Abstract
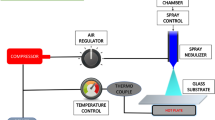
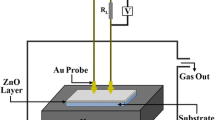
Pure and 5 % Fe-doped ZnO thin films (TFs) have been successfully deposited on Al2O3 substrate from pre-doped target material by RF magnetron sputtering technique. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns confirm the formation of both films in single phase wurtzite structure without any extra impurity peak. The calculated average crystallite sizes are found to be 22 and 17 nm for pure and Fe-doped ZnO TFs, respectively. The broadening in XRD peaks of Fe-doped ZnO TF occurs due to decrease in crystallite size and increase in lattice strain. Field emission scanning electron microscopy images exhibit that the particles growth in Fe-doped ZnO TF is more uniform and smaller than pure ZnO. Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy results confirm the existence of Fe dopants into ZnO matrix. The doping effect enhances the sensitivity of ZnO sensor almost three times for ethanol gas sensing, the improvement in the response time and recovery time is noticeable as the size reduction effect increases the surface to volume ratio, and resulting more numbers of ethanol gas molecules are adsorbed to produce a higher concentration of oxygen ions which leads a larger deviation in capacitance.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gedamu D, Paulowicz I et al (2014) Rapid fabrication technique for interpenetrated ZnO nanotetrapod networks for fast UV sensors. Adv Mater 26:1541–1550
Jin X et al (2013) A novel concept for self-reporting materials: stress sensitive photoluminescence in ZnO tetrapod filled elastomers. Adv Mater 25:1342–1347
Mishra YK et al (2012) Crystal growth behaviour in Au-ZnO nanocomposite under different annealing environments and photoswitchability. J Appl Phys 12:064308-5
Rout CS, Raju AR, Govindaraj A et al (2007) Ethanol and hydrogen sensors based on ZnO nanoparticles and nanowires. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 7:1923–1929
Fan Z et al (2004) Photoluminescence and polarized photodetection of single ZnO nanowires. Appl Phys Lett 85:6128–6130
Xing XY, Zheng KB, Chen GR et al (2006) Synthesis and electrical properties of ZnO nanowires. Micron 37:370–373
Alenezi MR, Henley SJ et al (2014) From 1D and 2D ZnO nanostructures to 3D hierarchical structures with enhanced gas sensing properties. Nanoscale 6:235–247
Baruwati B, Kumar DK et al (2006) Hydrothermal synthesis of highly crystalline ZnO nanoparticles: a competitive sensor for LPG and EtOH. Sens Actuators B 119:676–682
Liu X, Zhang J, Wang L et al (2011) 3D hierarchically porous ZnO structures and their functionalization by Au nanoparticles for gas sensors. J Mater Chem 21:349–356
Suchea M, Christoulakis S, Moschovis K et al (2006) ZnO transparent thin films for gas sensor applications. Thin Solid Films 515:551–554
Mridha S, Basak D (2006) Investigation of a p-CuO/n-ZnO thin film heterojunction for H2 gas-sensor applications. Semicond Sci Technol 21:928–932
Wan Q, Li QH, Chen YJ, Wang TH (2004) Fabrication and ethanol sensing characteristics of ZnO nanowire gas sensors. Appl Phys Lett 84:3654–3656
Wang JX, Sun XW, Yang Y et al (2006) Hydrothermally grown oriented ZnO nanorod arrays for gas sensing applications. Nanotechnology 17:4995–4998
de Lacy Costello BPJ, Ewen RJ et al (2000) The development of a sensor system for the early detection of soft rot in stored potato tubers. Meas Sci Technol 11:1685–1691
Zeng W, Liu T, Wang ZC (2010) UV light activation of TiO2-doped SnO2 thick film for sensing ethanol at room temperature. Mater Trans 51:243–245
Ho JJ, Fang YK, Wu KH, Hsieh WT et al (1998) High sensitivity ethanol gas sensor integrated with a solid-state heater and thermal isolation improvement structure for legal drink-drive limit detecting. Sens Actuators B 50:227–233
Zhang W-H, Zhang W-D, Zhou J-F (2010) Solvent thermal synthesis and gas-sensing properties of Fe-doped ZnO. J Mater Sci 45:209–215. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3920-y
Siciliano T, Di Giulio M, Tepore M (2009) Room temperature NO2 sensing properties of reactively sputtered TeO2 thin films. Sens Actuators B 137:644–648
Mun Y, Park S et al (2013) NO2 gas sensing properties of Au-functionalized porous ZnO nanosheets enhanced by UV irradiation. Ceram Int 39:8615–8622
Mishra YK, Kaps S et al (2013) Fabrication of macroscopically flexible and highly porous 3D semiconductor networks from interpenetrating nanostructures by a simple flame transport approach. Part Part Syst Charact 30:775–783
Han N, Chai L, Wang Q et al (2010) Evaluating the doping effect of Fe, Ti and Sn on gas sensing property of ZnO. Sens Actuators B 147:525–530
Jebril S, Kuhlmann H et al (2010) Epitactically Interpenetrated High Quality ZnO Nanostructured Junctions on Microchips Grown by the Vapor− Liquid− Solid Method. Cryst Growth Des 10:2842–2846
Hassan MM, Khan W et al (2014) Effect of size reduction on structural and optical properties of ZnO matrix due to successive doping of Fe ions. J Lumin 145:160–166
Gong H, Hu JQ, Wang JH, Ong CH, Zhu FR (2006) Nano-crystalline Cu-doped ZnO thin film gas sensor for CO. Sens Actuators B 115:247–251
Kim KJ, Park YR (2004) Optical investigation of Zn1−xFexO films grown on Al2O3(0001) by radio-frequency sputtering. J Appl Phys 96:4150–4153
Xu L, Li X (2010) Influence of Fe-doping on the structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel method. J Cryst Growth 312:851–855
Chen H, Gu SL, Liu W, Zhu SM, Zheng YD (2008) Influence of unintentional doped carbon on growth and properties of N-doped ZnO films. J Appl Phys 104:113511–113516
Chen SH, Yu CF et al (2008) Nanoscale surface electrical properties of aluminum zinc oxide thin films investigated by scanning probe microscopy. J Appl Phys 104:114314–114316
Sonawane BK et al (2008) Influence of post annealing on the structural andoptical properties of MgZnO films. Optoelectron Adv Mater-Rapid Commun 2:714–718
Lim SJ, Kwon SJ, Kim H, Park JS (2007) High performance thin film transistor with low temperature atomic layer deposition nitrogen-doped ZnO. Appl Phys Lett 91:183517-3
Zhang XA et al (2008) Enhancement-mode thin film transistor with nitrogen-doped ZnO channel layer deposited by laser molecular beam epitaxy. Thin Solid Films 516:3305–3308
Powder Diffraction File (2001) Joint Committee Power Diffraction Standards, ICDD, Card 36-1451. Newtown Square, PA
Cullity BD, Stock RS (2001) Elements of X-ray diffraction, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Cheng W, Ma X (2009) Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Fe-doped ZnO. J Phys Conf Ser 152:012039-7
Hassan MM, Ahmed AS, Chaman M et al (2012) Structural and frequency dependent dielectric properties of Fe3+ doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater Res Bull 47:3952–3958
Williamson GK, Hall WH (1953) X-ray line broadening from filed aluminium and wolfram. Acta Metall 1:22–31
Rambu AP et al (2013) Structure and gas sensing properties of nanocrystalline Fe-doped ZnO films prepared by spin coating method. J Mater Sci 48:4305–4312. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7245-5
Djelloul A, Aida M-S, Bougdira J (2010) Photoluminescence, FTIR and X-ray diffraction studies on undoped and Al-doped ZnO thin films grown on polycrystalline α-alumina substrates by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. J Lumin 130:2113–2117
Ivanova T, Harizanova A, Koutzarova T, Vertruyen B (2010) Study of ZnO sol–gel films: effect of annealing. Mater Lett 64:1147–1149
Hsueh TJ, Hsu CL, Chang SJ, Chen IC (2007) Laterally grown ZnO nanowire ethanol gas sensors. Sens Actuators B Chem 126:473–477
Zhu BL, Xie CS, Wang WY et al (2004) Improvement in gas sensitivity of ZnO thick film to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) by adding TiO2. Mater Lett 58:624–629
Kroger FA (1974) The chemistry of imperfect crystalls. North-Holland Publishing Co., Amsterdam, Netherlands
Sabioni ACS et al (2003) Comparative study of high temperature oxidation behaviour in AISI 304 and AISI 439 stainless steels. Mater Res 6:173–185
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Council of Science & Technology (CST), Govt. of UP, India for financial support to Centre of Excellence in Materials Science (Nanomaterials). One of the authors (M. Mehedi Hassan) is thankful to the University Grants Commission (UGC) for providing financial support in the form of Maulana Azad National Fellowship. The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by Ministry of Communication and Information Technology (MCIT), Govt. of India to Nano-Sensor Research Laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, M.M., Khan, W., Naqvi, A.H. et al. Fe dopants enhancing ethanol sensitivity of ZnO thin film deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. J Mater Sci 49, 6248–6256 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8349-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8349-2