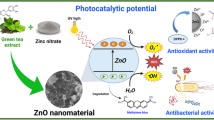
The aim of this work is to prepare and study titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) that were formed from the leaf extract of green tea using the green synthesis method. Plants were dried for seven days at room temperature and finely ground into a fine powder, after which chemical composition, HPLC analysis, characterization of TiO2 NPs, and biological evaluation processes were performed. In addition, TiO2 NPs synthesis was confirmed using UV-visible spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and highresolution–transmission electron microscope (HR–TEM). A close analysis indicates that the green tea extract contained polyphenols and flavonoids at varied levels, which may be responsible for its biological activities. HPLC examination indicates the presence of Gallic acid, Protocatechuic, p-hydroxybenzoic, Caffeine acid, Catechin, chlorogenic, rutin, coumaric acid, epicatechin gallate, apigenin-7-glucoside, ferulic acid, chrysin, quercetin, and cinnamic acid, might be responsible for their therapeutic potential. In vitro, antioxidant screening revealed that the scavenging effect of green tea extract has 50% inhibition (IC50) at a concentration level of 19.64 ± 0.13 μg/mL, whereas standard Vit. C showed that at 16.81 ± 0.10 μg/mL. However, in the case of the ABTS model, the scavenging effect of green tea extract has 50% inhibition (IC50) at a concentration level of 33.47 ± 0.21 μg/mL, whereas standard Vit. C showed the same at 29.47 ± 0.17 μg/mL. These results demonstrate that green tea is an excellent antioxidant (i.e., an effective anti-DPPH compound).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Costantini, E. Jacotot, D. Decaudin, and G. Kroemer, J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 92, No. 13, 1042–1053 (2000).
Y. Q. Liu and G. V. Lowry, Environ. Sci. Technol., 40, No. 19, 6085–6090 (2006).
N. Saleh, K. Sirk, Y. Liu, et al., Environ. Eng. Sci., 24, No. 1, 45–57 (2007).
P. Biswas and C. Y. Wu, J. Air Waste Manage Ass., 55, No. 6, 708–746 (2005).
A. D. Maynard, E. Michelson, Consumer Products Inventory, Washington D.C., Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars, 1–8 (2006).
B. R. Sankapal, M. C. Lux-Steiner, and A. Ennaoui, Appl. Surface Sci., 239, No. 2, 165–170 (2005).
O'Regan and B. M. Gratzel, Nature, 353, 737–740 (1991).
Ikezawa, Homyara, Kubota, Suzuki, S. H. Koh, R. S. Mutuga, F. Yoshioka, T. Nishiwaki, A. Ninomiya, Y. Takahashi, M. Baba, K. Kida, K. Hara, and T. Famakinwa, Thin Solid Films, 386, No. 2, 173–176 (2001).
H. Cheng, J. Ma, Z. Zhao, and L. Qi, Chem. Mater., 7, 663–671 (1995).
M. Gopal, W. J. M. Chan, and L. C. de Jonghe, J. Mater. Sci., 32, 6001–6008 (1997).
M. A. Fox and M. T. Dulay, Chem. Rev., 93, 341–357 (1993).
E. M. Paula e Silva, Ciência e Cultura, 60, 13–21 (2008).
14. G. Soler-Illia, A. Louis, and C. Sanchez, Chem. Mater., 14, No. 2, 750–759 (2002).
15. J. C. Yu, L. Z. Zhang, Z. Zheng, and J. C. Zhao, Chem. Mater., 15, No. 11, 2280–2286 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Abstract of article is published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 90, No. 5, p. 810, September–October, 2023.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saad, A.F., Selim, Y.A., Hamada, M. et al. Green Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Using Ethanolic Extract of Green Tea and Their Antioxidant Activities. J Appl Spectrosc 90, 1142–1148 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-023-01644-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-023-01644-1