Abstract
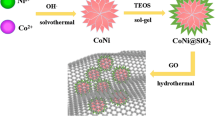
In this work, we successfully parepared the quaternary composites of CoNi@SiO2@graphene@PANI via a four-step method. The structures, chemical composition and morphologies of obtained composites are analyzed in detail. The electron microscopy results show spherical CoNi@SiO2 particles evenly dispersed into the surface of graphene@polyaniline nanosheets. The electromagnetic parameters indicate that CoNi@SiO2@graphene@PANI exhibits enhanced electromagnetic absorption properties compared to CoNi@SiO2, which can be mainly attributed to the improved impedance matching and multi-interfacial polarization. The maximum reflection loss of CoNi@SiO2@graphene@PANI can reach − 43 dB at 15.4 GHz and the absorption bandwidth with the reflection loss exceeding − 10 dB is 5.7 GHz (from 12.3 to 18 GHz) with the thickness of 2 mm. Our results demonstrate the quaternary composites composed of CoNi@SiO2 microparticles and rGO–PANI nanocomposites can serve as light weight and high-performance EM absorbing material.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Gairola, S. Gairola, V. Kumar et al., Barium ferrite and graphite integrated with polyaniline as effective shield against electromagnetic interference. Synth. Met. 221, 326–331 (2016)
W. Feng, Y. Wang, J. Chen et al., Reduced graphene oxide decorated with in situ growing ZnO nanocrystals: facile synthesis and enhanced microwave absorption properties. Carbon 108, 52–60 (2016)
X. Zhang, Y. Huang, P. Liu, Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanofibe-decorated graphene sheets by non-covalent interactions. Nano Micro Lett. 8, 131–136 (2016)
Q. Liu, Q. Cao, X. Zhao et al., Insights into size-dominant magnetic microwave absorption properties of CoNi microflowers via off-axis electron holography. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 4233–4240 (2015)
Y. Wang, W. Zhang, C. Luo et al., Superparamagnetic FeCo@SnO2 nanoparticles on graphene–polyaniline: synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Ceram. Int. 42, 12496–12502 (2016)
J. Yan, Y. Huang, P. Liu et al., Large-scale controlled synthesis of magnetic FeCo alloy with different morphologies and their high performance of electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. 28, 3159–3167 (2017)
B. Qu, C. Zhu, C. Li, X. Zhang et al., Coupling hollow Fe3O4–Fe nanoparticles with graphene sheets for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 3730–3735 (2016)
T. Wang, Z. Liu, M. Lu et al., Graphene–Fe3O4 nanohybrids: synthesis and excellent electromagnetic absorption properties. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 024314 (2013)
Y. Ren, C. Zhu, S. Zhang et al., Three-dimensional SiO2@ Fe3O4 core/shell nanorod array/graphene architecture: synthesis and electromagnetic absorption properties. Nanoscale 5, 12296–12303 (2013)
Y. Wang, W. Zhang, X. Wu et al., Conducting polymer coated metal-organic framework nanoparticles: facile synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic absorption properties. Synth. Met. 228, 18–24 (2017)
M. Rafique, L. Pan, A. Farid, From nano-dendrite to nano-sphere of Co100–xNix alloy: composition dependent morphology, structure and magnetic properties. J. Alloys Compd. 656, 443–451 (2016)
A. Hajalilou, S. Mazlan, A review on preparation techniques for synthesis of nanocrystalline soft magnetic ferrites and investigation on the effects of microstructure features on magnetic properties. Appl. Phys. A 122, 1–15 (2016)
S. Yan, L. Zhen, C. Xu et al., Microwave absorption properties of FeNi3 submicrometre spheres and SiO2@FeNi3 core–shell structures. J. Phys. D 43, 245003 (2010)
Y. Yang, Z. Li, C. Neo et al., Model design on calculations of microwave permeability and permittivity of Fe/SiO2 particles with core/shell structure. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 75, 230–235 (2014)
N. Li, C. Hu, M. Cao, Enhanced microwave absorbing performance of CoNi alloy nanoparticles anchored on a spherical carbon monolith. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 7685–7689 (2013)
R. Qiang, Y. Du, H. Zhao et al., Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C nanocubes toward efficient microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 13426–13434 (2015)
Y. Lü, Y. Wang, H. Li et al., MOF-derived porous Co/C nanocomposites with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 13604–13611 (2015)
J. Yuan, Q. Liu, S. Li et al., Metal organic framework (MOF)-derived carbonaceous Co3O4/Co microframes anchored on RGO with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances. Synth. Met. 228, 32–40 (2017)
M. Abbas, M. Islam, B.P. Rao, et al., Facile approach for synthesis of high moment Fe/ferrite and FeCo/ferrite core/shell nanostructures. Mater. Lett. 139, 161–164 (2015)
Y. Xu, G. Shen, H. Wu et al., Double-layer microwave absorber based on nanocrystalline CoFe2O4 and CoFe2O4/PANI multi-core/shell composites. Mater. Sci. Poland 35, 94–104 (2017)
Z. Zhu, An overview of carbon nanotubes and graphene for biosensing applications. Nano Micro Lett. 9, 25 (2017)
M. Han, X. Yin, Z. Hou et al., Flexible and thermostable graphene/SiC nanowire foam composites with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 11803–11810 (2017)
J. Yan, Y. Huang, C. Wei et al., Covalently bonded polyaniline/graphene composites as high-performance electromagnetic (EM) wave absorption materials, Compos. A 99, 121–128 (2017)
Y. Wang, Y. Fu, X. Wu et al., Synthesis of hierarchical core-shell NiFe2O4@MnO2 composite microspheres decorated graphene nanosheet for enhanced microwave absorption performance. Ceram. Int. 43, 11367–11375 (2017)
W. Hummers, R. Offeman, Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80, 1339 (1958)
M. Xue, F. Li, J. Zhu et al., Structure-based enhanced capacitance: in situ growth of highly ordered polyaniline nanorods on reduced graphene oxide patterns. Adv. Funct. Mater 22, 1284–1290 (2012)
Y. Yao, J. Zhang, L. Xue et al., Carbon-coated SiO2 nanoparticles as anode material for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 196, 10240–10243 (2012)
P. Liu, Y. Huang, J. Yan et al., Construction of CuS nanoflakes vertically aligned on magnetically decorated graphene and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 5536–5546 (2016)
J. An, J. Liu, Y. Zhou et al., Polyaniline-grafted graphene hybrid with amide groups and its use in supercapacitors. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 19699–19708 (2016)
P. Liu, Y. Huang, J. Yan et al., Magnetic graphene@PANI@ porous TiO2 ternary composites for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 6362–6370 (2016)
N. Zhang, Y. Huang, P. Liu et al., Synthesis of magnetical nanoparticles decorated with reduced graphene oxide as an efficient broad band EM wave absorber. J. Alloys Compd. 692, 639–646 (2017)
Y. Wang, H. Guan, C. Dong et al., Reduced graphene oxide (RGO)/Mn3O4 nanocomposites for dielectric loss properties and electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness at high frequency. Ceram. Int. 42, 936–942 (2016)
Y. Yang, C. Xu, Y. Xia et al., Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of FeCo nanoplates. J. Alloys Compd. 493, 549–552 (2010)
A. Aharoni, Exchange resonance modes in a ferromagnetic sphere. J. Appl. Phys. 69, 7762–7764 (1991)
D. Mercier, JCS. Levy, G. Viau et al., Magnetic resonance in spherical Co–Ni and Fe–Co–Ni particles. Phys. Rev. B 62, 532 – 544 (2000)
P. Liu, Y. Huang, X. Zhang, Cubic NiFe2O4 particles on graphene–polyaniline and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 107, 54–60 (2015)
X. Ding, Y. Huang, S. Li et al., Preparation and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of FeNi3 nanoalloys generated on graphene–polyaniline nanosheets. RSC Adv 6, 31440–31447 (2016)
X. Sun, J. He, G. Li et al., Facile preparation, high microwave absorption and microwave absorbing mechanism of RGO–Fe3O4 composites. RSC Adv. 3, 23638–23648 (2013)
Y. Chen, F. Zhang, G. Zhao et al., Synthesis, multi-nonlinear dielectric resonance, and excellent electromagnetic absorption characteristics of Fe3O4/ZnO core/shell nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 9239–9244 (2010)
B. Wen, X. Wang, W. Cao et al., Reduced graphene oxides: the thinnest and most lightweight materials with highly efficient microwave attenuation performances of the carbon world. Nanoscale 6, 5754–5761 (2014)
B. Wen, M. Cao, Z. Hou et al., Temperature dependent microwave attenuation behavior for carbon-nanotube/silica composites. Carbon 65, 124–139 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51672222), the Spaceflight Innovation Foundation of China, the Spaceflight Foundation of China (2014-HT-XGD) and the Seed Foundation of Innovation and Creation for Graduate Students in Northwestern Polytechnical University (Z2017048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Yan, J., Zhou, S. et al. Preparation and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of CoNi@SiO2 microspheres decorated graphene–polyaniline nanosheets. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 70–79 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7889-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7889-z