortezaali, R. Moradi, The correlation between the substrate temperature and morphological ZnO nanostructures for H2S gas sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 206, 30–34 (2014)
N.H. Al-Hardan, M.J. Abdullah, A. Abdul Aziz, H. Ahmad, L.Y. Low, ZnO thin films for VOC sensing applications. Vacuum 85, 101–106 (2010)
I. Elmi, S. Zampolli, E. Cozzani, F. Mancarella, G.C. Cardinali, Development of ultra-low-power consumption MOX sensors with ppb-level VOC detection capabilities for emerging applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 135, 342–351 (2008)
N. Kilinc, O. Cakmak, A. Kosemen, E. Ermek, S. Ozturk, Y. Yerli, Z.Z. Ozturk, H. Urey, Fabrication of 1D ZnO nanostructures on MEMS cantilever for VOC sensor application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 202, 357–364 (2014)
Y.V. Kaneti, J. Yue, X. Jiang, A. Yu, Controllable synthesis of ZnO nanoflakes with exposed (1010) for enhanced gas sensing performance. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 13153–13162 (2013)
W. Guo, T. Liu, H. Zhang, R. Sun, Y. Chen, W. Zeng, Z. Wang, Gas-sensing performance enhancement in ZnO nanostructures by hierarchical morphology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 166–167, 492–499 (2012)
K.M. Kim, H.R. Kim, K.I. Choi, H.J. Kim, J.H. Lee, ZnO hierarchical nanostructures grown at room temperature and their C2H5OH sensor applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 155, 745–751 (2011)
S. Ma, R. Li, C. Lv, W. Xu, X. Gou, Facile synthesis of ZnO nanorod arrays and hierarchical nanostructures for photocatalysis and gas sensor applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 192, 730–740 (2011)
M.R. Alenezi, T.H. Alzanki, A.M. Almeshal, A.S. Alshammari, M.J. Beliatis, S.J. Henley, S.R.P. Silva, Hierarchically designed ZnO nanostructure based high performance gas sensors. RSC Adv 4, 49521–49528 (2014)
M.R. Alenezi, S.J. Henley, N.G. Emerson, S.R.P. Silva, From 1D and 2D ZnO nanostructures to 3D hierarchical structures with enhanced gas sensing properties. Nanoscale 6, 235–247 (2014)
H. Zhang, R. Wu, Z. Chen, G. Liu, Z. Zhang, Z. Jiao, Self-assembly fabrication of 3D flower-like ZnO hierarchical nanostructures and their gas sensing properties. CrystEngComm 14, 1775–1782 (2012)
Z. Chen, Z. Lin, Y. Hong, N. Li, M. Xu, Hydrothermal synthesis of hierarchically porous Rh-doped ZnO and its high gas sensing performance to acetone. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2015). doi:10.1007/s10854-015-4069-x
D. Ju, H. Xu, Z. Qiu, J. Guo, J. Zhang, B. Cao, Highly sensitive and selective triethylamine-sensing properties of nanosheets directly grown on ceramic tube by forming NiO/ZnO PN heterojunction. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 200, 288–296 (2014)
D.X. Ju, H.Y. Xu, J. Zhang, J. Guo, B.Q. Cao, Direct hydrothermal growth of ZnO nanosheets on electrode for ethanol sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 201, 444–451 (2014)
S.L. Zhang, J.O. Lim, J.S. Huh, J.S. Noh, W. Lee, Two-step fabrication of ZnO nanosheets for high-performance VOCs gas sensor. Curr. Appl. Phys. 13S2, S156–S161 (2013)
W. Guo, T. Liu, Z. Guo, W. Zeng, Y. Chen, Z. Wang, Hydrothermal synthesis of ultrathin ZnO nanosheets and their gas-sensing properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 1764–1769 (2013)
J. Du, R. Zhao, S. Chen, H. Wang, J. Li, Z. Zhu, Self-assembly of gridlike zinc oxide lamellae for chemical-sensing applications. ACS Appl Mater. Interfaces 7, 5870–5878 (2015)
A. Zou, L. Hu, Y. Qiu, G. Cao, J. Yu, L. Wang, H. Zhang, B. Yin, L. Xu, High performance of 1-D ZnO microwire with curve-side hexagon as ethanol gas sensor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 4908–4912 (2015)
F. Li, H. Zhang, L. Hu, Y. Luo, Y. Zhao, Y. Qiu, J. Ji, L. Yue, A novel ethanol gas sensor based on ZnO microwire. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 4812–4816 (2013)
D. Calestani, R. Mosca, M. Zanichelli, M. Villani, A. Zappettini, Aldehyde detection by ZnO tetrapod-based gas sensors. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 15532–15536 (2011)
S. Tian, F. Yang, D. Zeng, C. Xie, Solution-processed gas sensors based on ZnO nanorods array with an exposed (0001) facet for enhanced gas-sensing properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 10586–10591 (2012)
L.J. Bie, X.N. Yan, J. Yin, Y.Q. Duan, Z.H. Yuan, Nanopillar ZnO gas sensor for hydrogen and ethanol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 126, 604–608 (2007)
Z. Wen, L. Zhu, Z. Zhang, Z. Ye, Fabrication of gas sensor based on mesoporous rhombus-shaped ZnO rod arrays. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 208, 112–121 (2015)
W. Guo, T. Liu, L. Huang, H. Zhang, Q. Zhou, W. Zeng, HMT assisted hydrothermal synthesis of various ZnO nanostructures: structure, growth and gas sensor properties. Physica E 44, 680–685 (2011)
X. Tian, L. Yang, X. Qing, K. Yu, X. Wang, Trace level detection of hydrogen gas using birnessite-type manganese oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 207A, 34–42 (2015)
F. Grasset, N. Saito, D. Li, D. Park, I. Sakaguchi, N. Ohashi, H. Haneda, T. Roisnel, S. Mornet, E. Duguet, Surface modification of zinc oxide nanoparticles by aminopropyltriethoxysilane. J. Alloys Comp. 360, 298–311 (2003)
F. Meng, N. Hou, S. Ge, B. Sun, Z. Jin, W. Shen, L. Kong, Z. Guo, Y. Sun, H. Wu, C. Wang, M. Li, Flower-like hierarchical structures consisting of porous single-crystalline ZnO nanosheets and their gas sensing properties to volatile organic compounds (VOCs). J. Alloys Comp. 626, 124–130 (2015)
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the Foundation of CAEP (426030302).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, X., Yu, K., Wang, X. et al. Influence of ammonia sources on the gas sensing properties of the direct grown ZnO nanomaterials. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 4711–4722 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4351-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4351-6