Abstract
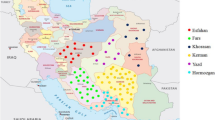
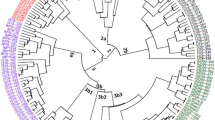
The reticulated iris is one of the most attractive wild ornamentals and bulbous irises and is widely distributed throughout the mountains of the Iraqi Kurdistan region. Because little is known about the genetic diversity and population structure of this plant species in Iraq, this study was undertaken to fill that gap. In the present study, 10 start codon-targeted (SCoT) polymorphic and 10 sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) markers were used to assess the genetic diversity and population structure of 50 wild reticulated iris accessions from five different sites in Iraqi Kurdistan. Overall, the SCoT and SRAP markers produced 135 and 87 polymorphic bands, respectively. The average number of polymorphic bands (TPB), number of observed alleles (Na), Shannon’s information index (I), effective number of alleles (Ne), expected heterozygosity or gene diversity (He), polymorphic information content, and unbiased expected heterozygosity (uHe) were 13.7, 1.54, 0.35, 1.40, 0.23, 0.31, and 0.25, respectively, for the SCoT markers and 8.7, 1.54, 0.36, 1.40, 0.24, 0.32, and 0.25, respectively, for the SRAP markers. According to the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean (UPGMA) dendrogram and structure analysis, SCoT markers grouped 50 reticulated iris accessions into two main clades with some subclades, SRAP markers separated these accessions into four main clades, and the combination of both markers divided all accessions into five main clades. The analysis of molecular variance revealed 80.00, 76.00, and 78.38% variability within populations using SCoT, SRAP, and SCoT+SRAP markers, respectively. Except for the private band numbers for the SCoT, SRAP, and SCoT+SRAP markers, population 3, population 1, and population 3 had the highest diversity indices, respectively. The highest genetic similarity among populations was revealed by the SRAP markers between population 2 and population 3, with 92% similarity. The findings of this study demonstrate the efficacy of these markers for determining genetic variation in iris accessions, in addition to their use in conserving germplasm and genome diversity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed DA, Tahir NA, Salih SH, Talebi R (2021) Genome diversity and population structure analysis of Iranian landrace and improved barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) genotypes using arbitrary functional gene-based molecular markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 68(3):1045–1060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-01047-7
Ahmed AA, Qadir SA, Tahir NA (2022) CDDP and ISSR markers-assisted diversity and structure analysis in Iraqi Mazu (Quercus infectoria Oliv.) accessions. All Life 15(1):247–261. https://doi.org/10.1080/26895293.2022.2042401
Ahmed AA, Qadir SA, Tahir NA (2023) Genetic variation and structure analysis of Iraqi valonia Oak (Quercus aegilops L.) populations using conserved DNA-derived polymorphism and inter-simple sequence repeats markers. Plant Mol Biol Rep 41(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-022-01347-5
Amirmoradi B, Talebi R, Karami E (2012) Comparison of genetic variation and differentiation among annual Cicer species using start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphism, DAMD-PCR, and ISSR markers. Plant Syst Evol 298:1679–1688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-012-0669-6
Aneja B, Yadav NR, Chawla V, Yadav RC (2012) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) molecular marker system and its applications in crop improvement. Mol Breed 30:1635–1648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-012-9747-2
Arnold ML (2000) Anderson’s paradigm: Louisiana irises and the study of evolutionary phenomena. Mol Ecol 9(11):1687–1698. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294x.2000.01090.x
Attari SZ, Shoor M, Ghorbanzadeh Neghab M, Tehranifar A, Malekzadeh Shafaroudi S (2016) Evaluation of genetic diversity of Iris genotypes (Iris spp) using ISSR. J Hortic Sci 30(3):376–382. https://doi.org/10.22067/JHORTS4.V30I3.28044
Aziz RR, Tahir NA (2023) Genetic diversity and structure analysis of melon (Cucumis melo L.) genotypes using URP, SRAP, and CDDP markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 70(3):799–813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-022-01462-y
Bublyk O, Andreev I, Kalendar R, Spiridonova K, Kunakh V (2013) Efficiency of different PCR-based marker systems for assessment of Iris pumila genetic diversity. Biologia 68(4):613–620. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-013-0192-4
Bublyk O, Andreev I, Parnikoza I, Kunakh V (2020) Population genetic structure of Iris pumila L. in Ukraine: effects of habitat fragmentation. Acta Biol Cracoviensia Bot 62(1):51–61
Chen H, Guo A, Wang J, Gao J, Zhang S, Zheng J, Huang X, Xi J, Yi K (2020) Evaluation of genetic diversity within asparagus germplasm based on morphological traits and ISSR markers. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26:305–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-019-00738-5
Choi B, Park I, So S, Myeong HH, Ryu J, Ahn YE, Shim KC, Song JH, Jang TS (2022) Comparative analysis of two Korean irises (Iris ruthenica and I. uniflora, Iridaceae) based on plastome sequencing and micromorphology. Sci Rep 12(1):9424. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-13528-z
Collard BC, Mackill DJ (2009) Start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphism: a simple, novel DNA marker technique for generating gene-targeted markers in plants. Plant Mol Biol Rep 27(1):86–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-008-0060-5
Guo DL, Guo MX, Hou XG, Zhang GH (2014) Molecular diversity analysis of grape varieties based on iPBS markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 52:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2013.10.008
Hajibarat Z, Saidi A, Hajibarat Z, Talebi R (2015) Characterization of genetic diversity in chickpea using SSR markers, start codon targeted polymorphism (SCoT) and conserved DNA-derived polymorphism (CDDP). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 21(3):365–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-015-0306-2
Jozghasemi S, Rabiei V, Soleymani A, Khalighi A (2016) Karyotype analysis of seven Iris species native to Iran. Caryologia 69(4):351–361. https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.2016.1239162
Karapetsi L, Pantelidis G, Pratsinakis ED, Drogoudi P, Madesis P (2021) Fruit quality traits and genotypic characterization in a pomegranate ex situ (Punica granatum L.) collection in Greece. Agriculture 11(6):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11060482
Khatib S, Faraloni C, Bouissane L (2022) Exploring the use of Iris species: antioxidant properties, phytochemistry, medicinal and industrial applications. Antioxidants 11(3):526. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11030526
Kiran Y, Yavas T, Dogan G (2022) Karyotype analysis of five Iris L. (Iridaceae) species from Turkey. Cytologia 87(3):251–254. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.87.251
Kushanov FN, Turaev OS, Ernazarova DK, Gapparov BM, Oripova BB, Kudratova MK, Rafieva FU, Khalikov KK, Erjigitov DS, Khidirov MT (2021) Genetic diversity, QTL mapping, and marker-assisted selection technology in cotton (Gossypium spp.). Front Plant Sci 12:779386. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.779386
Lamare A, Rao SR (2015) Efficacy of RAPD, ISSR and DAMD markers in assessment of genetic variability and population structure of wild Musa acuminata colla. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 21:349–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-015-0295-1
Li G, Quiros CF (2001) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 103:455–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220100570
Majeed HO (2021) Molecular inference of subgenus Hermodactyloides Spach for vascular flora of Iraq. Italus Hortus 28(3):36–48. https://doi.org/10.26353/j.itahort/2021.3.3648
Marimuthu SS, Subbaraya U, Durairajan SG, Rajendran S, Gopalakrishnan J, Shahul Hameed B, Palani D, Suthanthiram B (2019) Comparison of two different electrophoretic methods in studying the genetic diversity among plantains (Musa spp.) using ISSR markers. Electrophoresis 40(9):1265–1272. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201800456
Mekonnen T, Haileselassie T, Goodwin SB, Tesfayea K (2020) Genetic diversity and population structure of Zymoseptoria tritici in Ethiopia as revealed by microsatellite markers. Fungal Genet Biol 141:103413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2020.103413
Moat C, Rukšāns J, Becker P, Ciesielski K, Boens W (2019) ‘International Rock Gardener 112’, The Scottish Rock Garden Club
Pellicer J, Leitch IJ (2020) The Plant DNA C-values database (release 7.1): an updated online repository of plant genome size data for comparative studies. [New Phytologist]
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155(2):945–959. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/155.2.945
Rai MK (2023) Start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphism marker in plant genome analysis: current status and prospects. Planta 257(2):34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-023-04067-6
Rasul KS, Grundler FMW, Tahir NA (2022) Genetic diversity and population structure assessment of Iraqi tomato accessions using fruit characteristics and molecular markers. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 63(4):523–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-022-00429-3
Rasul KS (2023) Response of different tomato accessions to biotic and abiotic stresses. Dissertation, University of Sulaimani
Rice A, Glick L, Abadi S, Einhorn M, Kopelman NM, Salman-Minkov A, Mayzel J, Chay O, Mayrose I (2015) The chromosome counts database (CCDB)-a community resource of plant chromosome numbers. New Phytol 206(1):19–26
Tahir N, Lateef D, Rasul K, Rahim D, Mustafa K, Sleman S, Mirza A, Aziz R (2023a) Assessment of genetic variation and population structure in Iraqi barley accessions using ISSR, CDDP, and SCoT markers. Czech J Genet Plant Breed 59(3):148–159. https://doi.org/10.17221/112/2022-cjgpb
Tahir NAR, Rasul KS, Lateef DD (2023b) Effect of mixing oak leaf biomass with soil on cadmium toxicity and translocation in tomato genotypes. Heliyon 9(8):e18660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18660
Townsend C, Guest G (1985) Flora of Iraq, vol. 8: 128. Ministry of Agriculture & Agrarian Reform, Baghdad, pp 137–177
Wahyudi D, Nursita DC, Hapsari L (2022) Genetic diversity among and within genome groups of banana cultivars based on ISSR markers. Int J Agric Biol 2(6):366–374
Wang K, Kang J, Zhou H, Sun Y, Yang Q, Dong J, Meng L (2009) Genetic diversity of Iris lactea var. chinensis germplasm detected by inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR). Afr J Biotechnol 8(19):4856–4863
Wanjala BW, Obonyo M, Wachira FN, Muchugi A, Mulaa M, Harvey J, Skilton RA, Proud J, Hanson J (2013) Genetic diversity in Napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum) cultivars: implications for breeding and conservation. AoB Plants 5:plt022. https://doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/plt022
Wroblewska A, Brzosko E, Czarnecka B, Nowosielski J (2003) High levels of genetic diversity in populations of Iris aphylla L. (Iridaceae), an endangered species in Poland. Bot J Linn Soc 142(1):65–72. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1095-8339.2003.00162.x
Xu YF, Hussain K, Yan XF, Chen XH, Shao MN, Guan P, Qu B (2019) Genetic diversity and relationships among 15 species of Iris based on amplified fragment length polymorphism markers. Appl Ecol Environ Res. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1703_53695381
Zhao X, Zou G, Zhao J, Hu L, Lan Y, He J (2020) Genetic relationships and diversity among populations of Paris polyphylla assessed using SCoT and SRAP markers. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26:1281–1293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00808-z
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the people who worked at the College of Agricultural Engineering Sciences at the University of Sulaimani for their assistance and cooperation throughout the research process.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HOM: Collected plant materials; wrote the paper. JMF: Performed the experiments; Contributed reagents, materials, analysis tools or data. KSR: Conceived and designed the experiments; Performed the experiments; wrote the paper; and Contributed reagents, materials, analysis tools or data. DDL: Conceived and designed the experiments. NART: Conceived and designed the experiments; Analyzed and interpreted the data. Wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Majeed, H.O., Faraj, J.M., Rasul, K.S. et al. Evaluation of the genetic diversity and population structure of reticulated iris accessions in the Iraqi Kurdistan region using SCoT and SRAP markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-024-01884-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-024-01884-w