Abstract
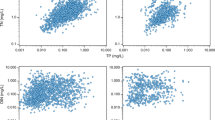
In the management of lakes for a healthy environment, it is crucial to assess the limiting nutrient(s) and understand its use efficiency of the phytoplankton production. We hypothesized that dissolved inorganic phosphorus (DIP) and/or nitrogen concentrations (DIN) describe the state of nutrient limitations on phytoplankton production. Using the 38 years of monthly limnological data at eight stations in Lake Kasumigaura, we analyzed the relationships between the available nutrients for building phytoplankton biomass and chlorophyll a (Chla). Better correlations were obtained by subtracting the nutrients in tripton (non-living particulate matter) from the total P and N (available nutrients: TP′ and TN′). We determined the thresholds for P and N limitation (DIP: 0.01 mg l−1; DIN: 0.15 mg l−1) using the slopes of regression, and we examined this assessment in one of four limitation conditions (only P, only N, both, or none) for the respective times and stations. Close relationships between TP′ and Chla for only the P limitation data and between TN′ and Chla for only the N limitation data were observed. Multiple regression models confirmed that TP′ and TN′ predominantly determined Chla in only the P and N limitation conditions, respectively. Factors affecting nutrient use efficiency were also discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, I. M., T. J. Williamson, M. J. Gonzalez & M. J. Vanni, 2020. Nitrate, ammonium, and phosphorus drive seasonal nutrient limitation of chlorophytes, cyanobacteria, and diatoms in a hyper-eutrophic reservoir. Limnology Oceanography 65(5): 962–978.
APHA, AWWA, WEF, 1995. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed. APHA, Washington.
Brown, J. H., J. F. Gillooly, A. P. Allen, V. M. Savage & G. B. West, 2004. Towards a metabolic theory in ecology. Ecology 85(7): 1771–1789.
Chorus, I. & E. Spijkerman, 2020. What Colin Reynolds could tell us about nutrient limitation, N:P ratios and eutrophication control. Hydrobiologia. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04377-w.
Davies, J. M., W. H. Nowlin, B. Matthews & A. Mazumder, 2010. Temporal discontinuity of nutrient limitation in plankton communities. Aquatic Sciences 72(4): 393–402.
Elliott, J. A. & L. May, 2008. The sensitivity of phytoplankton in Loch Leven (UK) to changes in nutrient load and water temperature. Freshwater Biology 53(1): 32–41.
Fastner, J., S. Abella, A. Litt, G. Morabito, L. Voros, K. Palffy, D. Straile, R. Kiimmerlin, D. Matthews, M. G. Phillips & I. Chorus, 2016. Combating cyanobacterial proliferation by avoiding or treating inflows with high P load-experiences from eight case studies. Aquatic Ecology 50(3): 367–383.
Fukushima, T. & H. Arai, 2015. Regime shifts observed in Lake Kasumigaura, a large shallow lake: analysis of a 40-year limnological record. Lakes and Reservoirs: Research and Management 20: 54–68.
Fukushima, T. & K. Muraoka, 1981. Current and vertical mixing in a shallow lake. Verhandlungen des Internationalen Verein Limnologie 21: 141–149.
Fukushima, T., M. Takahashi, B. Matsushita & Y. Okanishi, 2007. Land use/cover change and its drivers: a case in the watershed of Lake Kasumigaura, Japan. Landscape and Ecological Engineering 3: 21–31.
Fukushima, T., K. Kamiya, Y. Onda, A. Imai & K. Matsushige, 2010. Long-term changes in lake sediments and their influences on lake water quality in Japanese shallow lakes. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 177(3): 177–188.
Fukushima, T., B. Matsushita, W. Yang & L. M. Jaelani, 2018. Semi-analytical prediction of Secchi depth transparency in Lake Kasumigaura using MERIS data. Limnology 19: 89–100.
Fukushima, T., S. Komuro, T. Kitamura, Y. Nagahama & B. Matsushita, 2019. Decadal change in tripton concentration in a shallow lake. SN Applied Sciences 1: 1637.
Fukushima, T., S. Komuro, T. Kitamura, Y. Nagahama & B. Matsushita, 2020. Long-term changes in water mineral concentrations and their influence on sediment water content in a shallow lake. SN Applied Sciences 2: 1319.
Goldman, J. C., J. J. McCarthy & D. G. Peavey, 1979. Growth-rate influence on the chemical composition of phytoplankton in oceanic waters. Nature 279(5710): 210–215.
Goma, R. H., 1995. Dynamics of organic nitrogen in eutrophic Lake Kasumigaura, with special reference to urea and free amino acids. Dissertation to Tokyo University of Fisheries, 142 pp.
Guildford, S. J. & R. E. Hecky, 2000. Total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and nutrient limitation in lakes and oceans: Is there a common relationship? Limnology Oceanography 45(6): 1213–1223.
Guo, J. B., C. J. Zhang, G. C. Zheng, J. Xue & L. H. Zhang, 2018. The establishment of season-specific eutrophication assessment standards for a water-supply reservoir located in Northeast China based on chlorophyll-a levels. Ecological Indicators 85: 11–20.
Hakanson, L., A. C. Bryhn & J. K. Hytteborn, 2007. On the issue of limiting nutrient and predictions of cyanobacteria in aquatic systems. The Science of the Total Environment 379(1): 89–108.
Havens, K. E., T. Fukushima, P. Xie, T. Iwakuma, R. T. James, N. Takamura, T. Hanazato & T. Yamamoto, 2001. Nutrient dynamics and the eutrophication of shallow lakes Kasumigaura (Japan), Donghu (PR China), and Okeechobee (USA). Environmental Pollution 111: 263–272.
Hennemann, M. C. & M. M. Petrucio, 2016. High chlorophyll a concentration in a low nutrient context: discussions in a subtropical lake dominated by Cyanobacteria. Journal of Limnology 75(3): 520–530.
Ishikawa, T. & M. Tanaka, 1993. Diurnal stratification and its effects on wind-induced currents and water qualities in Lake Kasumigaura, Japan. Journal of Hydraulic Research 31(3): 307–322.
Kaushal, S. S. & W. M. Lewis, 2005. Fate and transport of organic nitrogen in minimally disturbed montane streams of Colorado, USA. Biogeochemistry 74(3): 303–321.
Kolzau, S., C. Wiedner, J. Rucker, J. Kohler, A. Kohler & A. M. Dolman, 2014. Seasonal patterns of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation in four German lakes and the predictability of limitation status from ambient nutrient concentrations. PLoS ONE 9(4): e96065.
Kohzu, A., S. Matsuzaki, S. Komuro, S. Matsumoto, K. Komatsu, N. Takamura, M. Nakagawa, A. Imai & T. Fukushima, 2019. Regime shift analysis for understanding the water quality dynamics in Lake Kasumigaura. Proceedings of 17th World Lake Conference, 365–367. (in Japanese with English abstract).
Lewis, W. M. & W. A. Wurtsbaugh, 2008. Control of lacustrine phytoplankton by nutrients: erosion of the phosphorus paradigm. International Review of Hydrobiology 93(4–5): 446–465.
Li, Y. P., C. Y. Tang, Z. B. Yu & K. Acharya, 2014. Correlations between algae and water quality: factors driving eutrophication in Lake Taihu, China. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology 11(1): 169–182.
Maberly, S. C., L. King, M. M. Dent, R. I. Jones & C. E. Gibson, 2002. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton and periphyton growth in upland lakes. Freshwater Biology 47(11): 2136–2152.
Maberly, S. C., J. A. Pitt, P. S. Davies & L. Carvalho, 2020. Nitrogen and phosphorus limitation and the management of small productive lakes. Inland Waters 10(2): 159–172.
Matsuoka, Y., T. Goda & M. Naito, 1986. An eutrophication model of Lake Kasumigaura. Ecological Modelling 31: 201–219.
Moss, B., E. Jeppesen, M. Sondergaard, T. L. Lauridsen & Z. W. Liu, 2013. Nitrogen, macrophytes, shallow lakes and nutrient limitation: resolution of a current controversy? Hydrobiologia 710(1): 3–21.
Nakamura, K. & M. Aizaki, 2016. Effects of suspended solid on light attenuation in the shallow and turbid Lake Kasumigaura, Japan: long-term variation of the light attenuation mechanism. Japan Journal of Limnology 77: 13–23. (in Japanese with English abstract).
Pisani, O., J. N. Boyer, D. C. Podgorski, C. R. Thomas, T. Coley & R. Jaffe, 2017. Molecular composition and bioavailability of dissolved organic nitrogen in a lake flow-influenced river in south Florida, USA. Aquatic Sciences 79(4): 891–908.
R Core Team, 2020. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/.
Rast, W. & J. A. Thornton, 2005. The Phosphorus loading concept and the OECD eutrophication programme: origin, application and capabilities. In O’Sullivan, P. E. & C. S. Reynolds (eds), The Lakes Handbook, Vol. 2. Blackwell Science Ltd., Malden: 354–385.
Reynolds, C. S. & P. S. Davies, 2001. Sources and bioavailability of phosphorus fractions in freshwaters: a British perspective. Biological Reviews 76(1): 27–64.
Rios, A. F., F. Fraga, F. F. Perez & F. G. Figueiras, 1998. Chemical composition of phytoplankton and particulate organic matter in the Ria de Vigo (NW Spain). Scientia Marina 62(3): 257–271.
Roelke, D. L., P. M. Eldridge & L. A. Cifuentes, 1999. A model of phytoplankton competition for limiting and nonlimiting nutrients: implications for development of estuarine and nearshore management schemes. Estuaries 22(1): 92–104.
Rowland, F. E., R. L. North, P. McEachern, D. V. Obrecht, T. B. Gurung, S. B. Jones & J. R. Jones, 2019. Phytoplankton nutrient deficiencies vary with season in sub-tropical lakes of Nepal. Hydrobiologia 833(1): 157–172.
Schallenberg, M. & C. W. Burns, 2004. Effects of sediment resuspension on phytoplankton production: teasing apart the influences of light, nutrients and algal entrainment. Freshwater Biology 49(2): 143–159.
Schelske, C. L., F. J. Aldridge & W. F. Kenney, 1999. Assessing nutrient limitation and trophic state in Florida lakes. In Reddy, K. R., G. A. O’Connor & C. L. Schelske (eds), Phosphorus Biogeochemistry in Subtropical Ecosystems. Lewis Publishers, Boca Roton, FL: 321–342.
Schindler, D. W., R. E. Hecky, D. I. Findlay, M. P. Stainton, B. R. Parker, M. J. Paterson & S. E. M. Kasian, 2008. Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: results of a 37-year whole-ecosystem experiment. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 105(32): 11254–11258.
Seki, T., T. Fukushima, A. Imai & K. Matsushige, 2006. Turbidity increase and sediment resuspension in Lake Kasumigaura. Proceedings of Japan Society of Civil Engineers G62: 122–134. (in Japanese with English abstract).
Somiya, I., H. Sumitomo, H. Tsuno, N. Matsuo & Y. Matsuoka, 1989. Water quality prediction model. In Iwasa, Y. (ed.), Engineering Limnology. Sankaido, Tokyo: 299–356. (in Japanese).
Sondergaard, M., T. L. Lauridsen, L. S. Johansson & E. Jeppesen, 2017. Nitrogen or phosphorus limitation in lakes and its impact on phytoplankton biomass and submerged macrophyte cover. Hydrobiologia 795(1): 35–48.
Steffen, W., K. Richardson, J. Rockstrom, S. E. Cornell, I. Fetzer, E. M. Bennett, R. Biggs, S. R. Carpenter, W. de Vries, C. A. de Wit, C. Folke, D. Gerten, J. Heinke, G. M. Mace, L. M. Persson, V. Ramanathan, B. Reyers & S. Sorlin, 2015. Planetary boundaries: guiding human development on a changing planet. Science 347(6223): 11.
Sterner, R. W., 2008. On the phosphorus limitation paradigm for lakes. International Review of Hydrobiology 93(4–5): 433–445.
Stumm, W., 2003. Chemical processes regulating the composition of lake waters. In O’Sullivan, P. E. & C. S. Reynolds (eds), The Lakes Handbook, Vol. 1. Blackwell Science Ltd., Malden, MA: 79–106.
Takamura, N. & M. Nakagawa, 2012. Phytoplankton species abundance in Lake Kasumigaura (Japan) monitored monthly or biweekly since 1978. Ecological Research 27: 837.
Vandergucht, D. M., J. M. Sereda, J. M. Davies & J. J. Hudson, 2013. A comparison of phosphorus deficiency indicators with steady state phosphate in lakes. Water Research 47(5): 1816–1826.
Vollenweider, R. A. & J. Kerekes, 1980. The loading concept as basis for controlling eutrophication philosophy and preliminary-results of the OECD program on eutrophication. Progress in Water Technology 12(2): 5–38.
WEPA, 2020. Lake Kasumigaura. http://www.wepa-db.net/policies/cases/kasumigaura/01-1.htm/. Accessed 1 May 2020.
Wetzel, R. G., 2001. Limnology, 3rd ed. Academic Press, San Diego, CA: 365–366.
Xiao, J., S. Y. Wang, Z. J. Zhou, Y. Zhang, C. L. Song, Y. Y. Zhou & X. Y. Cao, 2018. An enzymatic mechanism for balancing the stoichiometry of nitrogen and phosphorus in a shallow Chinese eutrophic lake. The Science of the Total Environment 630: 1071–1077.
Xu, H., H. W. Paerl, B. Q. Qin, G. W. Zhu & G. Gao, 2010. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnology Oceanography 55(1): 420–432.
Yang, W., B. Matsushita, J. Chen & T. Fukushima, 2011. Estimating constituent concentrations in case II waters from MERIS satellite data by semi-analytical model optimizing and look-up tables. Remote Sensing of Environment 115: 1247–1259.
Yuan, L. L. & J. R. Jones, 2020. Rethinking phosphorus-chlorophyll relationships in lakes. Limnology Oceanography 65(8): 1847–1857.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sport, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan (17H04475 and 17H01850). The data on lake water and sediment quality were provided by the Kasumigaura River Office, Kanto Regional Development Bureau, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT). Monitoring data on water quality and phytoplankton were also provided by the National Institute for the Environmental Studies (NIES). We are grateful to Dr. Yumi Magahama and Dr. Mariko Furukawa for helpful advice on the statistical analysis using R. We thank two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions for improving the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TF designed this study and analyzed the data. BM commented on draft version of the article. All authors have approved the final article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling editor: Judit Padisák.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukushima, T., Matsushita, B. Limiting nutrient and its use efficiency of phytoplankton in a shallow eutrophic lake, Lake Kasumigaura. Hydrobiologia 848, 3469–3487 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-021-04593-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-021-04593-y