Abstract
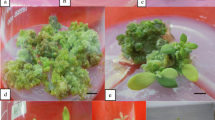
A rapid, prolific and reproducible protocol for in vitro shoot regeneration from mature cotyledons of Platanus acerifolia has been developed. The influences of different plant growth regulator (PGR) combinations and donor seedling ages on shoot regeneration were investigated. The results showed that the application of BA in conjunction with NAA was the most effective PGR combination for the induction of shoot regeneration. When cotyledon explants of 5-day-old seedlings were incubated on MS basal medium supplemented with 4.0 mg L−1 BA and 0.2 mg L−1 NAA, 67.6 ± 4.9% of the cotyledon segments produced adventitious shoots. These regenerated shoots were initially formed as stunted rosette cluster forms and were encouraged to elongate to produce distinct shoots by transfer onto MS medium containing 0.5 mg L−1 BA and 0.05 mg L−1 NAA; the resulting mean number of adventitious shoots per explant was 5.81 ± 0.36. The elongated shoots were readily induced to root (i.e. 89.3% of shoots) by incubation on ½-strength MS medium supplemented with 0.1 mg L−1 IBA. This is the first report of an efficient in vitro shoot regeneration protocol for P. acerifolia through direct organogenesis using cotyledon explants. Hence, this provides a more efficient basis for the Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Platanus than previously available.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benson EE (2000) Do free radicals have a role in plant tissue culture recalcitrance? In Vitro Cell Dev Biol-Plant 36:163–170. http://www.jstor.org/stable/4293332
Canli FA, Tian L (2009) Regeneration of adventitious shoots from mature stored cotyledons of Japanese plum (Prunus salicina Lind1). Sci Hortic 120(1):64–69. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2008.09.017
Cheng CH, Zang GG, Zhao LN, Gao CS, Tang Q, Chen JH, Guo XB, Peng DX, Su JG (2016) A rapid shoot regeneration protocol from the cotyledons of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Ind Crops Prod 83:61–65. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.12.035
Dong JZ, Jia SR (1991) High efficiency plant regeneration from cotyledons of watermelon (Citrullus vulgaris Schrad). Plant Cell Rep 9(10):559–562. doi:10.1007/BF00232331
Du N, Pijut PM (2008) Regeneration of plants from Fraxinus pennsylvanica hypocotyls and cotyledons. Sci Hortic 118(1):74–79. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2008.05.014
Floyd SK, Lerner VT, Friedman WE (1999) A developmental and evolutionary analysis of embryology in Platanus (platanaceae), abasal eudicot. Am J Bot 86(11):1523–1537. http://www.jstor.org/stable/2656790
Huang H, Li JC, OuYang KX, Zhao XH, Li P, Liao BY, Chen XY (2014) Direct adventitious shoot organogenesis and plant regeneration from cotyledon explants in Neolamarckia cadamba. Plant Biotechnol 31(2):115–121. http://doi.org/10.5511/plantbiotechnology.14.0125a
Ibrahim R, Debergh PC (2001) Factors controlling high efficiency adventitious bud formation and plant regeneration from in vitro leaf explants of roses (Rosa hybrida L.). Sci Hortic 88(1):41–57. doi:10.1016/S0304-4238(00)00189-8
Iglesias I, Rodríguez-Rajo FJ, Méndez J (2007) Behavior of Platanus hispanica pollen, an important spring aeroallergen in northwestern Spain. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 17(3):145. http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8535-901X
Jha AK, Prakash S, Jain N, Nanda K, Gupta SC (2002) Production of adventitious shoots and plantlets from the hypocotyl explants of Sesbania rostrata (Bremek & obrem). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol-Plant 38(5):430–434. doi:10.1079/IVP2002313
Joshi A, Kothari SL (2007) High copper levels in the medium improves shoot bud differentiation and elongation from the cultured cotyledons of Capsicum annuum L. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 88(2):127–133. doi:10.1007/s11240-006-9171-6
Kehie M, Kumaria S, Tandon P (2013) In vitro plantlet regeneration from cotyledon segments of Capsicum chinense Jacq. cv. Naga King Chili, and determination of capsaicin content in fruits of in vitro propagated plants by high performance liquid chromatography. Sci Hortic 164:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2013.08.018
Kothari SL, Joshi A, Kachhwaha S, Ochoa-Alejo N (2010) Chilli peppers—a review on tissue culture and transgenesis. Biotechnol Adv 28(1):35–48. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.08.005
Kumar V, Moyo M, Van Staden J (2016) Enhancing plant regeneration of Lachenalia viridiflora, a critically endangered ornamental geophyte with high floricultural potential. Sci Hortic 211:263–268. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2016.08.024
Li ZN, Fang F, Liu GF, Bao MZ (2007) Stable Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of London plane tree (Platanus acerifolia Willd.). Plant Cell Rep 26(5):641–650. doi:10.1007/s00299-006-0271-x
Liu GF, Bao MZ (2003) Adventitious shoot regeneration from in vitro cultured leaves of London plane tree (Platanus acerifolia Willd.). Plant Cell Rep 21:640–644. doi:10.1007/s00299-002-0569-2
Liu GF, Huang J, Chen LQ, Bao MZ (2002) Plant regeneration from excised hypocotyl explants of Platanus acerifolia Willd. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol-Plant 38(6):558–563. doi:10.1079/IVP2002350
Mali AM, Chavan NS (2016) In vitro rapid regeneration through direct organogenesis and ex-vitro establishment of Cucumis trigonus Roxb.—An underutilized pharmaceutically important cucurbit. Ind Crops Prod 83:48–54. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.12.036
Mante S, Scorza R, Cordts JM (1989) Plant regeneration from cotyledons of Prunus persica, Prunus domestica, and Prunus cerasus. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 19(1):1–11. doi:10.1007/BF00037771
Mazumdar P, Basu A, Paul A, Mahanta C, Sahoo L (2010) Age and orientation of the cotyledonary leaf explants determine the efficiency of de novo plant regeneration and Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation in Jatropha curcas L. S Afr J Bot 76(2):337–344. doi:10.1016/j.sajb.2010.01.001
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054
Salajova T, Salaj J (2001) Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration from cotyledon explants isolated from emblings and seedlings of hybrid firs. J Plant Physiol 158(6):747–755. doi:10.1078/0176-1617-00278
Sarwar M, Skirvin RM (1997) Effect of thidiazuron and 6-benzylaminopurine on adventitious shoot regeneration from leaves of three strains of ‘McIntosh’ apple (Malus domestica Borkh.). Sci Hortic 68:95–100. doi:10.1016/S0304-4238(96)00971-5
Suárez-Cervera M, Asturias JA, Vega-Maray A, Castells T, López-Iglesias C, Ibarrola I, Arilla C, Gabarayeva N, Seoane-Camba JA (2005) The role of allergenic proteins Pla a 1 and Pla a 2 in the germination of Platanus acerifolia pollen grains. Sex Plant Reprod 18(3):101–112. doi:10.1007/s00497-005-0002-4
Subiza J, Cabrera M, Valdivieso R, Subiza JL, Jerez M, Jiménez JA, Narganes MJ, Subiza E (1994) Seasonal asthma caused by airborne Platanus pollen. Clin Exp Allergy 24(12):1123–1129. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.1994.tb03317.x
Sun YH, Zhao YL, Wang XJ, Qiao GR, Chen GL, Yang Y, Zhou J, Jin L, Zhou RY (2009) Adventitious bud regeneration from leaf explants of Platanus occidentalis L. and genetic stability assessment. Acta Physiol Plant 31(1):33–41. doi:10.1007/s11738-008-0196-9
Thomas TD (2003) Thidiazuron induced multiple shoot induction and plant regeneration from cotyledonary explants of mulberry. Biol Plant 46(4):529–533. doi:10.1023/A:1024807426591
Wang H, Petri C, Burgos L, Alburquerque N (2013) Efficient in vitro shoot regeneration from mature apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) cotyledons. Sci Hortic 160:300–305. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2013.06.013
Zaerr JB, Mapes MO (1982) Action of growth regulators. In: Tissue culture in forestry, Springer, Dordrecht, pp 231–255. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-3538-4_9
Zarinjoei F, Rahmani MS, Shabanian N (2014) In vitro plant regeneration from cotyledon-derived callus cultures of leguminous tree Gleditsia caspica Desf. New Forest 45(6):829–841. doi:10.1007/s11056-014-9440-x
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the “Twelfth Five-Year Plan” of the National Science and Technology Research (Grant No. 2012BAD01B04), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31570696 and 31672187) and the Forestry Industry Research Special Funds for Public Welfare Projects (Grant No. 201304103). We thank Dr Alex McCormac (Mambo-Tox Ltd., Southampton, UK) for help with editing of the manuscript and all colleagues in our laboratory for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, Z., Zhang, Y., Shao, C. et al. A rapid and efficient in vitro shoot regeneration protocol using cotyledons of London plane tree (Platanus acerifolia Willd.). Plant Growth Regul 83, 245–252 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-017-0303-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-017-0303-2