Abstract
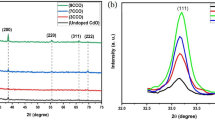
Influence of terbium (Tb) doping on structural, optical and morphological properties of radio frequency magnetron-sputtered ZnO films has been investigated using various characterization techniques. Investigations revealed the formation of hexagonal wurtzite structure of ZnO with preferential c-axis orientation, presence of oxygen vacancies, modification of surface morphology and surface roughness, and confirmation of oxidation states of elements present in ZnO and Tb-doped ZnO films. Subsequently, films deposited with varied Tb concentrations have been tested for ethanol vapor sensing. Doped films exhibited reduction in optimum operable temperature, enhancement in ethanol sensing response and improvement in response/recovery time in comparison with pristine ZnO. The observed improvement in doped samples has been attributed to modifications in surface properties such as morphology, surface roughness, basicity, structural disorder and oxygen vacancies introduced due to dopant incorporation.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang SL, Lim JO, Huh JS, Lee W (2012) Selective growth of ZnO nanorods and its gas sensor application. IEEE Sens J 12:3143–3148
Lupan O, Postica V, Grottrup J, Mishra AK, Leeuw NHD, Adelung R (2017) Enhanced UV and ethanol vapour sensing of the single 3-D ZnO tetrapod alloyed with Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Sens Actuators, B 245:448–461
Aswal DK, Gupta SK (2006) Science and technology of chemiresistor gas sensors. Nova Science Publishers, New York
Xu M, Li Q, Ma Y, Fan H (2014) Ni-doped ZnO nanorods gas sensor: enhanced gas-sensing properties, AC and DC electrical behaviours. Sens Actuators, B 199:403–409
Singh RC, Singh MP, Singh O, Chandi PS, Kumar R (2011) Effect of 100 MeV O 7 + ions irradiation on ethanol sensing response of nanostructures of ZnO and SnO2. Appl Phys A 98:161–166
Yoo R, Yoo S, Lee D, Kim J, Cho S, Lee W (2017) Highly selective detection of dimethyl methylphosphonate (DMMP) using CuO nanoparticles/ZnO flowers heterojunction. Sens Actuators, B 240:1099–1105
Yoo R, Cho S, Song MJ, Lee W (2015) Highly sensitive gas sensor based on Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles for detection of dimethyl methylphosphonate as a chemical warfare agent simulant. Sens Actuators, B 221:217–223
Holken I, Neubuser G, Postica V, Bumke L, Lupan O, Baum M, Mishra YK, Kienle L, Adelung R (2016) Sacrificial template synthesis and properties of 3-D hollow-silicon nano- and microstructures. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:20491–20498
Lupan O, Cretu V, Postica V, Ahmadi M, Cuenya BR, Chow L, Tiginyanu I, Viana B, Pauporte T, Adelung R (2016) Silver-doped zinc oxide single nanowire multifunctional nanosensor with a significant enhancement in response. Sens Actuators, B 223:893–903
Soleimanpour AM, Hou Y, Jayatissa AH (2011) The effect of UV irradiation on nanocrystalline zinc oxide thin films related to gas sensing characteristics. Appl Surf Sci 257:5398–5402
Woo HS, Kwak CH, Chung JH, Lee JH (2015) Highly selective and sensitive xylene sensors using Ni-doped branched ZnO nanowire networks. Sens Actuators, B 216:358–366
Hastir A, Kohli N, Kang OS, Singh RC (2016) Selective liquefied petroleum gas sensor based on nanocomposites of zinc chromium oxide. J Electroceram 37:170–178
Hjiri M, El Mir, Leonardi SG, Pistone A, Mavilia L, Neri G (2014) Al-doped ZnO for highly sensitive CO gas sensors. Sens Actuators, B 196:413–420
Dar GN, Umar A, Zaidi SA, Ibrahim AA, Abaker M, Baskoutas S, Al-Assiri MS (2012) Ce-doped ZnO nanorods for the detection of hazardous chemical. Sens Actuators, B 173:72–78
Shide W, Chao L, Wei W, Huanxin W, Yangliang S, Youqi Z, Lingzhen L (2010) Nd-doped SnO2: characterization and its gas sensing property. J Rare Earths 28:171–173
Matsuura M, Goto R, Tezuka N, Sugimoto S (2010) Influence of Nd oxide phase on the coercivity of Nd-Fe-B thin films. Mater Trans 51:1901–1904
Singh S, Singh A, Yadav BC, Dwivedi PK (2013) Fabrication of nano-beads structured perovskite type neodymium iron oxide film: its structural, optical, electrical and LPG sensing investigations. Sens Actuators, B 177:730–739
Tan TTY (2012) Rare earth nanotechnology. Taylor & Francis Group, LLC, London
Hastir A, Kohli N, Singh RC (2017) Comparative study on gas sensing properties of rare earth (Tb, Dy and Er) doped ZnO sensor. J Phys Chem Solids 105:23–34
Yang L, Tang Y, Hu A, Chen X, Liang K, Zhang L (2008) Raman scattering and luminescence study on arrays of ZnO doped with Tb3+. Phys B 403:2230–2234
Hastir A, Kohli N, Singh RC (2016) Temperature dependent selective and sensitive terbium doped ZnO nanostructures. Sens Actuators, B 231:110–119
Mirzaei A, Janghorban K, Hashemi B, Bonyani M, Leonardi SG, Neri G (2016) Highly stable and selective ethanol sensor based on α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles prepared by Pechini sol–gel method. Ceram Int 42:6136–6144
Occupational Safety and Health Administration United States Department of Labour (2012) https://www.osha.gov/dts/chemicalsampling/data/CH_239700.html
Maity A, Majumder SB (2015) NO2 sensing and selectivity characteristics of tungsten oxide thin films. Sens Actuators, B 206:423–429
Nigro RL, Toro RG, Malandrino G, Fragala IL, Fiorenza P, Raineri V (2007) Chemical stability of CaCu3Ti4O12 thin films grown by MOCVD on different substrates. Thin Solid Films 515:6470–6473
Park S, An S, Ko H, Jin C, Lee C (2013) Enhancement of ethanol sensing of TeO2 nanorods by Ag functionalization. Curr Appl Phys 13:576–580
Bao L, Ryley J, Li Z, Wilker C, Zhang L, Reardon D, Opila RL (2009) Conduction mechanism of sputtered BaTiO3BaTi3 film on Ni substrate. J Appl Phys 106:114114
Swann S (1988) Magnetron sputtering. Phys Technol 19:67
Singh O, Singh RC (2012) Enhancement in ethanol sensing response by surface activation of ZnO with SnO2. Mater Res Bull 47:557–561
Phan TL, Yu SC, Vincent R, Bui HM, Thanh TD, Lam VD, Lee YP (2010) Influence of Mn doping on structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Zn1−x MnxO nanorods. J Appl Phys 108:044910
Muchuweni E, Sathiaraj TS, Nyakotyo H (2016) Effect of gallium doping on the structural, optical and electrical properties of zinc oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Ceram Int 42:10066–10070
Lupan O, Postica V, Ababii N, Hoppe M, Cretu V, Tiginyanu I, Sontea V, Pauporte Th, Viana B, Adelung R (2016) Influence of CuO nanostructures morphology on hydrogen gas sensing performances. Microelectron Eng 164:63–70
Mosquera E, Michea CR, Morela M, Gracia F, Fuenzalida V, Zarated RA (2015) Zinc oxide nanoparticles with incorporated silver: structural, morphological, optical and vibrational properties. Appl Surf Sci 347:561–568
Teng XM, Fan HT, Pan SS, Ye C, Lia GH (2006) Influence of annealing on the structural and optical properties of ZnO: Tb thin films. J Appl Phys 100:053507
Mosquera E, Bernal J, Zarate RA, Mendoza F, Katiyar RS, Morell G (2013) Growth and electron field-emission of single-crystalline ZnO nanowires. Mater Lett 93:326–329
Shaabana ER, Yahiab IS, Metwallyc EGE (2012) Validity of Swanepoel’s method for calculating the optical constants of thick films. Acta Phys Pol, A 121:628
Dorranian D, Dejam L, Dorranian GM et al (2012) Optical characterization of Cu3N thin film with Swanepoel method. J Theor Appl Phys 6:13
Khallaf H, Chai G, Lupan O, Heinrich H, Park S, Schulte A, Chow L (2009) Investigation of chemical bath deposition of ZnO thin films using six different complexing agents. J Phys D Appl Phys 42:135304
Bhargava R, Sharma PK, Kumar S, Pandey AC, Kumar N (2010) Consequence of doping mediated strain and the activation energy on the structural and optical properties of ZnO: Cr nanoparticles. J Solid State Chem 183:1400–1408
Pal PP, Manam J (2013) Photoluminescence and thermoluminescence studies of Tb3+ doped ZnO nanorods. Mater Sci Eng, B 178:400–408
Pal SM, Bera S, Sarkar S, Sunirmal J (2014) Influence of Al doping on microstructural optical and photo-catalytic properties of sol–gel based nanostructured zinc oxide films on glass. RSC Adv 4:11552–11563
Bandopadhyay K, Mitra J (2015) Zn interstitials and O vacancies responsible for n-type ZnO: what do the emission spectra reveal? RSC Adv 5:23540–23547
Moulder JF, Strickle WF, Sobol PE, Bomben KD (1995) Handbook of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. ULVAC-PHI, Inc., Chigasaki
Kumar V, Som S, Kumar V, Kumar V, Ntwaeaborwa OM, Coetsee E, Swart HC (2014) Tunable and white emission from ZnO: Tb3+ nanophosphors for solid state lighting applications. Chem Eng J 255:541–552
Chen M, Wang X, Yu YH, Pei ZL, Bai XD, Sun C, Huang RF, Wen LS (2000) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and auger electron spectroscopy studies of Al-doped ZnO films. Appl Surf Sci 158:134–140
Kumar V, Kumar V, Som S, Duvenhage MM, Ntwaeaborwa OM, Swart HC (2014) Effect of Eu doping on the photoluminescence properties of ZnO nanophosphors for red emission applications. Appl Surf Sci 308:419–430
Kohli N, Singh O, Singh RC (2011) Influence of pH on particle size and sensing response of chemically synthesized chromium oxide nanoparticles to alcohols. Sens Actuators, B 158:259–264
Mishra RK, Kushwaha A, Sahay PP (2014) Influence of Cu doping on the structural, photoluminescence and formaldehyde sensing properties of SnO2 nanoparticles. RSC Adv 4:3904–3912
Zhang SL, Lim JO, Huh JS, Noh JS, Lee W (2013) Two-step fabrication of ZnO nanosheets for high-performance VOCs gas sensor. Curr Appl Phys 13:S156–S161
Postica V, Holken I, Schneider V, Kaidas V, Polonskyi O, Cretu V, Tiginyanu I, Faupel F, Adelung R, Lupan O (2016) Multifunctional device based on ZnO: Fe nanostructured films with enhanced UV and ultra-fast ethanol vapour sensing. Mater Sci Semicond Process 49:20–33
Chen J, Yan X, Liu W, Xue Q (2011) The ethanol sensing property of magnetron sputtered ZnO thin films modified by Ag ion implantation. Sens Actuators, B 160:1499–1503
Zheng K, Gu L, Sun D, Mo XL, Chen G (2010) The properties of ethanol gas sensor based on Ti doped ZnO nanotetrapods. Mater Sci Eng, B 166:104–107
Chou SM, Teoh LG, Lai WH, Su YH, Hon MH (2006) ZnO: Al thin film gas sensor for detection of ethanol vapor. Sensors 6:1420–1427
Kuo GH, Wang HP, Hsu HH, Wang J, Chiu YM, Jou CJG, Hsu TF, Chen FL (2009) Sensing of ethanol with nanosize Fe-ZnO thin films. J Nanomater. doi:10.1155/2009/316035
Hassan MM, Khan W, Naqvi AH, Mishra P, Islam SS (2014) Fe dopants enhancing ethanol sensitivity of ZnO thin film deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. J Mater Sci 49:6248–6256. doi:10.1007/s10853-014-8349-2
Rambu AP, Doroftei C, Ursu L, Iacomi F (2013) Structure and gas sensing properties of nanocrystalline Fe-doped ZnO films prepared by spin coating method. J Mater Sci 48:4305–4312. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7245-5
Sivalingam D, Gopalakrishnan JB, Rayappan JBB (2012) Structural, morphological, electrical and vapour sensing properties of Mn doped nanostructured ZnO thin films. Sens Actuators, B 166–167:624–631
Tarwal NL, Rajgure AV, Patil JY, Khandekar MS, Suryavanshi SS, Patil PS, Gang MG, Kim JH, Jang JH (2013) A selective ethanol gas sensor based on spray-derived Ag–ZnO thin films. J Mater Sci 48:7274–7282. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7547-7
Stambolova I, Konstantinov K, Vassilev S, Peshev P, Tsacheva T (2000) Lanthanum doped SnO2 and ZnO thin films sensitive to ethanol and humidity. Mater Chem Phys 63:104–108
Cheong HW, Lee MJ (2006) Sensing characteristics and surface reaction mechanism of alcohol sensors based on doped SnO2. J Ceram Process Res 7:183–191
Sharma RK, Bhatnagar MC, Sharma GL (1997) Mechanism of highly sensitive and fast response Cr doped TiO2 oxygen gas sensor. Sens Actuators, B 45:209–215
Acknowledgements
Anita Hastir would like to acknowledge financial support from the INSPIRE Fellowship, Department of Science & Technology, India, and USIEF for providing Fulbright-Nehru Doctoral Fellowship. Thanks to University of Delaware, USA, and UGC-UPE, India, DST-FIST, India, for providing instrumental facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure. S1
Schematic of sensing unit. (a) Testing chamber and (b) data acquisition system where RL is load resistance and RS is sensor resistance (DOCX 27 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hastir, A., Opila, R.L., Kohli, N. et al. Deposition, characterization and gas sensors application of RF magnetron-sputtered terbium-doped ZnO films. J Mater Sci 52, 8502–8517 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1059-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1059-9