Abstract
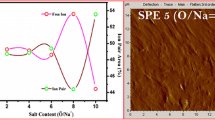
Porous solid polymer electrolytes (SPE) were prepared in the form of thin films by phase inversion by direct immersion in non-solvent acetone or methanol, using a copolymer of polyacrylonitrile and poly (vinyl acetate) in ethylene carbonate/dimethylene carbonate (EC/DMC 1:1 v/v) as plasticizer, which contained different LiClO4 percentages. SEM images revealed pores on a micrometer scale (average diameter around 2 μm) distributed inside and on the surface of the films. XRD patterns revealed a predominantly amorphous behavior, favorable to the ionic conduction process. Thin films presented low glass transition temperatures (T g), between −67 and −58 °C. Thin films showed a thermal stability higher than those obtained for the gels. Thin films (average thickness of 22 μm) showed ionic conductivity around 10−10 S cm−1 and 10−7 S cm−1 by immersion in acetone and methanol, respectively. The porous thin films when were swollen in liquid electrolyte, the maximum ionic conductivity value reached was of 2.5 × 10−4 S cm−1 with 10 % LiClO4 at 25 °C. The oxidation of the SPE only occurred around 4.5 V for the gel and 4.8 V versus Li/Li+ for the SPE thin film, thus resulting in a wide electrochemical stability. A stable passive layer at the interface between the polymer electrolyte and lithium metal was formed within the first 10 h and maintained during 4 weeks. The cell containing LiCoO2 in thin-film electrolyte presented the one well-known plateaux for the Li-ion intercalation in the 4 V region.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jung HG, Hassoun J, Park JB, Sun YK, Scrosati B (2012) An improved high-performance lithium–air battery. Nat Chem 4(1):579–585
Scrosati B, Garche J (2010) Lithium batteries: status, prospects and future. J Power Sources 45(9):2419–2430
Lu L, Hana X, Lia J, Huab J, Ouyang M (2013) A review on the key issues for lithium-ion battery management in electric vehicles. J Power Sources 226:272–288
Hossain S (1995) Rechargeable Lithium Batteries (Ambient Temperature), Handbook of Batteries, 2
Dissanayake MAKL, Divarathne HKDWMNR, Thotawatthage CA, Dissanayake CB, Senadeera GKR, Bandara BMR (2014) Dye sensitized solar cells based on electrospun polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibre membrane gel electrolyte. Electrochim Acta 130:76–81
Dias FB, Plomp L, Veldhuis JBJ (2000) Trends in polymer electrolyte for secondary lithium batteries. J Power Sources 88(2):169–191
Silva RA (1999) Estudo de Eletrólitos Poliméricos a base de Poliéter por spectroscopia Raman, Análise Térmica e Condutividade Iônica. Tese de Doutorado, UFMG
Fautex D, Massucco A, Mclin M (1995) Lithium polymer electrolyte rechargeable battery. Electrochim Acta 40(13):2185–2190
Cunha FOV (2005) Desenvolvimento de redes de polímeros interpenetrantes (IPN) para a aplicação como eletrólito polimérico. Tese de Doutorado, UFRGS
Amaral FA (2005) Propriedades estruturais e eletroquímicas de espinélios de lítio e manganês dopados para uso em baterias de lítio. Tese de Doutorado, UFSCAR
Florjanczyk Z, Bzducha W, Langwald N, Dygas JR, Krok F, Faraj B (2000) Lithium gel polyelectrolytes based on crosslinked maleic anhydride–styrene copolymer. Electrochima Acta 45(21):3563–3571
Owens BB, Skarstad PM, Untereker DF (1995) Solid-electrolytes cells. In: Linden D (ed) Handbook of Batteries, 2nd edn. Hill Book, New York
Akashi H, Sekai K, Tanaka K (1998) A novel fire-retardant polyacrylonitrile-based gel electrolyte for lithium batteries. Electrochim Acta 43(10):1193–1197
Kumar GG, Munichandraiah N (1999) Reversibility of Mg/Mg2+ couple in a gel polymer electrolyte. Electrochim Acta 44(15):2663–2666
Ballard DGH, Chesire P, Mann TS, Przeworshi JE (1990) Ionic conductivity in organic solids derived from amorphous macromolecules. Macromolecules 23(5):1256–1264
Fonseca CP, Neves S (2002) Characterization of polymer electrolytes based on poly(dimethyl siloxane-co-ethylene oxide. J Power Sources 104(1):85–89
Benedict TJ, Banumath IS, Veluchamy A, Gangadharan R, Zulfihar AA, Rajendran S (1998) Characterization of plasticized solid polymer electrolyte by XRD and AC Impedance methods. J Power Sources 75(1):171–174
Yogesh SJ, Gupta S, Singh K, Bhattachaya A (2008) Porometry studies of the polysulfone membranes on addition of poly (ethylene glycol) in gelation bath during preparation. J Mex Chem Soc (Guanajuato) 52(2):140–144
Amaral FA, Dalmolin C, Canobre SC, Bochhi N, Rocha-Filho RC, Biaggio SR (2007) Electrochemical and physical properties of poly (acrylonitrile)/poly (vinyl acetate)-based gel electrolytes for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 164(1):379–385
Radici Group. http://www.radicigroup.com/en/news-media/press-releases/brazil-radicigroup-focuses-its-development-work-on-carbon fibre-precursor-14872. Accessed 10 January 2013
Panero S, Scrosati B (2000) Gelification of liquid-polymer systems: a valid approach for the development of various types of polymer electrolyte membranes. J Power Sources 90(1):13–19
Appetecchi GB, Croce F, Marassi R, Persi L, Romagnoli P, Scrosati B (1999) Lithium insertion into carbonaceous materials and transition metal oxides from high performance polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 45(1):23–30
Rajendran S, Bama VS (2010) A study on the effect of various plasticizers in poly (vinyl acetate)-poly (methyl methacrylate) based gel electrolytes. J Non-Cryst Solids (Amsterdam) 356(50):2764–2768
Ohzuku T, Ueda A, Nagayama M (1993) Electrochemistry and structural chemistry of LiNiO2 ( m) for 4 volt secondary lithium cells. J Electrochem Soc 140(7):1862–1870
Ozawa K (1994) Lithium-ion rechargeable batteries with LiCoO2 and carbon electrodes: the LiCoO2/C system. Solid State Ionics 69(3):212–221
Kumar Y, Hashmi SA, Pandey GP (2011) Lithium ion transport and ion–polymer interaction in PEO based polymer electrolyte plasticized with ionic liquid. Solid State Ionics (Amsterdam) 201(1):73–80
Avrillon R, Deschamps A, Driancourt JC, Mileo E (1990) Les techniques de séparation de gaz par membranes. Oil Gas Sci Technol 45(4):507–524
Work WJ, Horie K, Hess RFT (2004) Macromolecular division subcommittee on macromolecular terminology Stepto. Pure Appl Chem 76(11):1985–2007
Xue TJ, Mckinney MA, Wilkie CA (1997) The thermal degradation of polyacrylonitrile. Polym Degrad Stab (Essex, England) 58(1):193–202
Gopalan AI, Santhosh P, Manesh KM, Nho JH, Kim SH, Hwang CG, Lee KP (2008) Development of electrospun PVdF–PAN membrane-based polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. J Membr Sci 325(2):683–690
Junior CAR, Pardini LC, Alves NP, Fleming RR (2011). Estudo termogravimétrico da poliacrilonitrila com o plastificante glicerol, 11° Congresso Brasileiro de Polímeros, Anais
Jayathilaka PARD, Dissanayake MAKL, Albinsson I, Mellander BE (2003) Dielectric relaxation, ionic conductivity and thermal studies of the gel polymer electrolyte system PAN/EC/PC/LiTFSI. Solid State Ionics 156(1):179–195
Song JY, Wang YY, Wan CC (1999) Review of gel-type polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 77(2):183–197
Rezende CA, Luchesi C, Barbo MLP, Duek EAR (2005) Membranas de poli (ácido lático-co-ácido glicólico) como curativos para pele. Polímeros (São Carlos) 15:232–238
Silverstain MS, Najary Y, Lumelsky Y, Von Lampe I, Grader GS, Shter GE (2004) Complex formation and degradation in poly (acrylonitrile-co-vinyl acetate) containing metal nitrates. Polymer 45(3):937–947
Vieira WG (2009). Ciência e tecnologia dos materiais. Alagoas: UFAL
Wang Z, Huang B, Xue R, Huang X, Chen L (1999) Spectroscopic investigation of interactions among components and ion transport mechanism in polyacrylonitrile based electrolytes. Solid State Ionics (Amsterdam) 121(1):141–156
Huang B, Wang Z, Chen L, Xue R, Wang F (1996) The mechanism of lithium ion transport in polyacrylonitrile-based polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 91(3):279–284
Huang B, Wang Z, Li G, Huang H, Xue R, Chen L, Wang F (1996) Lithium ion conduction in polymer electrolytes based on PAN. Solid State Ionics 85(1–4):79–84
Gray FM (1997) Polymer electrolytes. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Letchworth
Park M, Zhang X, Chung M, Less GB, Sastry AM (2010) A review of conduction phenomena in Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources 195(24):7904–7929
Lee S, Kim E-Y, Lee H, Oh E-S (2014) Effects of polymeric binders on electrochemical performances of spinel lithium manganese oxide cathodes in lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 269:418–423
Borghini MC, Mastragostino M, Zanelli A (1996) Reliability of lithium batteries with crosslinked polymer electrolytes. Electrochemical Acta 41(15):2369–2373
Croce F, Scrosati B (1993) Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. J Power Sources 43:9–19
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the Radici Crylor of Brazil for providing the PAN/PVA copolymer and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG) for technical support. This work was supported by FAPEMIG (grants APQ 2279/2010). L. C. T. Morais and R. G. Rocha are grateful to FAPEMIG for their scholarships (FAPEMIG 2013- EXA041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amaral, F.A., Sousa, R.M., Morais, L.C.T. et al. Preparation and characterization of the porous solid polymer electrolyte of PAN/PVA by phase inversion. J Appl Electrochem 45, 809–820 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-015-0816-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-015-0816-1