Abstract
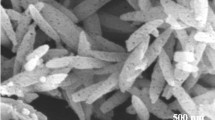
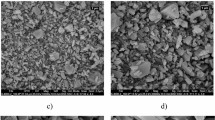
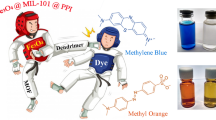
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), a new type of porous functional material, have attracted widespread attention in the field of adsorption separation, medicine, and catalysis, etc., due to their unique adjustable pore structure and large specific surface. The defective zirconium-based MOF is rich in terminal Zr–OH induced by the lack of linkers and the μ3-OH originating from the Zr cluster, exhibiting high affinity for the carboxyl and sulfonic acid groups in the dyes. We report the performance of two defective zirconium-based MOFs (MOF-808 and MIL-140C) to remove Eosin y (EY), Methyl orange (MO), and Orange g from the water. Owing to the strong affinity, larger specific surface area, and better-matched pore structure, MOF-808 exhibits higher adsorption capacity for EY and MO, with maximum adsorption capacities of 661.7 mg g−1 and 532.4 mg g−1, respectively. The adsorption kinetics, thermodynamics, adsorption cycle performance, and adsorption mechanism of two MOFs for three dyes were investigated. Adsorption thermodynamics and XPS analysis certified that both chemical adsorption and physical adsorption occur during the adsorption process, especially chemical adsorption. Desorption and regeneration tests demonstrate that both MOF-808 and MIL-140C maintained their high adsorption capacity after four cycles, indicating two MOFs are favorable candidates for removing pollutants.
Graphical abstract

In this article, the adsorption performance of MOF-808 and MIL-140C on three different sizes and structures of anionic dyes is mainly studied. The results show that MOF-808 has better adsorption performance for EY and MO. At the same time, the adsorption results show that the chemical adsorption between the adsorbate and the MOFs material plays a leading role in the adsorption, resulting in a high adsorption capacity for EY, although the EY molecule has a larger molecular size.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files]. All data, models, and code generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
References
Gupta V (2009) Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal–a review. J Environ Manage 90:2313–2342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.11.017
Shahid M, Mohammad F (2013) Recent advancements in natural dye applications: a review. J Clean Prod 53:310–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.03.031
Wang P, Yao J, Wang G, Hao F, Shrestha S, Xue B et al (2019) Exploring the application of artificial intelligence technology for identification of water pollution characteristics and tracing the source of water quality pollutants. Sci Total Environ 693:133440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.246
Quesada HB, Baptista ATA, Cusioli LF, Seibert D, de Oliveira BC, Bergamasco R (2019) Surface water pollution by pharmaceuticals and an alternative of removal by low-cost adsorbents: a review. Chemosphere 222:766–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.009
Goel P (2006) Water pollution causes, effects and control, new age International. New Delhi; https://doi.org/10.12691/aees-6-4-4
Daneshvar E, Vazirzadeh A, Niazi A, Kousha M, Naushad M, Bhatnagar A (2017) Desorption of methylene blue dye from brown macroalga: effects of operating parameters, isotherm study and kinetic modeling. J Clean Prod 152:443–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.119
Tissera ND, Wijesena RN, Yasasri H, de Silva KN, de Silva RM (2020) Fibrous keratin protein bio micro structure for efficient removal of hazardous dye waste from water: surface charge mediated interfaces for multiple adsorption desorption cycles. Mater Chem Phys 246:122790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.122790
Molavi H, Hakimian A, Shojaei A, Raeiszadeh M (2018) Selective dye adsorption by highly water stable metal-organic framework: long term stability analysis in aqueous media. Appl Surf Sci 445:424–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.03.189
Dahiya D, Nigam PS (2020) Waste management by biological approach employing natural substrates and microbial agents for the remediation of dyes’ wastewater. Appl Sci 10(8):2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10082958
He Y, Chen K, Srinivasakannan C, Li S, Yin S, Peng J et al (2018) Intensified extraction and separation Pr (III)/Nd (III) from chloride solution in presence of a complexing agent using a serpentine microreactor. Chem Eng J 354:1068–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.193
Gao S, Chen Y, Su J, Wang M, Wei X, Jiang T et al (2017) Triboelectric nanogenerator powered electrochemical degradation of organic pollutant using Pt-free carbon materials. ACS Nano 11:3965–3972. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b00422
Chen C, Zhang T, Lv L, Chen Y, Tang W, Tang S (2021) Destroying the structure of extracellular polymeric substance to improve the dewatering performance of waste activated sludge by ionic liquid. Water Res 199:117161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117161
Shi X-R, Chen X-L, Hao Y-L, Li L, Xu H-J, Wang M-M (2018) Magnetic metal-organic frameworks for fast and efficient solid-phase extraction of six Sudan dyes in tomato sauce. J Chromatogr B 1086:146–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.04.022
He Y, Tang S, Yin S, Li S (2021) Research progress on green synthesis of various high-purity zeolites from natural material-kaolin. J Clean Prod 306(9):127248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127248
Chen Y, Shen C, Wang J, Xiao G, Luo G (2018) Green synthesis of Ag–TiO2 supported on porous glass with enhanced photocatalytic performance for oxidative desulfurization and removal of dyes under visible light. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:13276–13286. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b02860
Hamoud HI, Finqueneisel G, Azambre B (2017) Removal of binary dyes mixtures with opposite and similar charges by adsorption, coagulation/flocculation and catalytic oxidation in the presence of CeO2/H2O2 Fenton-like system. J Environ Manage 195:195–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.07.067
James SL (2003) Metal-organic frameworks. Chem Soc Rev 32:276–288. https://doi.org/10.1039/B200393G
Chen X, Chen D, Li N, Xu Q, Lu J (2020) Modified-MOF-808-loaded polyacrylonitrile membrane for highly efficient, simultaneous emulsion separation and heavy metal ion removal. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(35):39227–39235. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c10290
Peng Y, Huang H, Zhang Y, Kang C, Chen S, Song L et al (2018) A versatile MOF-based trap for heavy metal ion capture and dispersion. Nat Commun 9:187. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02600-2
Wang Z, Lei Q, Wang Z, Yuan H, Liu J (2020) In-situ synthesis of free-standing FeNi-oxyhydroxide nanosheets as a highly efficient electrocatalyst for water oxidation. Chem Eng J 395:125180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125180
Huang WY, Wang GQ, Li WH, Li TT, Ding YJ (2020) Porous ligand creates new reaction route: bifunctional single-atom palladium catalyst for selective distannylation of terminal alkynes. Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chempr.2020.06.020
Zhang X, Tang Y, Zhang F, Lee CS (2016) A novel aluminum-graphite dual-ion battery. Adv Energy Mater 6:1502588. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201502588
Tong X, Zhang F, Ji B, Sheng M, Tang Y (2016) Carbon-coated porous aluminum foil anode for high-rate, long-term cycling stability, and high energy density dual-ion batteries. Adv Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201603735
Ji B, Zhang F, Song X, Tang Y (2017) A novel potassium-ion-based dual-ion battery. Adv Mater 29:1700519. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201700519
Wang R, Yuan Y, Zhang J, Zhong X, Liu J, Xie Y et al (2021) Embedding Fe 2 P nanocrystals in bayberry-like N, P-enriched carbon nanospheres as excellent oxygen reduction electrocatalyst for zinc-air battery. J Power Sources 501:230006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2021.230006
Zhang X, Sun X, Lv T, Weng L, Zhang S (2020) Preparation of PI porous fiber membrane for recovering oil-paper insulation structure. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 31:13344–13351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03888-5
Zhang K, Qiu L, Tao J, Zhong X, Lin Z, Wang R et al (2021) Recovery of gallium from leach solutions of zinc refinery residues by stepwise solvent extraction with N235 and Cyanex 272. Hydrometallurgy 205:105722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2021.105722
Wang R, Xie H, Lai X, Liu J-B, Li J, Qiu G (2021) Visible light-enabled iron-catalyzed selenocyclization of N-methoxy-2-alkynylbenzamide. Molecular Catalysis 515:111881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2021.111881
Meng W, Jiang C, Zhang S, Song X, Tang Y, Cheng HM (2018) Reversible calcium alloying enables a practical room-temperature rechargeable calcium-ion battery with a high discharge voltage. Nat Chem 10:667–672. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-018-0045-4
Yang M, Kong Q, Feng W, Yao W, Wang Q (2021) Hierarchical porous nitrogen, oxygen, and phosphorus ternary doped hollow biomass carbon spheres for high-speed and long-life potassium storage. Carbon Energy 4:45–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/cey2.157
Safaei M, Foroughi MM, Ebrahimpoor N, Jahani S, Omidi A, Khatami M (2019) A review on metal-organic frameworks: synthesis and applications. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 118:401–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.06.007
Wu D, Liu J, Jin J, Cheng J, Wang YY (2019) New doubly interpenetrated MOF with [Zn 4 O] clusters and its doped isomorphic mof: sensing, dye, and gas adsorption capacity. Cryst Growth Des 19:6774–6783. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.9b01193
Gandara-Loe J, Souza BE, Missyul A, Giraldo G, Tan JC, Silvestre-Albero J (2020) MOF-based polymeric nanocomposite films as potential materials for drug delivery devices in ocular therapeutics. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:30189–30197. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c07517
Sharma A, Sahoo SC, Kumar G, Mehta SK, Kataria R (2021) Synthesis and characterization of 1D-Co/Zn MOFs having potential for efficient dye adsorption from wastewater. J Mol Struct 1226:129327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129327
El-Sewify IM, Radwan A, Shahat A, El-Shahat M, Khalil MM (2022) Superior adsorption and removal of aquaculture and bio-staining dye from industrial wastewater using microporous nanocubic Zn-MOFs. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 329:111506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111506
Ahmad K, Parveen S, Aziz T, Naseem HA, Ashfaq M, Rauf A (2021) Metal organic framework (KIUB-MOF-1) as efficient adsorbent for cationic and anionic dyes from brackish water. J Mol Struct 1242:130898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.130898
Zhang A, Liu B, Liu M, Xie Z, Feng G (2021) The adsorption properties of defect controlled metal-organic frameworks of UiO-66. Sep Purif Technol 270:118842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118842
Zhang X, Wang X, Fan W, Wang Y, Sun D (2019) A multifunctional Zr-MOF for rapid removal of Cr2O72-, efficient gas adsorption/separation, and catalytic performance. Mater Chem Front 4:1150–1157. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QM00612E
Kalaj M, Palomba JM, Bentz KC, Cohen SM (2019) Multiple functional groups in UiO-66 improve chemical warfare agent simulant degradation. Chem Commun 55:5367–5370. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CC02252J
Razavi SAA, Morsali A (2019) Ultrasonic-assisted linker exchange (USALE): a novel post-synthesis method for controlling the functionality, porosity, and morphology of MOFs. Chem Eur J 25:10876–10885. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201901554
He L, Li M-X, Chen F, Yang S-S, Ding J, Ding L et al (2021) Novel coagulation waste-based Fe-containing carbonaceous catalyst as peroxymonosulfate activator for pollutants degradation: role of ROS and electron transfer pathway. J Hazard Mater 417:126113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126113
Zango ZU, Jumbri K, Sambudi NS, Ramli A, Abu Bakar NHH, Saad B et al (2020) A critical review on metal-organic frameworks and their composites as advanced materials for adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of emerging organic pollutants from wastewater. Polymers 12(11):2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112648
Ly HGT, Fu G, Kondinski A, Bueken B, De Vos D, Parac-Vogt TN (2018) Superactivity of MOF-808 toward peptide bond hydrolysis. J Am Chem Soc 140:6325–6335. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b01902
Li S, Qi B, Luo J, Zhuang Y, Wan Y (2021) Ultrafast selective adsorption of pretreatment inhibitors from lignocellulosic hydrolysate with metal-organic frameworks: performance and adsorption mechanisms. Sep Purif Technol 275:119183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119183
Zhu X, Li B, Yang J, Li Y, Zhao W, Shi J et al (2015) Effective adsorption and enhanced removal of organophosphorus pesticides from aqueous solution by Zr-based MOFs of UiO-67. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1021/am5059074
Zhuang S, Cheng R, Wang J (2019) Adsorption of diclofenac from aqueous solution using UiO-66-type metal-organic frameworks. Chem Eng J 359:354–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.150
Lin K-YA, Liu Y-T, Chen S-Y (2016) Adsorption of fluoride to UiO-66-NH2 in water: stability, kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. J Colloid Interface Sci 461:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.08.061
Wu H, Chua YS, Krungleviciute V, Tyagi M, Chen P, Yildirim T et al (2013) Unusual and highly tunable missing-linker defects in zirconium metal-organic framework UiO-66 and their important effects on gas adsorption. J Am Chem Soc 135:10525–10532. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja404514r
Samy M, Ibrahim MG, Fujii M, Diab KE, ElKady M, Alalm MG (2021) CNTs/MOF-808 painted plates for extended treatment of pharmaceutical and agrochemical wastewaters in a novel photocatalytic reactor. Chem Eng J 406:127152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127152
Hu Z, Kundu T, Wang Y, Sun Y, Zeng K, Zhao D (2020) Modulated hydrothermal synthesis of highly stable MOF-808 (Hf) for methane storage. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:17042–17053. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c04486
Xu J, Liu J, Li Z, Wang X, Wang Z (2019) Synthesis, structure and properties of Pd@ MOF-808. J Mater Sci 54:12911–12924. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03786-0
Das A, D’Alessandro D (2015) Tuning the functional sites in metal-organic frameworks to modulate CO2 heats of adsorption. Cryst Eng Comm 17:706–718. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE01341G
Zango ZU, Jumbri K, Sambudi NS, Bakar HHA, Garba ZN, Isiyaka HA et al (2021) Selective adsorption of dyes and pharmaceuticals from water by UiO metal-organic frameworks: a comprehensive review. Polyhedron 210:115515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2021.115515
Corbett JF (1972) Pseudo first-order kinetics. J Chem Educ 49:663. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed049p663
Mckay Y (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Langmuir I (1917) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 143:1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4929609
Freundlich H (1932) Of the adsorption of gases. Section II. Kinetics and energetics of gas adsorption. Introductory paper to section II. Trans Faraday Soc 28:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1039/TF9322800195
Zhang M, Yu Z, Yu H (2020) Adsorption of Eosin Y, methyl orange and brilliant green from aqueous solution using ferroferric oxide/polypyrrole magnetic composite. Polym Bull 77:1049–1066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02792-1
Achemaoui M, Boukoussa B, Adel M, Me Kki A, Hamacha RB (2020) Dyes adsorption, antifungal and antibacterial properties of metal loaded mesoporous silica: effect of metal and calcination treatment. Mater Chem Phys 256:0254–0584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123704
Guo XZ, Han SS, Yang JM, Wang XM, Quan S (2020) Effect of synergistic interplay between surface charge, crystalline defects, and pore volume of MIL-100(Fe) on adsorption of aqueous organic dyes. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:2113–2122. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b05715
Xu MY, Jiang HL, Xie ZW, Li ZT, He FA (2020) Highly efficient selective adsorption of anionic dyes by modified β-cyclodextrin polymers. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 108:114–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2020.01.005
Niu C, Zhang N, Hu C, Zhang C, Xing Y (2021) Preparation of a novel citric acid-crosslinked Zn-MOF/chitosan composite and application in adsorption of chromium(VI) and methyl orange from aqueous solution. Carbohyd Polym 258:117644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117644
Makrygianni M, Lada ZG, Manousou A, Aggelopoulos CA, Deimede V (2019) Removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solution by novel pyrrolidinium-based Polymeric Ionic Liquid (PIL) as adsorbent: Investigation of the adsorption kinetics, equilibrium isotherms and the adsorption mechanisms involved. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103163
Ahmadijokani F, Mohammadkhani R, Ahmadipouya S, Shokrgozar A, Arjmand M (2020) Superior chemical stability of UiO-66 metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for selective dye adsorption. Chem Eng J 399:125346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125346
Mga B (2019) Synthesis and characterization of a biodegradable Cellulose acetate-montmorillonite composite for effective adsorption of Eosin Y - ScienceDirect. Carbohyd Polym 206:863–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.11.040
Lawal IA, Dolla TH et al (2019) Synthesis and characterization of deep eutectic solvent functionalized CNT/ZnCo2O4 nanostructure: kinetics, isotherm and regenerative studies on Eosin Y adsorption - ScienceDirect. J Environ Chem Eng 7:102877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.102877
Lin X, Luo X, Long Y (2014) A sorbent of carboxymethyl cellulose loaded with zirconium for the removal of fluoride from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 252:415–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.008
Acknowledgements
Thanks for the financial support of Shaanxi Natural Science Foundation (No. 2021JZ-11).
Funding
Thanks for the Innovation Foundation for Doctor Dissertation of Northwestern Polytechnical University under CX201964, and Shaanxi Natural Science Foundation (No. 2021JZ-11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BL synthesized MOFs and studied their adsorption properties for dyes and was the main contributor to the manuscript; ZX revised the manuscript several times and helped analyze the adsorption data; characterization and analysis of MOFs materials were done by ML and YL; AZ helps solve various problems encountered in the experiment.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
I declare that we have no competing interest.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Andrea de Camargo.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Liu, M., Xie, Z. et al. Performance of defective Zr-MOFs for the adsorption of anionic dyes. J Mater Sci 57, 5438–5455 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-06874-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-06874-w