Abstract
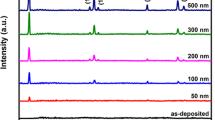
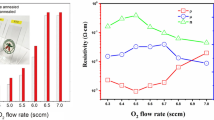
Nb-doped TiO2 (referred hereafter as NTO) thin films were deposited by sol–gel spin coating method to investigate their use as transparent conducting electrode (TCE). A range of Nb x Ti1−x O2 (x = 0, 0.003, 0.005, 0.008, 0.01, 0.015, 0.02) compositions were synthesized and deposited as thin films via spin coating. The films were deposited at room temperature and showed crystallization on annealing at 550 °C for 1 h in air. The X-ray diffraction confirms formation of anatase TiO2 by showing dominant peak at 2θ ~25.5° corresponding to (101) reflection plane. Raman spectroscopy shows the characteristics modes of TiO2. Surface topography and morphology measured by atomic force microscopy and field-emission scanning electron microscopy exhibit smooth and uniform deposition of films. Optical transmittance reduces from 85 to 70% as Nb content increases from 0 to 2 at.%. Meanwhile, electrical resistivity attained a minimum value of 3.65 Ω cm for 2 at.% Nb doping. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis exhibits shifting of Ti 2p peak which confirms substitution by Nb5+ in TiO2 lattice and Nb–O–Ti bond formation. Transmission electron microscope and selected area electron diffraction patterns reveal that films consist of Nb and crystalline phase of TiO2. All films were characterized by Fourier transmission infrared spectroscopy and thermogravimetric analysis. Present study reports low-cost and effective fabrication of TCE for optoelectronic applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chopra KL, Major S, Pandya DK (1983) Transparent conductors—a status review. Thin Solid Films 102:1–46. doi:10.1016/0040-6090(83)90256-0
Minami T (2008) Present status of transparent conducting oxide thin-film development for indium–tin-oxide (ITO) substitutes. Thin Solid Films 516:5822–5828. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2007.10.063
Ellmer K (2012) Past achievements and future challenges in the development of optically transparent electrodes. Nat Photonics 6:808–816. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2012.282
Exarhos GJ, Zhou X-D (2007) Discovery-based design of transparent conducting oxide films. Thin Solid Films 515:7025–7052. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2007.03.014
Guillén C, Herrero J (2011) TCO/metal/TCO structures for energy and flexible electronics. Thin Solid Films 520:1–17. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2011.06.091
Sharma V, Vyas R, Bazylewski P et al (2016) Probing the highly transparent and conducting SnOx/Au/SnOx structure for futuristic TCO applications. RSC Adv 6:29135–29141. doi:10.1039/C5RA24422F
Sharma V, Singh S, Asokan K, Sachdev K (2016) A study on 100 MeV O7+ irradiated SnO2/Ag/SnO2 multilayer as transparent electrode for flat panel display application. Nuclear Inst Methods Phys Res B. doi:10.1016/j.nimb.2016.04.059
Duta M, Simeonov S, Teodorescu V et al (2016) Structural and electrical properties of Nb doped TiO2 films prepared by the sol–gel layer-by-layer technique. Mater Res Bull 74:15–20. doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2015.10.009
Kasai J, Hitosugi T, Moriyama M et al (2010) Properties of TiO2-based transparent conducting oxide thin films on GaN(0001) surfaces. J Appl Phys. doi:10.1063/1.3326943
Hung KH, Lee PW, Hsu WC et al (2011) Transparent conducting oxide films of heavily Nb-doped titania by reactive co-sputtering. J Alloys Compd 509:10190–10194. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.08.020
Fallah M, Zamani-Meymian M-R, Rahimi R, Rabbani M (2014) Effect of annealing treatment on electrical and optical properties of Nb doped TiO2 thin films as a TCO prepared by sol–gel spin coating method. Appl Surf Sci 316:456–462. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.08.029
Lee JK, Jung HS, Valdez JA et al (2006) Room temperature ferromagnetism of Co doped TiO2 using ion implantation and defect engineering. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B 250:279–282. doi:10.1016/j.nimb.2006.04.171
Su H, Huang YT, Chang YH et al (2015) The synthesis of Nb-doped TiO2 nanoparticles for improved-performance dye sensitized solar cells. Electrochim Acta 182:230–237. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2015.09.072
Uyanga E, Gibaud A, Daniel P et al (2014) Structural and vibrational investigations of Nb-doped TiO2 thin films. Mater Res Bull 60:222–231. doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2014.08.035
Zhang WF, He YL, Zhang MS et al (2000) Raman scattering study on anatase TiO2 nanocrystals. J Phys D Appl Phys 33:912–916. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/33/8/305
De Trizio L, Buonsanti R, Schimpf AM et al (2013) Nb-doped colloidal TiO2 nanocrystals with tunable infrared absorption. Chem Mater 25:3383–3390. doi:10.1021/cm402396c
Parker JC, Siegel RW (1990) Raman microprobe study of nanophase TiO2 and oxidation-induced spectral changes. J Mater Res 5:1246–1252. doi:10.1557/JMR.1990.1246
Parker JC, Siegel RW (1990) Calibration of the Raman spectrum to the oxygen stoichiometry of nanophase TiO2. Appl Phys Lett 57:943–945. doi:10.1063/1.104274
Mazzolini P, Russo V, Casari CS et al (2016) Vibrational–electrical properties relationship in donor-doped TiO2 by Raman spectroscopy. J Phys Chem C 120:18878–18886. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b05282
Yang J, Zhang X, Wang C et al (2012) Solar photocatalytic activities of porous Nb-doped TiO2 microspheres prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Solid State Sci 14:139–144. doi:10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2011.11.010
Yang M, Hume C, Lee S et al (2010) Correlation between photocatalytic efficacy and electronic band structure in hydrothermally grown TiO2 nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 114:15292–15297. doi:10.1021/jp103764n
Perumal S, Sambandam GC, Prabu MK, Ananthakumar S (2014) Synthesis and characterization studies of nano TiO2 prepared via sol–gel method. Int J Res Eng Technol 3:651–657
Battiston G, Gerbasi R, Porchia M (1994) Influence of substrate on structural properties of TiO2 thin films obtained via MOCVD. Thin Solid Films 239:186–191
Sambandam CG, Mohamed AP (2014) Synthesis and characterization studies of solvothermally synthesized undoped and ag-doped TiO2 nanoparticles using toluene as a solvent. J Eng Res Appl 4:184–187
Al-taweel SS, Saud HR (2016) New route for synthesis of pure anatase TiO2 nanoparticles via utrasound-assisted sol–gel method D = β cos θ. J Chem Pharm Res 8(2):620–626
Nikolay T, Larina L, Shevaleevskiy O, Ahn BT (2011) Electronic structure study of lightly Nb-doped TiO2 electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells. Energy Environ Sci 4:1480. doi:10.1039/c0ee00678e
Gan L, Wu C, Tan Y et al (2014) Oxygen sensing performance of Nb-doped TiO2 thin film with porous structure. J Alloys Compd 585:729–733. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.09.161
Singh S, Sharma V, Sachdev K (2016) Investigation of post annealing effects on Nb:TiO2 transparent conducting thin films. Adv Sci Lett 22:3773–3776
Wang M, Gao Y, Chen Z et al (2013) Transparent and conductive W-doped SnO2 thin films fabricated by an aqueous solution process. Thin Solid Films 544:419–426. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2013.02.088
Wang Y, Smarsly BM, Djerdj I (2010) Niobium doped TiO2 with mesoporosity and its application for lithium insertion. Chem Mater 22:6624–6631. doi:10.1021/cm1020977
Sibu CP, Kumar SR, Mukundan P, Warrier KGK (2002) Structural modifications and associated properties of lanthanum oxide doped sol–gel nanosized titanium oxide. Chem Mater 14:2876–2881. doi:10.1021/cm010966p
Potlog T, Dumitriu P, Dobromir M et al (2015) Nb-doped TiO2 thin films for photovoltaic applications. Mater Des 85:558–563. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2015.07.034
Wang C, Li J, Dho J (2014) Post-deposition annealing effects on the transparent conducting properties of anatase Nb:TiO2 films on glass substrates. Mater Sci Eng B Solid-State Mater Adv Technol 182:1–5. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2013.11.021
Tauc J (1974) Optical properties of amorphous semiconductors. Amorph Liq Semicond. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-8705-7_4
Chen M, Pei ZL, Wang X et al (2000) Intrinsic limit of electrical properties. J Phys D Appl Phys 33:2538–2548
van der Pauw LJ (1958) A method of measuring the resistivity and Hall coefficient on lamellae of arbitrary shape. Philips Tech Rev 20:220–224
Liu J, Zhao X, Duan L et al (2011) Influence of annealing process on conductive properties of Nb-doped TiO2 polycrystalline films prepared by sol–gel method. Appl Surf Sci 257:10156–10160. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.07.009
Zhao L, Zhao X, Liu J et al (2010) Fabrications of Nb-doped TiO2 (TNO) transparent conductive oxide polycrystalline films on glass substrates by sol–gel method. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 53:475–479. doi:10.1007/s10971-009-2102-3
Rao CNR, Sarma DD, Vasudevan S, Hegde MS (1979) Study of transition metal oxides by photoelectron spectroscopy. Proc R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 367:239–252. doi:10.1098/rspa.1979.0085
Sanjinés R, Tang H, Berger H et al (1994) Electronic structure of anatase TiO2 oxide. J Appl Phys 75:2945–2951. doi:10.1063/1.356190
Berko A, Ulrych I, Prince KC (1998) Encapsulation of Rh nanoparticles supported on TiO2(110)-(1x1) surface: XPS and STM studies. J Phys Chem B 102:3379–3386. doi:10.1021/jp973255g
Song Z, Hrbek J, Osgood R (2005) Formation of TiO2 nanoparticles by reactive-layer-assisted deposition and characterization by XPS and STM. Nano Lett 5:1327–1332. doi:10.1021/nl0505703
Atashbar MZ, Sun HT, Gong B et al (1998) XPS study of Nb-doped oxygen sensing TiO2 thin films prepared by sol–gel method. Thin Solid Films 326:238–244
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Department of Physics, MNIT Jaipur. The authors are grateful to Materials Research Centre, MNIT Jaipur, for various fabrication and characterization facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Sharma, V. & Sachdev, K. Investigation of effect of doping concentration in Nb-doped TiO2 thin films for TCO applications. J Mater Sci 52, 11580–11591 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1328-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1328-7