Abstract
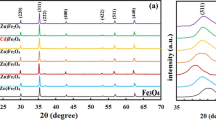
Preparation and electrical properties of sintered bodies consisting of monophase cubic spinel oxides, Mn(2.25-X)FeXNi0.75O4 (0≦X≦2.25), were investigated. Sintered bodies with monophase cubic spinel structure were prepared by heat-treatment for 48 h in air at 1000 °C and/or 1200 °C to convert them into a cubic spinel structure after sintering at 1400 °C in Ar. The relationship between ln (σ) and T −1 was expressed as straight lines for all compositions, indicating that these oxides have intrinsic NTC thermistor characteristics. Here, σ is electrical conduction. The relationship of the specimens in the region of 0≦X≦2.125 was seen to consist of two straight lines with slightly different slopes. Turning points were observed near 300 °C. It was thought that the carrier concentration changed based on the disproportionation reaction of Mn3+ in the octahedral site (B site) of the spinel structure. For specimens with X below 1.5, the electrical conduction was considered to be mainly due to an electron jump between Mn3+ and Mn4+ in the B site. For specimens with X above 1.875, the conduction was considered to be mainly due to an electron jump between Fe2+ and Fe3+ in the B site. It was found that the activation energy of the mobility between Fe ions is lower than that between Mn ions. The electrical conduction of the sintered bodies was concluded to be controlled by a small polaron hopping mechanism.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Yokoyama, K. Kondo, K. Komeya, T. Meguro, Y. Abe, T. Sasamoto, J. Mater. Sci. 30, 1845 (1995)
T. Yokoyama, Y. Abe, T. Meguro, K. Komeya, K. Kondo, S. Kaneko, T. Sasamoto, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 35, 5775 (1996)
T. Yokoyama, T. Meguro, K. Kato, S. Okazaki, D. Ito, J. Tatami, T. Wakihara, K. Komeya, J. Electroceram. 31, 353 (2013)
T. Yokoyama, K. Kato, T. Meguro, J. Tatami, T. Wakihara, K. Komeya, S. Okazaki, D. Ito, J. Ceram. Processing Research 16, 531 (2015)
T. Yokoyama, R. Ichida, S. Morimoto, S. Okazaki, D. Ito, Y. Koshiba, T. Meguro, Mater. Sci. Tech. Jpn. 49, 276 (2012)
E. J. W. Verwey, E. L. Heilmann, J. Chem. Phys. 15, 174 (1947)
A. P. B. Sinha, N. R. Sanjana, A. B. Biswas, Acta Cryst 10, 439 (1957)
F. S. Galasso, International series of monographs in solid state physics, volume 7, structure and properties of inorganic solids (Pergamon Press Inc., Oxford, 1970), p. 211
P. A. Cox, The electronic structure and chemistry of solids (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1987), p. 166
T. Yokoyama, Y. Kumashiro, Y. Abe, T. Meguro, K. Komeya, J. Aust. Ceramic Soc. 34, 30 (1998)
S. E. Dorris, T. O. Mason, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 71, 379 (1988)
N. Cusack, P. Kendall, Proc. Phys. Soc. 72, 898 (1958)
R. D. Shannon, Acta Cryst. A32, 751 (1976)
G. H. Jonker, S. Van Houten, In Halbleiterprobleme, ed. By F. S. Köhn (Frieder Vieweg & Sohn, Braunschweing, 1961), p. 118
S. Okamoto, K. Kohn, Magunetoseramikkusu, ed. By T. Yamaguchi and H. Yanagida (Gihodosyuppan, Tokyo, 1985), p. 9
P. A. Cox, The electronic structure and chemistry of solids (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1987), p. 134
T. Kaino, R. Kanno, Zairyokagaku-kisotooyo- (Totyokagakudojin, Tokyo, 2008), p. 115
Y. Ikuhara, C. Ohtsuki, M. Kusunoki, K. Koumoto, M. Gomi, K. Tanaka, T. Tsurumi, A. Nakahira, A. Matsuda, M. Miyayama, Mukikinozairyo, ed. By K. Koumoto (Totyokagakudojin, Tokyo, 2009) p. 127
S. P. Mitoff, Progr. Ceram. Sci. 4, 217 (1966)
G. W. Rathenad, J. B. Goodenough, J. Appl. Phys. 39, 403 (1968)
J. B. Goodenough, Progr. Solid State Chem. 5, 145 (1971)
φ. Johannesen, P. Kofstad, J. Mater. Educ. 7, 915 (1985)
P. A. Cox, The electronic structure and chemistry of solids (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1987), p. 195
A. J. Moulson, J. M. Herbert, Electroceramics (John Wiley & Sons Ltd., England, 2003), p. 5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yokoyama, T., Yamazaki, A., Meguro, T. et al. Preparation and electrical properties of sintered bodies composed of Mn(2.25-X)FeXNi0.75O4 (0≦X≦2.25) with cubic spinel structure. J Electroceram 37, 151–157 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-016-0050-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-016-0050-1