Abstract
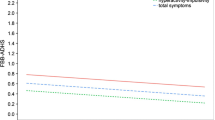
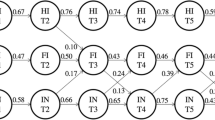
Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a complex and heterogeneous disorder consisting of inattentive and hyperactive/impulsive behaviors. Although, the multidimensionality of ADHD is widely accepted, questions remain regarding the extent to which the components of this disorder are overlapping or distinct. Further, although the same measures are generally used to assess inattentive, hyperactive, and impulsive behaviors across childhood, it has been argued that the structure and measurement of inattentive, hyperactive, and impulsive behaviors may be susceptible to developmental influences. The purpose of this study was to examine the factor structure and measurement invariance of inattentive and hyperactive/impulsive behaviors in a large group of children (N = 10,047) ranging in grade level from preschool to grade 4. A bifactor model with a general factor and two specific factors of inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity fit the data best. This finding held across all groups and all grade levels. In general, the bifactor model demonstrated measurement invariance from kindergarten through grade 4 but not for preschool. Implications for the understanding and measurement of inattentive, hyperactive, and impulsive behaviors across early and middle childhood are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The potential impact of within-grade age on the findings was examined by calculating the amount of variance in item-level scores accounted for by age within grade. With few exceptions, age accounted for less than 1% in item-level scores across items. For most items, the amount of variance accounted for by age was less than .04%. Age ranges are as follows: Preschool: 39 months to 103 months; Kindergarten: 52 months to 107 months; Grade 1: 54 months to 107 months; Grade 2: 59 months to 124 months; 66 months to 139 months; Grade 4: 95 months to 148 months.
References
American Psychiatric Association. (1968). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM- IV (4th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed., text rev.). Washington, DC: Author.
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
Arias, V. B., Ponce, F. P., Martínez-Molina, A., Arias, B., & Núñez, D. (2016). General and specific attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder factors of children 4 to 6 years of age: An exploratory structural equation modeling approach to assessing symptom multidimensionality. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 123, 125–137. https://doi.org/10.1037/abn0000115.
Arnett, A. B., Pennington, B. F., Friend, A., Willcutt, E. G., Byrne, B., Samuelsson, S., & Olson, R. K. (2013). The SWAN captures variance at the negative and positive ends of the ADHD symptom dimension. Journal of Attention Disorders, 17, 152–162.
Barbaresi, W. J., Colligan, R. C., Weaver, A. L., Voigt, R. G., Killian, J. M., & Katusic, S. K. (2013). Mortality, ADHD, and psychosocial adversity in adults with childhood ADHD: A prospective study. Pediatrics, 131, 637–644. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2012-2354.
Biederman, J., Mick, E., & Faraone, S. V. (2000). Age-dependent decline of symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Impact of remission definition and symptom type. American Journal of Psychiatry, 5, 816–818.
Burns, G. L., Boe, B., Walsh, J. A., Sommers-Flanagan, R., & Teegarden, L. A. (2001). A confirmatory factor analysis on the DSM-IV ADHD and ODD symptoms: What is the best model for the organization of these symptoms? Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 29, 339–349. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010314030025.
Caci, H. M., Morin, A. J., & Tran, A. (2016). Teacher ratings of the ADHD-RS IV in a community sample: Results from the ChiP-ARD study. Journal of Attention Disorders, 20, 434–444. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054712473834.
Coghill, D., & Seth, S. (2011). Do the diagnostic criteria for ADHD need to change? Comments on the preliminary proposals of the DSM-5 ADHD and disruptive behavior disorders committee. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 20, 75–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-010-0142-4.
Connor, C. M., Phillips, B. M., Kim, Y.-S. G., Lonigan, C. J., Kaschak, M. P., Crowe, E., Dombek, J., & Al Otaiba, S. (2018). Examining the efficacy of targeted component interventions on language and literacy for third and fourth graders who are at risk of comprehension difficulties. Scientific Studies of Reading, 22, 462–484. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888438.2018.1481409.
DuPaul, G. J., Power, T. J., Anastopoulos, A. D., Reid, R., McGoey, K. E., & Ikeda, M. J. (1997). Teacher ratings of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder symptoms: Factor structure and normative data. Psychological Assessment, 9, 436–444. https://doi.org/10.1037/1040-3590.9.4.436.
DuPaul, G. J., Reid, R., Anastopoulos, A. D., Lambert, M. C., Watkins, M. W., & Power, T. J. (2016). Parent and teacher ratings of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms: Factor structure and normative data. Psychological Assessment, 28, 214–225. https://doi.org/10.1037/pas0000166.
Espy, K. A. (2004). Using developmental, cognitive, and neuroscience approaches to understand executive control in young children. Developmental Neuropsychology, 26, 379–384. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326942dn2601_1.
Evans, S. W., Allen, J., Moore, S., & Strauss, V. (2005). Measuring symptoms and functioning of youth with ADHD in middle schools. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 33, 695–706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-005-7648-0.
Frick, P. J., & Nigg, J. T. (2012). Current issues in the diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, oppositional defiant disorder, and conduct disorder. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 8, 77–107. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032511-143150.
Gómez, R., Vance, A., & Gómez, R. M. (2017). Validity of the ADHD bifactor model in general community samples of adolescents and adults, and a clinic-referred sample of children and adolescents. Journal of Attention Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054713480034.
Hartung, C. M., Lefler, E. K., Tempel, A. B., Armendariz, M. L., Sigel, B. A., & Little, C. S. (2010). Halo effects in ratings of ADHD and ODD: Identification of susceptible symptoms. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 32, 128–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-009-9135-3.
Hu, L. T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 6, 1–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705519909540118.
Lahey, B. B., Pelham, W. E., Loney, J., Lee, S. S., & Willcutt, E. (2005). Instability of the DSM-IV subtypes of ADHD from preschool through elementary school. Archives of General Psychiatry, 62, 896–902. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.62.8.896.
Lakes, K. D., Swanson, J. M., & Riggs, M. (2012). The reliability and validity of the English and Spanish strengths and weaknesses of ADHD and Normal behavior rating scales in a preschool sample continuum measures of hyperactivity and inattention. Journal of Attention Disorders, 16, 510–516. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054711413550.
Larsson, H., Dilshad, R., Lichtenstein, P., & Barker, E. D. (2011). Developmental trajectories of DSM-IV symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Genetic effects, family risk and associated psychopathology. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 52, 954–963. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02379.x.
Leopold, D. R., Christopher, M. E., Burns, G. L., Becker, S. P., Olson, R. K., & Willcutt, E. G. (2016). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and sluggish cognitive tempo throughout childhood: Temporal invariance and stability from preschool through ninth grade. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 57, 1066–1074. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12505.
Lonigan, C. J., & Burgess, S. R. (2017). Dimensionality of reading skills with elementary-school-age children. Scientific Studies of Reading, 21, 239–253. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888438.2017.1285918.
Lonigan, C. J., & Milburn, T. F. (2017). Identifying the dimensionality of oral language skills of typically developing preschool through fifth-grade children. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 60, 2185–2198. https://doi.org/10.1044/2017_JSLHR-L-15-0402.
Lonigan, C. J., Burgess, S. R., & Schatschneider, C. (2018). Examining the simple view of reading with elementary school children: Still simple after all these years. Remedial and Special Education, 39, 260–273. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741932518764833.
MacCallum, R. C., Browne, M. W., & Sugawara, H. M. (1996). Power analysis and determination of sample size for covariance structure modeling. Psychological Methods, 1, 130–149. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989X.1.2.130.
Martel, M. M., Roberts, B., Gremillion, M., von Eye, A., & Nigg, J. T. (2011). External validation of bifactor model of ADHD: Explaining heterogeneity in psychiatric comorbidity, cognitive control, and personality trait profiles within DSM-IV ADHD. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 39, 1111–1123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-011-9538-y.
McGoey, K. E., Schreiber, J., Venesky, L., Westwood, W., McGuirk, L., & Schaffner, K. (2015). Factor structure of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder symptoms for children age 3 to 5 years. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 33, 430–438. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734282914554255.
Molina, B. S., Smith, B. H., & Pelham, W. E. (2001). Factor structure and criterion validity of secondary school teacher ratings of ADHD and ODD. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 29, 71–82. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005203629968.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (2014). Mplus: Statistical analysis with latent variables: User’s guide. Los Angeles: Muthén & Muthén.
Muthén, B., & Satorra, A. (1995). Complex sample data in structural equation modeling. Sociological Methodology, 25, 216–316 Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org/stable/271070.
Raiker, J. S., Rapport, M. D., Kofler, M. J., & Sarver, D. E. (2012). Objectively-measured impulsivity and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): Testing competing predictions from the working memory and behavioral inhibition models of ADHD. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 40, 699–713.
Swanson, J. M., Schuck, S., Mann, M, Carlson, C., Hartman, K., Sergeant, J., et al. (2001). Categorical and dimensional definitions and evaluations of symptoms of ADHD: The SNAP and SWAN rating scales. Available at: http://adhd.net. Accessed 15 Nov 2015.
Toplak, M. E., Pitch, A., Flora, D. B., Iwenofu, L., Ghelani, K., Jain, U., & Tannock, R. (2009). The unity and diversity of inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity in ADHD: Evidence for a general factor with separable dimensions. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37, 1137–1150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-009-9336-y.
Toplak, M. E., Sorge, G. B., Flora, D. B., Chen, W., Banaschewski, T., Buitelaar, J., et al. (2012). The hierarchical factor model of ADHD: Invariant across age and national groupings? Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 53, 292–303. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02500.x.
Trizano-Hermosilla, I., & Alvarado, J. M. (2016). Best alternatives to Cronbach’s alpha reliability in realistic conditions: Congeneric and asymmetrical measurements. Frontiers in Psychology, 7(769). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00769.
Ullebø, A. K., Breivik, K., Gillberg, C., Lundervold, A. J., & Posserud, M. B. (2012). The factor structure of ADHD in a general population of primary school children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 53, 927–936. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2012.02549.x.
Wagner, F., Martel, M. M., Cogo-Moreira, H., Maia, C. R. M., Pan, P. M., Rohde, L. A., & Salum, G. A. (2015). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder dimensionality: The reliable ‘g’ and the elusive ‘s’ dimensions. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 25, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-015-0709-1.
Willcutt, E. G., Nigg, J. T., Pennington, B. F., Solanto, M. V., Rohde, L. A., Tannock, R., et al. (2012). Validity of DSM-IV attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptom dimensions and subtypes. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 121, 991–1010.
Willoughby, M. T., Blanton, Z. E., & Investigators, F. L. P. (2015). Replication and external validation of a bi-factor parameterization of attention deficit/hyperactivity symptomatology. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 44(1), 68–79.
Wolraich, M. L., Lambert, E. W., Baumgaertel, A., Garcia-Tornel, S., Feurer, I. D., Bickman, L., & Doffing, M. A. (2003). Teachers' screening for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Comparing multinational samples on teacher ratings of ADHD. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 31, 445–455. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023847719796.
Yuan, K. H., & Bentler, P. M. (2000). Three likelihood-based methods for mean and covariance structure analysis with nonnormal missing data. Sociological Methodology, 30, 165–200. https://doi.org/10.1111/0081-1780.00078.
Acknowledgements
This research and report was supported by grants from the Institute of Education Sciences, US Department of Education (R305F100027) and the Eunice Kennedy Schriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (HD052120). The views expressed herein are those of the authors and have not been reviewed or approved by the granting agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no potential conflict of interest to report.
Ethical Approval
Procedures for all projects were approved by Florida State University’s Institutional Review Board.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from children’s parents or legal guardians before data collection began.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 86 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allan, D.M., Lonigan, C.J. Examination of the Structure and Measurement of Inattentive, Hyperactive, and Impulsive Behaviors from Preschool to Grade 4. J Abnorm Child Psychol 47, 975–987 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-018-0491-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-018-0491-x