Abstract
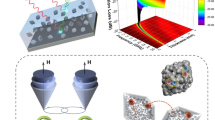
Herein, functionalized carbon nanospheres (CNs) are encapsulated within reduced graphene oxide (rGO) layers as a high-performance microwave-absorbing material. The obtained sandwich-like CNs@rGO nanocomposite is characterized by a well-matched characteristic impedance and multiple dielectric relaxation processes, resulting in a strong reflection loss (–33.09 dB at 14.01 GHz) and broad effective bandwidth of 12.2–17.6 GHz (5.4 GHz) with a low thickness of 2.0 mm, which is superior to many reported carbon absorbers and even some magnetic absorbers. This remarkable microwave absorption property is ascribed to the sandwich structure, indicating that the as-prepared sandwich-like CNs@rGO nanocomposites are potential candidates for lightweight microwave absorption materials.
Graphic abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Y, Gao X, Lin CH, Shi LY, Li XH, Wu GL (2019) Metal organic frameworks-derived Fe-Co nanoporous carbon/graphene composite as a high-performance electromagnetic wave absorber. J Alloy Compd 785:765–773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.271
Shi YN, Gao XH, Qiu J (2019) Synthesis and strengthened microwave absorption properties of three-dimensional porous Fe3O4/graphene composite foam. Ceram Int 45:3126–3132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.10.212
Sun QL, Sun L, Cai YY, Ye W, Xu SJ, Ji T, Yuan GJ (2019) Fe3O4-intercalated reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites with enhanced microwave absorption properties. Ceram Int 45:18298–18305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.06.042
Jia ZR, Gao ZG, Kou KC, Feng AL, Zhang CH, Xu BH, Wu GL (2020) Facile synthesis of hierarchical A-site cation deficiency perovskite LaxFeO3-y/RGO for high efficiency microwave absorption. Comput Commun 20:100344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2020.04.010
Randjelović MS, Momčilović MZ, Enke D, Mirčeski V (2019) Electrochemistry of hydrogen peroxide reduction reaction on carbon paste electrodes modified by Ag- and Pt-supported carbon microspheres. J Solid State Electrochem 23:1257–1267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-019-04226-4
Yan TN, Xu JL, Chu ZY, Liu EH, Yang L, Wang CH (2017) Hydrothermal synthesis and electrochemical properties of N-doped activated carbon microspheres. Int J Electrochem Sci 12:6118–6128. https://doi.org/10.20964/2017.07.20
Cui M, Ren S, Zhao H, Xue Q, Wang L (2018) Polydopamine coated graphene oxide for anticorrosive reinforcement of water-borne epoxy coating. Chem Eng J 335:255–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.172
Rathnayake RMNM, Wijayasinghe HWMAC, Pitawala HMTGA, Yoshimura M, Huang HH (2017) Synthesis of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide by needle platy natural vein graphite. Appl Surf Sci 393:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.10.008
Lv HL, Ji GB, Liu W, Zhang HQ, Du YW (2015) Achieving hierarchical hollow Carbon@Fe@Fe3O4 nanospheres with superior microwave absorption properties and lightweight features. J Mater Chem C 3:10232–10241. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TC02512E
Kuang B, Song W, Ning M, Li J, Zhao Z, Guo D, Cao M, Jin H (2018) Chemical reduction dependent dielectric properties and dielectric loss mechanism of reduced graphene oxide. Carbon 127:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.10.092
Li YZ, Zhang YF, Zhang HR, Xing TL, Chen GQ (2019) A facile approach to prepare a flexible sandwich-structured supercapacitor with rGO-coated cotton fabric as electrodes. RSC Adv 9(8):4180–4189. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra00171a
Fu XY, Liu L, Yu YF, Lv HJ, Zhang Y, Hou SL, Chen AB (2019) Hollow carbon spheres/hollow carbon nanorods composites as electrode materials for supercapacitor. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 101:244–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.04.043
Wang X, Wang XJ, Zhao JF, Song JK, Su CL, Wang ZC (2018) Surface modified TiO2 floating photocatalyst with PDDA for efficient adsorption and photocatalytic inactivation of microcystis aeruginosa. Water Res 131:320–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.062
Li ZW, Mi HY, Liu L, Bai ZY, Zhang JP, Zhang Q, Qiu JS (2018) Nano-sized ZIF-8 anchored polyelectrolyte-decorated silica for nitrogen-rich hollow carbon shell frameworks toward alkaline and neutral supercapacitors. Carbon 136:176–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.04.075
Du J, Liu L, Yu YF, Zhang Y, Chen AB (2019) N-doping carbon sheet and core-shell mesoporous carbon sphere composite for high-performance supercapacitor. J Ind Eng Chem 76:450–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.04.012
Sheng HZ, Shao L, Chen JJ, Bao WJ, Wang FB, Xia XH (2011) Catalyst-free synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene via thermal annealing graphite oxide with melamine and its excellent electrocatalysis. ACS Nano 5(6):4350–4358. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn103584t
Xiang YF, Banks MK, Wu RX, Xu WJ, Chen S (2018) Synthesis of thermo-sensitive PDDA-co-PNIPAM/graphene hybrid via electrostatic interactions and its thermal modulated phase transition. Mater Chem Phys 220:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.08.070
Yang DQ, Rochette JF, Sacher E (2005) Spectroscopic evidence for π–π interaction between poly (diallyl dimethylammonium) chloride and multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem B 109:4481–4484. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp044511+
Mohamadi M, Kowsari E, Asl VH, Yousefzadeh M, Chinnappan A, Ramakrishna S (2020) Highly-efficient microwave absorptivity in reduced graphene oxide modified with PTA@ imidazolium based dicationic ionic liquid and fluorine atom. Compos Sci Technol 188:107960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.107960
Wang G, Zhang M, Chen D, Chen D, Guo QL, Feng XF, Niu TC, Liu XS et al (2018) Seamless lateral graphene p–n junctions formed by selective in situ doping for high-performance photodetectors. Nat Commun 9:5168. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07555-6
Zhang YL, Wang XX, Cao MS (2018) Confinedly implanted NiFe2O4-rGO: cluster tailoring and highly tunable electromagnetic properties for selective-frequency microwave absorption. Nano Res 11:1426–1436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1758-1
Yang HB, Ye T, Lin Y, Liu M (2015) Excellent microwave absorption property of ternary composite: Polyaniline-BaFe12O19–CoFe2O4 powders. J Alloy Compd 653:135–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.08.272
Tian CH, Du YC, Xu HY, Xue JL, Chu WL, Qiang R, Han XJ, Xu P (2017) Differential shrinkage induced formation of yolk-shell carbon microspheres toward enhanced microwave absorption. Appl Phys Lett 111(13):133103. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4989750
Liu W, Tan SJ, Yang ZH, Ji GB (2018) Hollow graphite spheres embedded in porous amorphous carbon matrices as lightweight and low-frequency microwave absorbing material through modulating dielectric loss. Carbon 138:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.06.009
Quan B, Liang X, Ji G, Lv J, Dai S, Xu G, Du Y (2017) Laminated graphene oxide-supported high-efficiency microwave absorber fabricated by an in situ growth approach. Carbon 129:310–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.12.026
Li DP, Sun YC, Wang X, Wu S, Han SC, Yang Y (2017) Development of a hollow carbon sphere absorber displaying the multiple-reflection effect to attenuate electromagnetic waves. RSC Adv 7(60):37983–37989. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra04547f
Shu RW, Li WJ, Wu Y, Zhang JB, Zhang GY (2019) Nitrogen-doped Co-C/MWCNTs nanocomposites derived from bimetallic metal-organic frameworks for electromagnetic wave absorption in the X-band. Chem Eng J 362:513–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.090
Wang Y, Wu XM, Zhang WZ, Luo CY, Li JH, Wang YJ (2018) Fabrication of flower-like Ni0.5Co0.5(OH)2@PANI and its enhanced microwave absorption performances. Mater Res Bull 98:59–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.10.004
Wu GL, Zhang HX, Luo XX, Yang LJ, Lv HL (2019) Investigation and optimization of Fe/ZnFe2O4 as a wide-band electromagnetic absorber. J Colloid Interface Sci 536:548–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.10.084
Dong S, Zhang XH, Hu PT, Zhang WZ, Han JC, Hu P (2019) Biomass-derived carbon and polypyrrole addition on SiC whiskers for enhancement of electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem Eng J 359:882–893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.101
Wang Y, Du YC, Qiang R, Tian CH, Xu P, Han XJ (2016) Interfacially engineered sandwich-like rGO/carbon microspheres/rGO composite as an efficient and durable microwave absorber. Adv Mater Interfaces 3(7):1500684. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201500684
Wang L, Huang Y, Huang HJ (2014) Synthesis and high-performance microwave absorption of graphene foam/polyaniline nanorods. Mater Lett 124:89–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.11.116
Li G, Xie TS, Yang SL, Jin JH, Jiang JM (2012) Microwave absorption enhancement of porous carbon fibers compared with carbon nanofibers. J Phys Chem C 116(16):9196–9201. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp300050u
Zhang HX, Wang BB, Feng AL, Zhang N, Jia ZR, Huang ZY, Liu XH, Wu GL (2019) Mesoporous carbon hollow microspheres with tunable pore size and shell thickness as efficient electromagnetic wave absorbers. Compos Part B 167:690–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.03.055
Feng AL, Jia ZR, Zhao Y, Lv HL (2018) Development of Fe/ Fe3O4@C composite with excellent electromagnetic absorption performance. J Alloy Compd 745:547–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.02.255
Wu JM, Ye ZM, Liu WX, Liu ZF, Chen J (2017) The effect of GO loading on electromagnetic wave absorption properties of Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide hybrids. Ceram Int 43:13146–13153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.07.007
Qiu S, Lyu HL, Liu JR, Liu YZ, Wu NN, Liu W (2016) Facile synthesis of porous nickel/carbon composite microspheres with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption by magnetic and dielectric losses. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 82:0258–20266. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b03159
Xia L, Zhang XY, Yang YN, Zhang J, Zhang B, Wang HT (2018) Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties of laminated SiCNW-Cf/lithium–aluminum–silicate (LAS) composites. J Alloy Compd 748:154–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.044
Shu RW, Zhang GY, Zhang JB, Wang X, Wang M, Gan Y, Shi JJ, He J (2018) Fabrication of reduced graphene oxide/multi-walled carbon nanotubes/zinc ferrite hybrid composites as high-performance microwave absorbers. J Alloy Compd 736:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.11.084
Chen XL, Wang W, Shi T, Wu GL, Lu Y (2020) One pot green synthesis and EM wave absorption performance of MoS2@nitrogen doped carbon hybrid decorated with ultrasmall cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Carbon 163:202–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.03.005
Liu PJ, VMH N, Yao ZJ, Zhou JT, Lei YM, Yang ZH, Kong LB, (2017) Microwave absorption properties of double-layer absorbers based on Co0.2Ni0.4Zn0.4 Fe2O4 ferrite and reduced graphene oxide composites. J Alloy Compd 701:841–849. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-017-0612-5
Liu PB, Zhang YQ, Yan J, Huang Y, Xia L, Guang ZX (2019) Synthesis of lightweight N-doped graphene foams with open reticular structure for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem Eng J 368:285–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.193
Cole KS, Cole RH (1941) Dispersion and absorption in dielectrics I alternating current characteristics. J Chem Phys 9(4):341–351. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1750906
Li ZJ, Lin H, Ding SQ, Ling HL, Wang T, Miao ZQ, Zhang M, Meng A et al (2020) Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances of Fe3O4@C decorated walnut shell-derived porous carbon. Carbon 167:148–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.05.070
Huang Y, Yan J, Zhou SH, Yang JY, Liu PB (2018) Preparation and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of CoNi@SiO2 microspheres decorated graphene–polyaniline nanosheets. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29:70–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7889-z
Liu QH, Cao Q, Bi H, Liang CY, Yuan KP, She W, Yang YJ, Che RC (2016) CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv Mater 28(3):486–490. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201503149
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (Su Caijiao [2018] No. 192) and the Graduate Innovation Project of Nantong University College of Textiles and Clothing (FZ201909).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript. QS and YC contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Naiqin Zhao.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Q., Cai, Y., Sun, L. et al. Preparation of sandwich-like CNs@rGO nanocomposites with enhanced microwave absorption properties. J Mater Sci 56, 1492–1503 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05350-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05350-7